Resolution defines the clarity and detail of an image or display, measured in pixels, impacting the overall visual experience. Higher resolution provides sharper, more detailed visuals, enhancing your ability to see fine details and improving image quality. Explore the rest of the article to understand how resolution affects different devices and when higher resolution truly matters.
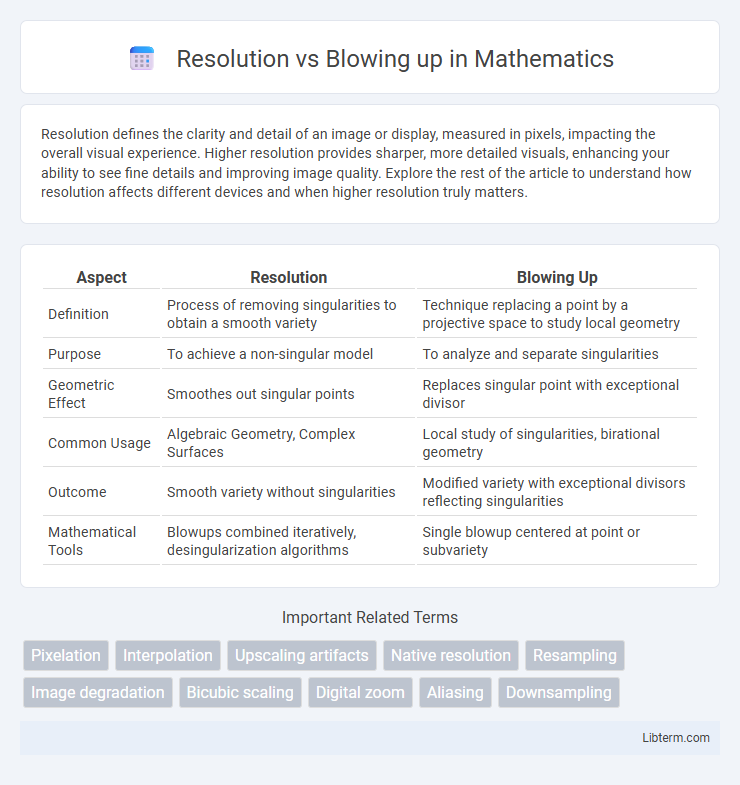
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Resolution | Blowing Up |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of removing singularities to obtain a smooth variety | Technique replacing a point by a projective space to study local geometry |
| Purpose | To achieve a non-singular model | To analyze and separate singularities |
| Geometric Effect | Smoothes out singular points | Replaces singular point with exceptional divisor |
| Common Usage | Algebraic Geometry, Complex Surfaces | Local study of singularities, birational geometry |
| Outcome | Smooth variety without singularities | Modified variety with exceptional divisors reflecting singularities |
| Mathematical Tools | Blowups combined iteratively, desingularization algorithms | Single blowup centered at point or subvariety |
Understanding Image Resolution
Image resolution refers to the detail an image holds, measured in pixels per inch (PPI) or dots per inch (DPI), which directly affects clarity and sharpness. Blowing up an image involves enlarging it beyond its original resolution, often leading to pixelation and loss of quality because the image data must be interpolated. Understanding image resolution is crucial for maintaining visual fidelity during resizing and ensuring optimal display on various devices and print media.
What Does It Mean to “Blow Up” an Image?
To "blow up" an image means to increase its size significantly, often beyond the original resolution, which can lead to pixelation and loss of detail. Resolution defines the number of pixels per inch (PPI) or dots per inch (DPI), determining image clarity and sharpness at a given size. Enlarging a low-resolution image without proper upscaling techniques results in a blurry or blocky appearance, highlighting the importance of starting with a high-resolution file for quality preservation.
Key Differences: Resolution vs Blowing Up
Resolution enhances image clarity by increasing pixel density, resulting in sharper and more detailed visuals, whereas blowing up involves enlarging an image beyond its original size, often causing pixelation and loss of quality. Resolution is measured in pixels per inch (PPI) or dots per inch (DPI), directly affecting the image's sharpness, while blowing up relies on interpolation methods that cannot add genuine detail. Understanding the distinction is crucial for maintaining image integrity in graphic design and printing applications.
How Resolution Affects Image Quality
Resolution directly influences image quality by determining the number of pixels within an image, with higher resolution yielding sharper and more detailed visuals. Increasing resolution enhances clarity and allows for larger print sizes without visible pixelation, maintaining image integrity. Blowing up an image without sufficient resolution causes pixelation and loss of detail, resulting in a degraded and blurry appearance.
The Science Behind Image Enlargement
Resolution defines the number of pixels in an image, directly impacting its clarity and detail when viewed at different sizes. Blowing up an image involves increasing its dimensions beyond the original pixel count, often causing pixelation and loss of sharpness due to insufficient resolution. Advanced algorithms like AI-driven upscaling work by interpolating missing pixels and enhancing edge detail, mitigating quality degradation during enlargement.
Common Myths About Resolution and Enlargement
Many people mistakenly believe that increasing image resolution automatically improves quality, but blowing up low-resolution images often leads to pixelation and loss of detail. Resolution refers to the number of pixels in an image, and enlarging an image without proper interpolation causes distortion, not clarity. Understanding the difference between native resolution and artificial enlargement is essential for accurate image editing and printing.
Tools and Techniques for Upscaling Images
Resolution enhancement involves using advanced algorithms such as convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and generative adversarial networks (GANs) to increase image clarity without creating artifacts. Blowing up images relies on interpolation methods like bicubic or Lanczos to enlarge pictures but often results in pixelation and loss of detail. Tools such as Adobe Photoshop's Preserve Details 2.0, Topaz Gigapixel AI, and AI-based upscaling software offer refined techniques combining machine learning and image processing to achieve superior upscaling results.
Pros and Cons of Increasing Image Size
Increasing image size through resolution enhancement improves detail and clarity, allowing for better print quality and close-up views. However, blowing up an image without sufficient original resolution can cause pixelation, loss of sharpness, and visible artifacts, reducing overall image quality. High-resolution scaling demands more processing power and storage, making it less efficient for web use or limited devices.
Best Practices for Maintaining Quality When Enlarging
Maintaining image quality when enlarging involves using resolution enhancement techniques such as interpolation methods like bicubic or Lanczos, which preserve edge sharpness and minimize pixelation. Utilizing vector graphics or AI-powered upscaling tools ensures scalability without loss of detail, especially for logos and line art. Always work with the highest original resolution available and avoid excessive digital zooming to maintain clarity and prevent blurring during enlargement.
Choosing the Right Resolution for Your Needs
Choosing the right resolution depends on the intended use, with higher resolutions providing greater detail and clarity for printing and large displays, while lower resolutions suffice for web content and quick sharing. Blowing up an image beyond its native resolution often results in pixelation and loss of quality due to limited pixel data. Optimizing resolution ensures sharp visuals and efficient file sizes, balancing quality and performance for specific project requirements.
Resolution Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com