A choice of law clause specifies which jurisdiction's laws will govern the interpretation and enforcement of a contract, providing clarity and predictability for all parties involved. This clause helps mitigate legal risks by ensuring disputes are resolved under a known legal framework. Explore the rest of the article to understand how to draft an effective choice of law clause tailored to your needs.
Table of Comparison
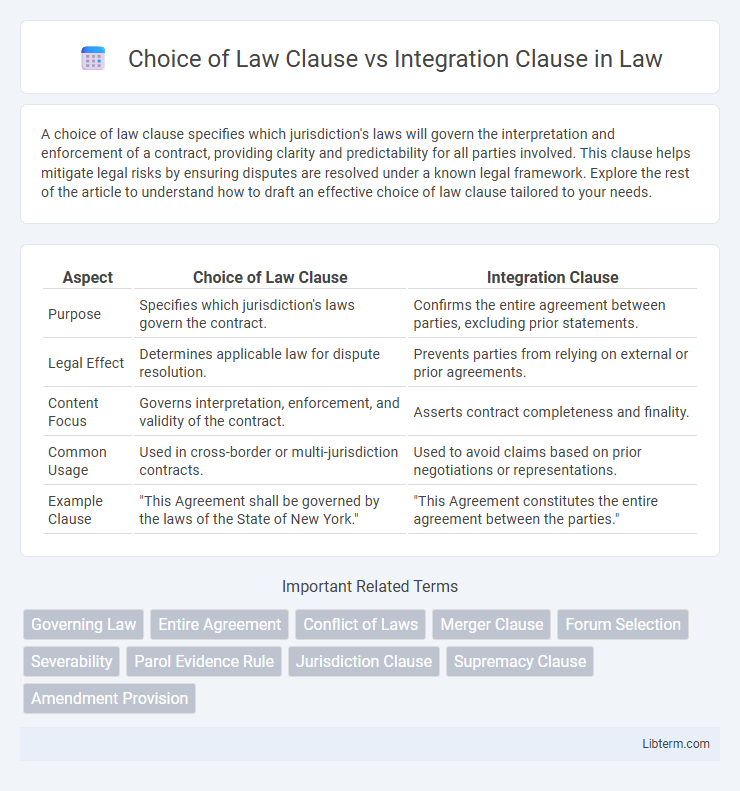
| Aspect | Choice of Law Clause | Integration Clause |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Specifies which jurisdiction's laws govern the contract. | Confirms the entire agreement between parties, excluding prior statements. |
| Legal Effect | Determines applicable law for dispute resolution. | Prevents parties from relying on external or prior agreements. |
| Content Focus | Governs interpretation, enforcement, and validity of the contract. | Asserts contract completeness and finality. |
| Common Usage | Used in cross-border or multi-jurisdiction contracts. | Used to avoid claims based on prior negotiations or representations. |
| Example Clause | "This Agreement shall be governed by the laws of the State of New York." | "This Agreement constitutes the entire agreement between the parties." |
Introduction to Contract Clauses
Choice of law clauses specify which jurisdiction's laws will govern disputes arising from the contract, ensuring legal clarity and predictability. Integration clauses, also known as merger clauses, confirm that the written contract represents the entire agreement between parties, preventing reliance on prior negotiations or external statements. Both clauses play critical roles in contract interpretation and enforcement by defining governing legal frameworks and the completeness of the contract terms.
Defining the Choice of Law Clause
The Choice of Law Clause specifies which jurisdiction's laws govern the interpretation and enforcement of a contract, providing legal certainty and predictability for parties involved. This clause is crucial in international contracts where multiple legal systems could apply, ensuring disputes are resolved under the chosen legal framework. Unlike the Integration Clause, which confirms that the written contract is the complete and final agreement, the Choice of Law Clause focuses solely on designating the applicable legal system for contractual issues.
Understanding the Integration Clause
The Integration Clause, also known as the Entire Agreement Clause, ensures that the written contract represents the complete and final agreement between the parties, excluding any prior negotiations or agreements. This clause prevents either party from claiming that external documents or oral statements modify or override the contract terms, thereby providing clarity and reducing disputes. Understanding the Integration Clause is essential to uphold the contract's integrity and avoid conflicting interpretations in legal proceedings.
Key Differences Between the Clauses
A Choice of Law Clause specifies which jurisdiction's laws will govern the interpretation and enforcement of the contract, impacting dispute resolution and legal predictability. In contrast, an Integration Clause confirms that the written contract represents the entire agreement between parties, excluding any prior oral or written statements. While the Choice of Law Clause determines the applicable legal framework, the Integration Clause ensures contract completeness and prevents reliance on extraneous communications.
Legal Significance of Each Clause
The Choice of Law Clause establishes the jurisdiction whose laws will govern the interpretation and enforcement of the contract, providing predictability and reducing legal disputes by clarifying applicable legal standards. The Integration Clause, also known as the Entire Agreement Clause, legally affirms that the written contract embodies the complete and final agreement between parties, preventing the introduction of prior or extraneous agreements in legal proceedings. Both clauses enhance contractual certainty by defining the governing legal framework and the scope of the agreement's terms.
Impact on Contract Interpretation
The Choice of Law Clause determines which jurisdiction's laws govern the contract, significantly influencing how contractual terms are interpreted and enforced. The Integration Clause establishes that the written contract represents the entire agreement, limiting the use of external evidence in interpretation and emphasizing the document's language. Together, these clauses shape the framework within which courts resolve ambiguities and disputes in contract interpretation.
Common Scenarios for Usage
Choice of law clauses are commonly used in contracts involving parties from different jurisdictions to specify which legal system will govern disputes, ensuring predictability and reducing litigation costs. Integration clauses frequently appear in finalized agreements to confirm that the written contract represents the entire understanding between the parties, preventing reliance on prior negotiations or external statements. Both clauses play crucial roles in commercial contracts, with choice of law clauses addressing governing law issues and integration clauses safeguarding against claims based on alleged oral or side agreements.
Drafting Best Practices
Drafting best practices for choice of law clauses emphasize clear identification of the governing jurisdiction to avoid ambiguity and potential disputes, often specifying the exact state or country's laws to apply. Integration clauses should explicitly state that the written contract represents the entire agreement between parties, preventing the inclusion of external or prior agreements that could complicate enforcement. Combining precise language in both clauses strengthens contract enforceability and reduces litigation risks by minimizing interpretive uncertainties.
Potential Pitfalls and Risks
Choice of Law Clause determines which jurisdiction's laws govern a contract, but selecting an inappropriate or conflicting law can lead to unpredictable enforcement and increased litigation costs. Integration Clause establishes the contract as the complete and final agreement, potentially excluding prior oral or written agreements, which might inadvertently omit critical terms or create disputes over omitted understandings. Both clauses require precise drafting to mitigate risks such as jurisdictional disputes, unintended contract scope limitations, or challenges in proving parties' original intentions.
Conclusion: Importance in Contractual Agreements
Choice of law clauses ensure clarity on which jurisdiction's legal rules govern contractual disputes, reducing uncertainty and potential litigation costs. Integration clauses confirm that the written contract represents the complete and final agreement between parties, preventing reliance on external statements or prior agreements. Both clauses are crucial for safeguarding parties' intentions, minimizing disputes, and enhancing enforceability in complex contractual agreements.
Choice of Law Clause Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com