Overlay technology enhances visual presentations by layering images or information without obstructing the main view, providing a seamless integration of data. This technique is widely used in graphic design, video production, and augmented reality to improve user experience and communication clarity. Discover how overlay can transform your projects by exploring the full article.
Table of Comparison
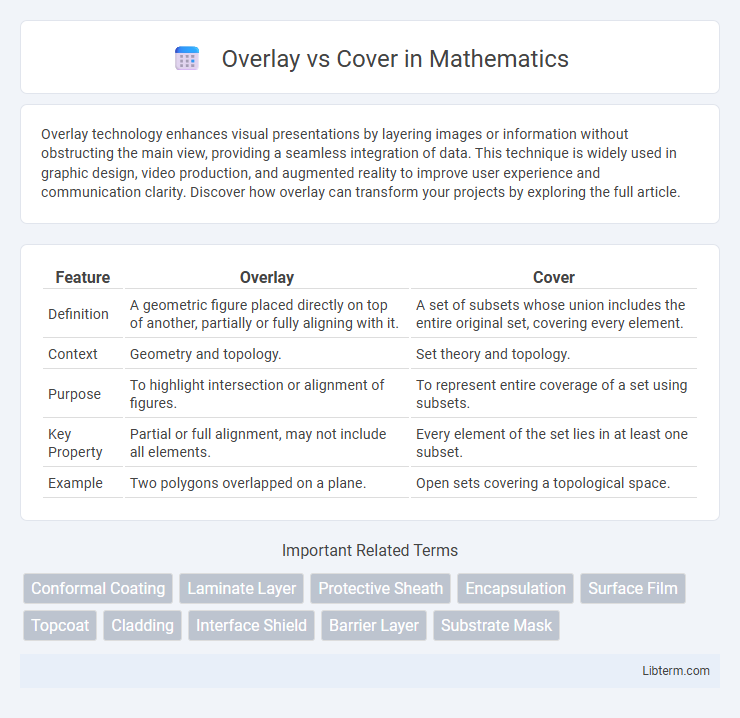
| Feature | Overlay | Cover |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A geometric figure placed directly on top of another, partially or fully aligning with it. | A set of subsets whose union includes the entire original set, covering every element. |
| Context | Geometry and topology. | Set theory and topology. |
| Purpose | To highlight intersection or alignment of figures. | To represent entire coverage of a set using subsets. |
| Key Property | Partial or full alignment, may not include all elements. | Every element of the set lies in at least one subset. |
| Example | Two polygons overlapped on a plane. | Open sets covering a topological space. |
Introduction: Understanding Overlay and Cover
Overlay refers to a graphical element that is placed over another element to enhance visual appeal or provide additional information without obstructing the underlying content. Cover typically denotes a full or partial element that completely obscures the content beneath it, often used for emphasis or protection. Understanding the differences between overlay and cover helps in designing user interfaces and web layouts that balance visibility and interaction effectively.
Definition of Overlay
Overlay refers to a graphical element or layer placed on top of existing content to enhance visual presentation or provide additional information without completely obscuring the background. Unlike a cover, which typically hides or replaces the underlying content, an overlay allows partial visibility, maintaining context while adding supplementary details or interactive features. Commonly used in web design, overlays support user engagement by displaying tooltips, menus, or highlights dynamically.
Definition of Cover
Cover refers to a design element that fully conceals underlying content or images, ensuring no part of the original is visible. It typically acts as a solid or semi-transparent layer that completely masks the background for emphasis or readability. In contrast, an overlay partially reveals what lies beneath, blending visual layers without total obstruction.
Key Differences Between Overlay and Cover
Overlay and cover differ mainly in purpose and application; an overlay is a semi-transparent layer placed above content to enhance visibility or add effects, while a cover fully conceals the underlying element. Overlays often support interactive elements like buttons or tooltips, whereas covers are primarily used to block access or emphasize a modal window. In design and web development, choosing between overlay and cover depends on the desired user interaction and visual impact, with overlays maintaining context and covers restricting visibility.
Common Uses of Overlays
Overlays are commonly used in graphic design and web development to create visual effects such as highlighting text, enhancing images, or adding textures without altering the original content. They serve as semi-transparent layers that improve readability and user engagement on websites, often applied in hero sections, modals, and photo galleries. In contrast to covers, overlays maintain interaction with underlying elements while providing aesthetic enhancement or functional emphasis.
Common Uses of Covers
Covers are frequently used to protect surfaces and objects from damage, dust, moisture, or wear, making them essential in environments like construction sites, furniture maintenance, and vehicle protection. Common covers include tarp covers for outdoor equipment, mattress covers for hygiene and allergy prevention, and slipcovers for furniture preservation and style updates. These applications emphasize durability, ease of use, and effectiveness in extending the lifespan of covered items.
Benefits of Using Overlays
Overlays enhance user experience by providing interactive elements that improve navigation and content visibility without disrupting the underlying page structure. They allow for focused attention on specific information, such as notifications, forms, or media, increasing engagement and conversion rates. Utilizing overlays also reduces page reloads, resulting in faster interaction and better performance, essential for maintaining user retention and SEO benefits.
Advantages of Using Covers
Covers offer superior protection by fully encasing surfaces, effectively preventing damage from moisture, dust, and wear compared to overlays. They provide an easy-to-clean barrier that extends the lifespan of underlying materials, reducing maintenance costs. Utilizing covers enhances durability and maintains optimal functionality in both residential and industrial applications.
Overlay vs Cover: Which to Choose?
Overlay provides a semi-transparent layer allowing underlying content to remain partially visible, enhancing user focus without complete obstruction, while cover fully hides the background content for maximum emphasis on the foreground element. Choose overlay when subtlety and context retention are essential for user experience, such as in modal dialogs or tooltips. Opt for cover in scenarios requiring full attention shift, like fullscreen popups or critical alerts, where background distraction must be eliminated.
Conclusion: Making the Right Choice
Choosing between overlay and cover depends on the specific use case and desired user experience; overlays are ideal for drawing focused attention without navigating away, while covers are better suited for creating immersive, full-screen interactions. Understanding the context, such as whether you need to display supplementary information or replace content entirely, guides the optimal selection. Prioritizing user engagement and interface clarity ensures the right balance between visibility and usability.
Overlay Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com