Abstraction simplifies complex systems by focusing on essential features while hiding unnecessary details, enabling clearer understanding and efficient problem-solving. This concept is widely applied in software development, design, and everyday decision-making to manage complexity and improve communication. Explore the rest of the article to discover how abstraction can enhance Your approach to various challenges.
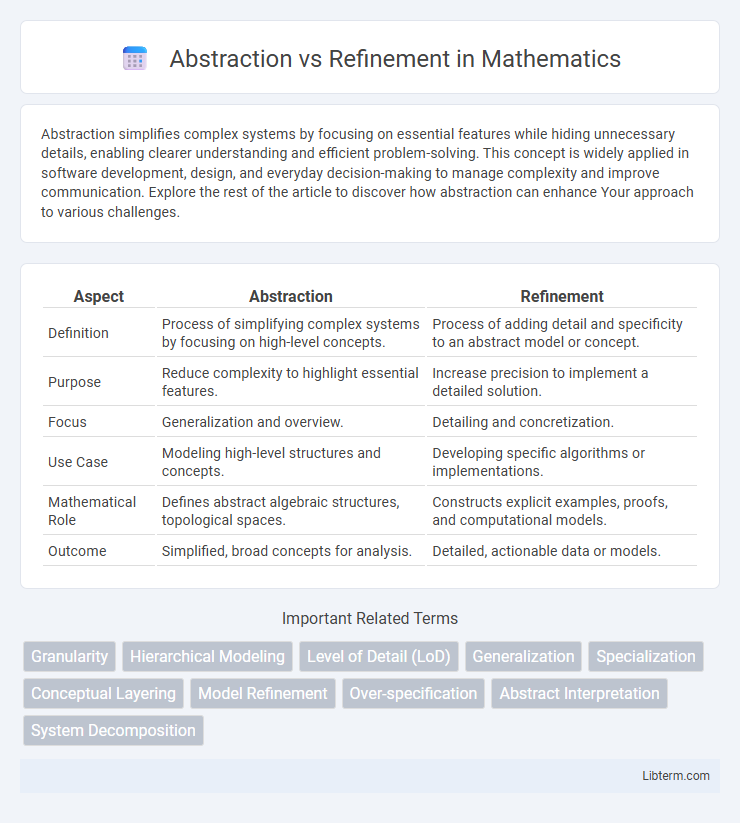
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Abstraction | Refinement |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of simplifying complex systems by focusing on high-level concepts. | Process of adding detail and specificity to an abstract model or concept. |
| Purpose | Reduce complexity to highlight essential features. | Increase precision to implement a detailed solution. |
| Focus | Generalization and overview. | Detailing and concretization. |
| Use Case | Modeling high-level structures and concepts. | Developing specific algorithms or implementations. |
| Mathematical Role | Defines abstract algebraic structures, topological spaces. | Constructs explicit examples, proofs, and computational models. |
| Outcome | Simplified, broad concepts for analysis. | Detailed, actionable data or models. |
Introduction to Abstraction and Refinement
Abstraction simplifies complex systems by hiding unnecessary details, enabling focus on high-level functionality and essential features. Refinement progressively adds detail to abstract models, ensuring each step maintains consistency with the initial design while approaching concrete implementation. Both techniques enhance software development by balancing clarity with precision, supporting effective problem-solving and system evolution.
Defining Abstraction in Computing
Abstraction in computing involves simplifying complex systems by focusing on essential features while hiding irrelevant details to improve understanding and manageability. It enables developers to create models or interfaces that represent real-world concepts without exposing underlying implementation complexities. This process supports modularity, code reuse, and efficient problem-solving across various levels of software design and development.
Understanding Refinement in System Design
Refinement in system design involves progressively elaborating abstract specifications into detailed, concrete implementations while preserving correctness and intended behavior. It enables developers to verify consistency and enhance system reliability by methodically decomposing high-level models into executable components. Effective refinement ensures scalability and maintainability by bridging conceptual designs with practical applications through systematic validation and iteration.
Key Differences Between Abstraction and Refinement
Abstraction simplifies complex systems by hiding detailed implementation and emphasizing essential features, while refinement involves adding detailed specifications to abstract models to make them more concrete. Key differences include abstraction's role in generalizing and reducing complexity versus refinement's focus on elaboration and precision enhancement in system design. Abstraction supports high-level understanding and modularity, whereas refinement ensures correctness and completeness through successive detailed development.
The Role of Abstraction in Problem Solving
Abstraction plays a crucial role in problem solving by enabling the simplification of complex systems into manageable models that highlight essential features while ignoring irrelevant details. This process facilitates clearer understanding, efficient communication, and the design of scalable solutions by focusing on high-level concepts rather than low-level implementations. Leveraging abstraction allows developers and analysts to tackle intricate problems systematically, improving problem decomposition and reducing cognitive load.
The Purpose of Refinement in Development
Refinement in development aims to transform high-level abstractions into detailed, implementable components, enhancing clarity and precision throughout the design process. It systematically eliminates ambiguity by breaking down complex models into concrete specifications, facilitating accurate coding and testing. This process ensures that initial abstract concepts evolve into effective, functional solutions aligned with project requirements.
Practical Examples of Abstraction vs Refinement
Abstraction in software engineering simplifies complex systems by hiding details, such as using an interface to represent various database operations without exposing implementation specifics. Refinement involves incrementally adding detail to an abstract concept, like transforming a high-level design into detailed code modules that specify exact behavior. Practical examples include designing a payment system where abstraction defines the payment methods interface, while refinement develops specific classes for credit card and PayPal payments.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Abstraction
Abstraction simplifies complex systems by hiding unnecessary details, enabling developers to focus on high-level functionality and improve code maintainability. This approach reduces cognitive load, enhances modularity, and facilitates easier debugging and testing. Drawbacks include the potential for oversimplification, which can obscure important implementation details and lead to reduced performance or difficulties in understanding lower-level system behavior.
Advantages and Challenges of Refinement
Refinement enhances software development by transforming abstract models into detailed designs, improving code accuracy and maintainability. This process uncovers hidden requirements and potential errors early, reducing costly revisions during later stages. However, refinement can be time-consuming and requires careful management to avoid complexity and ensure consistency across evolving system specifications.
Choosing Between Abstraction and Refinement
Choosing between abstraction and refinement depends on the complexity and scope of the problem. Abstraction simplifies by highlighting essential features and ignoring irrelevant details, making it ideal for high-level design and communication. Refinement, on the other hand, incrementally adds detail and precision, best suited for implementation phases where accuracy and completeness are critical.
Abstraction Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com