Simple inheritance allows a subclass to inherit properties and methods from a single parent class, enabling code reuse and streamlined organization. This fundamental concept in object-oriented programming enhances maintainability and reduces redundancy. Explore the rest of the article to understand how simple inheritance can improve your coding practices.
Table of Comparison
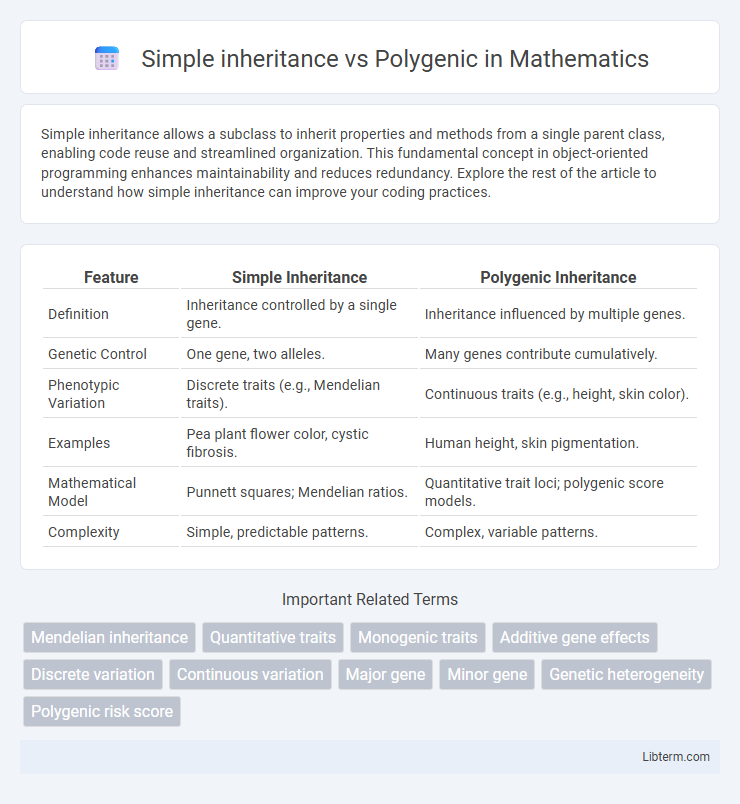
| Feature | Simple Inheritance | Polygenic Inheritance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Inheritance controlled by a single gene. | Inheritance influenced by multiple genes. |
| Genetic Control | One gene, two alleles. | Many genes contribute cumulatively. |
| Phenotypic Variation | Discrete traits (e.g., Mendelian traits). | Continuous traits (e.g., height, skin color). |
| Examples | Pea plant flower color, cystic fibrosis. | Human height, skin pigmentation. |
| Mathematical Model | Punnett squares; Mendelian ratios. | Quantitative trait loci; polygenic score models. |
| Complexity | Simple, predictable patterns. | Complex, variable patterns. |
Introduction to Genetic Inheritance
Simple inheritance involves traits controlled by a single gene with distinct alleles, producing clear Mendelian patterns such as dominant and recessive traits. Polygenic inheritance occurs when multiple genes contribute to a single trait, resulting in continuous variation often seen in characteristics like height, skin color, and weight. Understanding these inheritance types is crucial for studying genetic diversity and predicting trait expression in offspring.
What Is Simple (Mendelian) Inheritance?
Simple (Mendelian) inheritance involves traits controlled by a single gene with clear dominant and recessive alleles, resulting in predictable genetic patterns across generations. Polygenic inheritance contrasts by involving multiple genes contributing to a single trait, producing continuous variation rather than distinct categories. Mendelian inheritance principles, established by Gregor Mendel, form the foundation for understanding monogenic traits such as pea plant flower color or human blood type.
Key Features of Simple Inheritance
Simple inheritance involves traits controlled by a single gene with clear dominant or recessive alleles, resulting in predictable phenotypic ratios according to Mendelian genetics. Key features include discrete, easily observable traits such as pea plant flower color or blood type, with inheritance patterns following classic Mendel's laws of segregation and independent assortment. Unlike polygenic inheritance, simple inheritance does not involve multiple genes contributing additive effects, making genetic prediction straightforward and less influenced by environmental factors.
Polygenic Inheritance Explained
Polygenic inheritance involves multiple genes contributing to a single trait, producing continuous variation such as height or skin color, unlike simple inheritance where a single gene controls a trait with distinct phenotypes. Each gene involved in polygenic traits adds a small effect, resulting in a wide range of possible outcomes influenced by environmental factors. This complex genetic interaction challenges prediction and categorization, highlighting the multifactorial nature of many human characteristics.
Main Characteristics of Polygenic Traits
Polygenic traits are controlled by multiple genes, each contributing a small effect, resulting in continuous variation such as height, skin color, and weight. Unlike simple inheritance patterns where traits are determined by a single gene with dominant or recessive alleles, polygenic inheritance leads to a wide range of phenotypes influenced by environmental factors. These traits exhibit a normal distribution pattern in populations, reflecting the cumulative impact of numerous genetic loci.
Differences Between Simple and Polygenic Inheritance
Simple inheritance involves traits controlled by a single gene with clear dominant or recessive alleles, resulting in predictable Mendelian ratios. Polygenic inheritance, however, involves multiple genes contributing cumulatively to a trait, producing continuous variation such as height or skin color. The main difference lies in the genetic complexity, where simple inheritance affects discrete traits and polygenic inheritance influences quantitative traits with environmental interactions.
Real-Life Examples of Simple Inheritance
Simple inheritance involves traits controlled by a single gene with clear dominant or recessive alleles, exemplified by Mendelian traits such as pea plant flower color or cystic fibrosis in humans. Polygenic inheritance, in contrast, describes traits influenced by multiple genes, resulting in continuous variation like human height or skin color. Real-life examples of simple inheritance are easily observed in conditions such as sickle cell anemia and Huntington's disease, where a single gene mutation dictates the phenotype.
Real-Life Examples of Polygenic Inheritance
Polygenic inheritance involves multiple genes contributing to a single trait, resulting in continuous variation, unlike simple inheritance where traits follow Mendelian patterns with dominant and recessive alleles. Real-life examples of polygenic inheritance include human skin color, height, and eye color, all of which show a wide range of phenotypes due to the combined effect of several genes. These traits are influenced by environmental factors and genetic interactions, making prediction more complex compared to simple Mendelian traits like pea plant flower color or blood type.
Importance in Genetic Counseling
Simple inheritance involves traits controlled by a single gene, making risk prediction and genetic counseling more straightforward with clear inheritance patterns such as autosomal dominant or recessive. Polygenic inheritance entails multiple genes contributing to a trait, complicating risk assessment due to the interaction of numerous genetic variants and environmental factors. Understanding both inheritance types is crucial in genetic counseling for accurate risk evaluation, personalized management strategies, and informed family planning decisions.
Summary: Which Inheritance Pattern Applies?
Simple inheritance involves traits controlled by a single gene with clear dominant or recessive alleles, resulting in predictable Mendelian patterns. Polygenic inheritance describes traits influenced by multiple genes, producing continuous variation and complex phenotypes, such as height or skin color. Determining the inheritance pattern depends on whether the trait shows discrete categories typical of simple inheritance or a spectrum of phenotypes characteristic of polygenic traits.
Simple inheritance Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com