Segmentation divides a market or audience into distinct groups based on shared characteristics, enabling more targeted and effective marketing strategies. Understanding these segments helps you tailor messaging, products, and services to meet specific needs and preferences, increasing engagement and conversion rates. Explore the rest of the article to learn how precise segmentation can transform your marketing efforts.
Table of Comparison
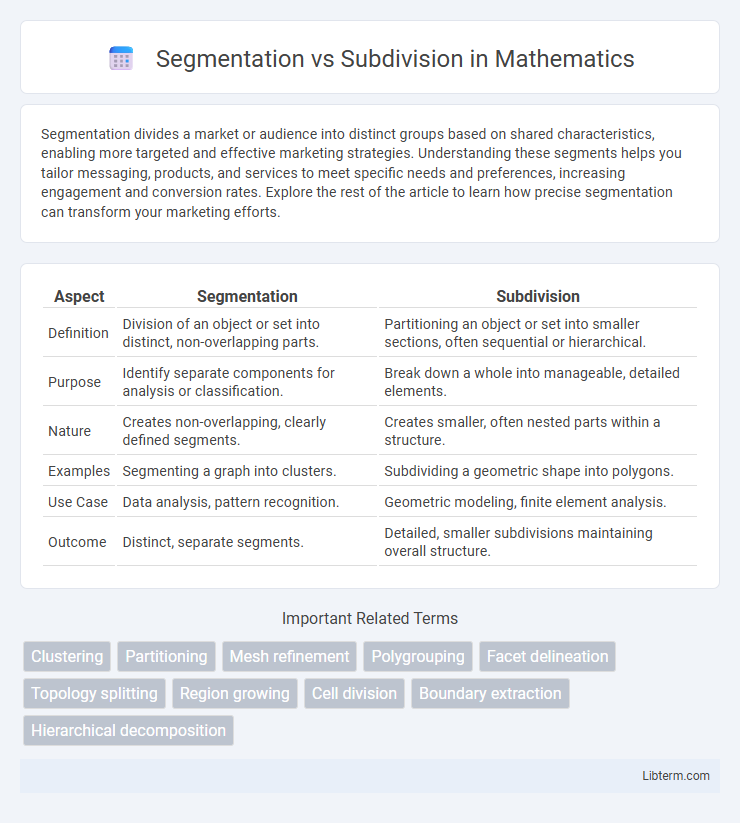
| Aspect | Segmentation | Subdivision |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Division of an object or set into distinct, non-overlapping parts. | Partitioning an object or set into smaller sections, often sequential or hierarchical. |
| Purpose | Identify separate components for analysis or classification. | Break down a whole into manageable, detailed elements. |
| Nature | Creates non-overlapping, clearly defined segments. | Creates smaller, often nested parts within a structure. |
| Examples | Segmenting a graph into clusters. | Subdividing a geometric shape into polygons. |
| Use Case | Data analysis, pattern recognition. | Geometric modeling, finite element analysis. |
| Outcome | Distinct, separate segments. | Detailed, smaller subdivisions maintaining overall structure. |
Introduction to Segmentation and Subdivision
Segmentation involves dividing a broad market or population into smaller, distinct groups based on shared characteristics like demographics, behavior, or needs, enabling targeted marketing and personalized strategies. Subdivision refers to further breaking down these segments into more specific units or categories to enhance focus and accuracy in addressing particular traits or preferences. Understanding the foundational differences between segmentation and subdivision helps businesses optimize resource allocation and tailor campaigns effectively to diverse audience subsets.
Defining Segmentation
Segmentation involves dividing a broad market or audience into distinct groups based on shared characteristics such as demographics, behaviors, or needs to enable targeted marketing strategies. This process enhances customer understanding and improves product positioning by addressing specific segment demands. Defined segments allow businesses to allocate resources effectively and maximize marketing ROI through personalized communication and tailored offerings.
Understanding Subdivision
Subdivision refers to the process of dividing a larger entity, such as land or data sets, into smaller, more manageable parts for detailed analysis or development. In real estate, subdivision typically involves creating plots from a larger parcel to facilitate sale or construction, following legal and zoning regulations. Understanding subdivision is essential for optimizing resource allocation, improving organizational clarity, and enhancing targeted marketing strategies.
Key Differences Between Segmentation and Subdivision
Segmentation divides a market into distinct groups based on shared characteristics such as demographics, behavior, or needs, allowing targeted marketing strategies. Subdivision refers to splitting an existing segment into smaller, more specific groups to refine focus and increase marketing precision. Key differences include segmentation being the initial grouping process, while subdivision is a further breakdown within those groups to enhance customization.
Common Applications of Segmentation
Segmentation is commonly used in marketing to divide a broad consumer or business market into sub-groups based on shared characteristics like demographics, behavior, or needs, enabling targeted advertising and personalized campaigns. It plays a crucial role in image processing and computer vision, where it isolates objects or regions within an image for recognition or analysis. In healthcare, patient segmentation aids in tailoring treatment plans by categorizing patients according to disease type, severity, or response to therapy, improving outcomes and resource allocation.
Common Uses of Subdivision
Subdivision commonly refers to the process of dividing land into smaller plots for residential, commercial, or industrial development, facilitating organized urban planning and property management. It plays a critical role in real estate, enabling developers to create housing communities, commercial complexes, and infrastructure projects with clear legal boundaries. Subdivision also supports zoning regulations and enhances resource allocation by defining specific land uses within a larger parcel.
Advantages of Segmentation
Segmentation offers enhanced data management by dividing databases or memory into variable-sized, logical units, improving efficiency and reducing fragmentation compared to fixed-size subdivision blocks. It supports better protection and sharing, allowing specific segments to be independently accessed and secured, which benefits multitasking environments. Additionally, segmentation facilitates easier program modification and growth, as individual segments can be resized or replaced without affecting others.
Benefits of Subdivision
Subdivision enhances land use efficiency by dividing large parcels into smaller, market-ready lots, attracting diverse buyers and increasing property value. It simplifies legal ownership, facilitates infrastructure development, and improves access to utilities, promoting organized urban growth. This process supports tailored zoning and planning, enabling sustainable community design and optimized resource allocation.
Choosing Between Segmentation and Subdivision
Choosing between segmentation and subdivision depends on the specific goals and context of data analysis or marketing strategies. Segmentation involves dividing a broad market into distinct groups based on shared characteristics such as demographics, behaviors, or needs, enabling targeted messaging and product offerings. Subdivision breaks these segments further into smaller, more detailed units to enhance precision but may require more resources and detailed data to maintain effectiveness.
Conclusion: Which Method is Right for You?
Choosing between segmentation and subdivision depends on the specific goals and complexity of your data analysis. Segmentation is ideal for dividing a market into distinct groups based on shared characteristics, optimizing targeted marketing strategies and customer insights. Subdivision works best for breaking down a dataset into smaller parts when detailed, granular analysis is required, particularly in geographic or hierarchical data contexts.
Segmentation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com