A minstrel was a medieval European entertainer skilled in music, storytelling, and poetry, often performing in courts or public spaces. They played a vital role in preserving oral traditions and spreading news, using instruments like the lute and harp. Discover more about the fascinating history and cultural impact of minstrels in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
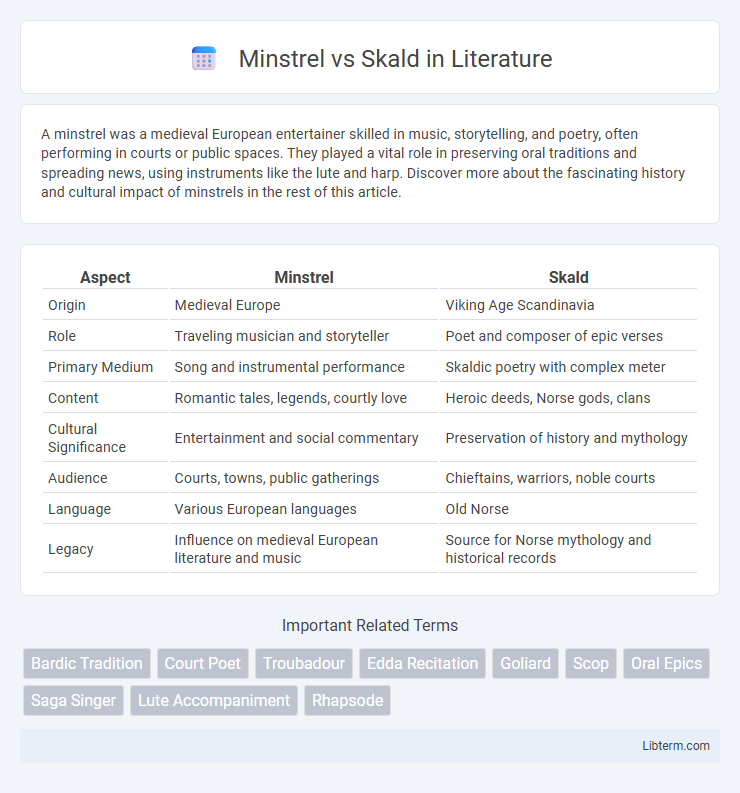
| Aspect | Minstrel | Skald |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Medieval Europe | Viking Age Scandinavia |
| Role | Traveling musician and storyteller | Poet and composer of epic verses |
| Primary Medium | Song and instrumental performance | Skaldic poetry with complex meter |
| Content | Romantic tales, legends, courtly love | Heroic deeds, Norse gods, clans |
| Cultural Significance | Entertainment and social commentary | Preservation of history and mythology |
| Audience | Courts, towns, public gatherings | Chieftains, warriors, noble courts |
| Language | Various European languages | Old Norse |
| Legacy | Influence on medieval European literature and music | Source for Norse mythology and historical records |
Introduction to Minstrels and Skalds
Minstrels and Skalds were medieval bardic figures known for their storytelling and musical talents, often serving as cultural historians and entertainers. Minstrels typically performed songs, poems, and stories across European courts, while Skalds were Norse poets specialized in composing and reciting complex verse to praise chieftains and document heroic deeds. Both played crucial roles in preserving oral traditions and enhancing the cultural identity of their societies.
Historical Origins and Background
Minstrels originated in medieval Europe as wandering musicians and entertainers who performed songs, poetry, and storytelling to courts and public gatherings, often preserving oral traditions. Skalds, rooted in Norse culture during the Viking Age, served as poets and historians composing intricate verses celebrating heroes and events, closely tied to royal courts in Scandinavia. Both roles share the function of cultural transmission, but minstrels emphasized entertainment across social classes while skalds specialized in ceremonial praise and historical record within elite circles.
Roles in Society: Minstrel vs Skald
Minstrels served as versatile entertainers throughout medieval Europe, combining music, storytelling, and poetry to engage a broad audience in courts and public spaces. Skalds, primarily prominent in Norse culture, held a more specialized and revered role as poets and historians who preserved oral traditions, praised chieftains, and reinforced social values through complex, alliterative verse. While minstrels catered to entertainment and popular culture, skalds reinforced political and cultural identity within Viking and Scandinavian societies.
Key Differences in Music and Performance
Minstrels typically performed secular music with solo vocal and instrumental storytelling, often using simple melodies and direct lyrics to engage audiences in taverns or courts. Skalds focused on complex, poetic compositions called skaldic poetry, emphasizing intricate meter and kennings, performed primarily to honor nobles and record historical events. The minstrel's style was more accessible and entertainment-driven, while the skald's performance highlighted lyrical complexity and social prestige.
Language and Literary Styles
Minstrels primarily employed simple narrative poetry and ballads rooted in oral tradition, using accessible language to engage a broad audience. Skalds favored complex kennings and intricate meter, composing sophisticated verses rich in alliteration and metaphor that reflected Norse cultural values. The linguistic style of skaldic poetry emphasized formality and artistic craftsmanship, contrasting the minstrel's emphasis on storytelling and entertainment.
Instruments Used by Minstrels and Skalds
Minstrels commonly played lutes, harps, and flutes, using these string and wind instruments to accompany their songs and storytelling performances. Skalds primarily employed the harp, an essential instrument in Norse poetic tradition, enhancing sagas and epic recitations with its resonant sound. The distinct choice of instruments highlights the cultural contexts of minstrels in medieval Europe and skalds in Viking Scandinavia.
Notable Figures and Legendary Stories
Minstrels and Skalds both served as important storytellers and poets in medieval cultures, with Skalds primarily associated with Norse tradition and figures like Egill Skallagrimsson, whose sagas blend historical feats with poetic brilliance. Minstrels, prevalent in medieval Europe, often celebrated chivalric and local legends, with notable figures such as Adam de la Halle, whose works bridged popular song and courtly poetry. Legendary stories from Skaldic tradition frequently focus on Norse gods, heroic battles, and exploration, while Minstrels commonly recounted tales of knights, romance, and feudal valor.
Cultural Impact and Legacy
Minstrels shaped medieval European culture by preserving oral traditions and influencing early music and poetry, serving as key entertainers and storytellers in courts and public spaces. Skalds, rooted in Norse heritage, significantly impacted Scandinavian literature and mythology through complex and formalized verse, solidifying heroic narratives and cultural identity. Both roles contributed lasting legacies to their respective regions by enriching linguistic heritage and inspiring modern artistic expressions.
Minstrel and Skald Traditions by Region
Minstrel traditions thrive in Western Europe, particularly in England and France, emphasizing storytelling, lyrical ballads, and musical poetry that blend entertainment with historical narration. Skald traditions originate from Norse and Icelandic cultures, focusing on complex, alliterative verse and heroic tales that honor gods and warriors, often performed in royal courts. Both traditions reflect their regions' cultural identities, with minstrels fostering communal storytelling and skalds preserving warrior heritage through elaborate oral compositions.
Conclusion: Influence on Modern Storytelling
Minstrels and skalds both shaped the foundation of modern storytelling through their oral traditions and poetic performances. Minstrels, with their widespread use of music and popular tales in medieval Europe, influenced narrative techniques in folk and popular literature. Skalds preserved the heroic and historical narratives of Norse culture, contributing rich mythological elements that inspire contemporary fantasy and epic storytelling.
Minstrel Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com