Collapsible designs enhance portability and save space by allowing objects to fold or collapse efficiently. This feature is especially useful for furniture, containers, and tools, making them practical for various environments. Discover how incorporating collapsible elements can improve your everyday convenience in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
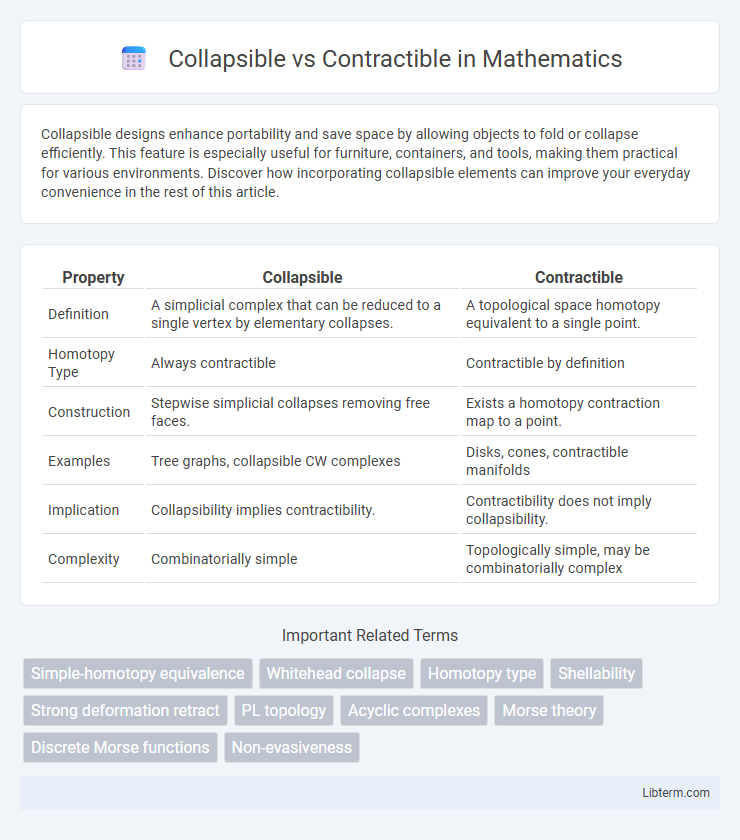
| Property | Collapsible | Contractible |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A simplicial complex that can be reduced to a single vertex by elementary collapses. | A topological space homotopy equivalent to a single point. |
| Homotopy Type | Always contractible | Contractible by definition |
| Construction | Stepwise simplicial collapses removing free faces. | Exists a homotopy contraction map to a point. |
| Examples | Tree graphs, collapsible CW complexes | Disks, cones, contractible manifolds |
| Implication | Collapsibility implies contractibility. | Contractibility does not imply collapsibility. |
| Complexity | Combinatorially simple | Topologically simple, may be combinatorially complex |
Introduction: Understanding Collapsible and Contractible
Collapsible and contractible refer to distinct concepts in topology, where a collapsible complex can be reduced to a point through a sequence of elementary collapses, preserving homotopy type. Contractible spaces are those that can continuously shrink to a single point within the space, implying that their identity map is homotopic to a constant map. Understanding the difference is crucial in algebraic topology, where collapsibility implies contractibility, but contractibility does not necessarily imply collapsibility.
Definitions: What Are Collapsible and Contractible?
Collapsible spaces are topological structures that can be reduced to a point through a sequence of elementary collapses, simplifying their complexes while preserving homotopy type. Contractible spaces are those that can be continuously shrunk to a single point within the space, implying they are homotopy equivalent to a point. While every collapsible space is contractible, not all contractible spaces are collapsible, highlighting a key distinction in algebraic topology.
Key Differences Between Collapsible and Contractible
Collapsible refers to a structure or object designed to fold down into a smaller, more compact form for easy storage or transport, while contractible describes a material or entity that can shrink or reduce in size through internal forces or mechanisms. The key difference lies in collapsibility being a deliberate design feature for physical manipulation, whereas contractibility often involves natural or physiological changes such as muscle contraction. Understanding these distinctions is crucial in fields ranging from product design to biology, where functionality and adaptation impact performance and usability.
Use Cases for Collapsible Structures
Collapsible structures excel in user interface design where dynamic content management is crucial, such as navigation menus, FAQs, and dashboards, allowing users to expand or hide sections without page reloads. Their use enhances user experience by reducing clutter and enabling users to focus on relevant information, particularly in mobile applications and responsive web designs. Industries leveraging collapsible elements include e-commerce for product filters, education for course content organization, and content management systems to streamline data presentation.
Use Cases for Contractible Structures
Contractible structures excel in topological data analysis, enabling simplification of complex shapes while preserving intrinsic properties for efficient computation. They are widely used in robotics for path planning, allowing robots to navigate spaces by collapsing redundant pathways without losing connectivity information. In computer graphics, contractible models support mesh optimization and surface reconstruction, reducing computational load while maintaining geometric integrity.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Collapsible
Collapsible components offer significant advantages such as space-saving design and improved user interface by hiding content until needed, which enhances page aesthetics and usability. However, collapsible elements can pose accessibility challenges for screen readers and may require additional scripting to ensure smooth animations and state management. Their primary disadvantage lies in potential user confusion if content is hidden without clear indicators, leading to overlooked information or reduced discoverability.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Contractible
Contractible elements offer advantages such as improved user experience by allowing content to be hidden or shown with a simple click, reducing clutter and saving screen space. They enhance website performance by loading only essential data initially, which decreases load times and bandwidth usage. However, contractible components may negatively impact accessibility if not properly designed, and overuse can confuse users or hide important information unintentionally.
Performance and Efficiency Comparison
Collapsible structures improve performance by enabling on-demand content expansion, reducing initial load times and saving memory resources. Contractible elements enhance efficiency through minimal resource usage by allowing users to hide unnecessary details, optimizing rendering processes and interaction speed. Both approaches contribute to streamlined user experiences by managing content visibility, with collapsible designs favoring dynamic data handling and contractible designs emphasizing static content management.
Real-World Examples and Applications
Collapsible structures, such as folding bicycles and collapsible tents, enable compact storage and ease of transport, making them ideal for urban commuting and outdoor activities. Contractible objects, like retractable stadium roofs and collapsible medical devices, allow components to shrink or fold within a fixed space, optimizing functionality in confined environments. Both collapsible and contractible designs prioritize efficiency and versatility in industries ranging from transportation and architecture to healthcare and consumer products.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Collapsible and Contractible
Choosing between collapsible and contractible elements depends on user interface needs and content complexity. Collapsible sections offer simplified navigation with clear expansion and contraction, ideal for organizing large amounts of information. Contractible elements provide more interactive control, suitable for dynamic content where space-saving is crucial without sacrificing accessibility.
Collapsible Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com