T2 technology revolutionizes industrial automation by enhancing precision and efficiency in manufacturing processes. Its advanced sensors and real-time data analytics empower your systems to reduce downtime and improve product quality. Explore the full article to discover how T2 can transform your operations and boost productivity.
Table of Comparison
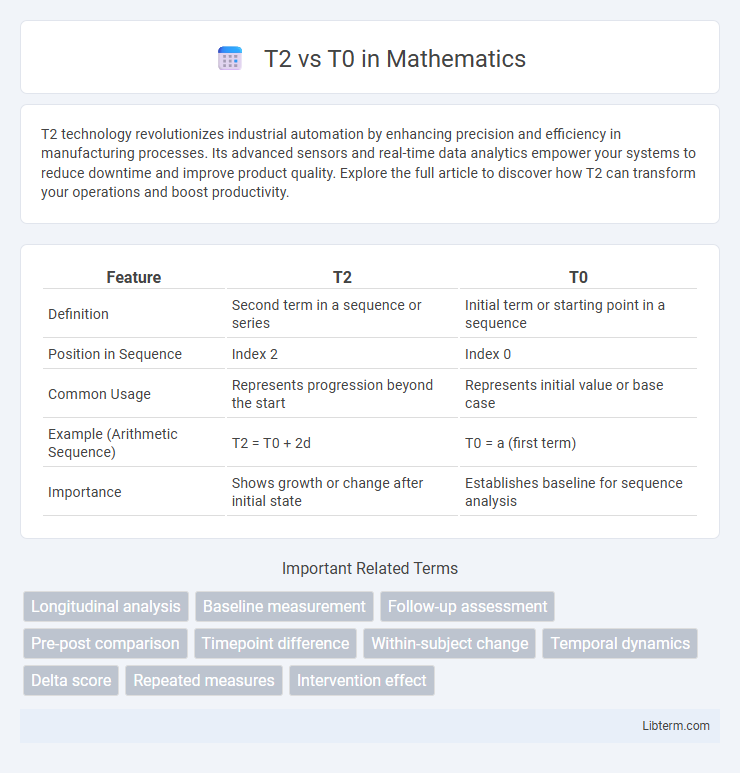
| Feature | T2 | T0 |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Second term in a sequence or series | Initial term or starting point in a sequence |
| Position in Sequence | Index 2 | Index 0 |
| Common Usage | Represents progression beyond the start | Represents initial value or base case |
| Example (Arithmetic Sequence) | T2 = T0 + 2d | T0 = a (first term) |
| Importance | Shows growth or change after initial state | Establishes baseline for sequence analysis |
Introduction to T2 and T0
T2 and T0 refer to different time zone offsets from Coordinated Universal Time (UTC), with T0 representing UTC+0 and T2 typically indicating UTC+2. T0 often serves as the baseline for global timekeeping and standardization, placing it at the prime meridian without any additional offset. T2 is commonly used in regions observing daylight saving or located east of the prime meridian, affecting scheduling, communications, and timestamp accuracy in those areas.
Definition of T2 and T0
T0 refers to the time of an initial event or baseline measurement, often serving as the starting point for tracking changes or progress. T2 denotes a specific subsequent time point or measurement occurring after T0, used to assess development or outcomes at that stage. Precise definitions of T0 and T2 depend on the context, such as clinical trials, project timelines, or experimental protocols.
Key Differences Between T2 and T0
T2 and T0 refer to different settlement protocols in financial markets, with T2 meaning settlement occurs two business days after the trade date, while T0 implies same-day settlement. The key difference lies in liquidity and risk management: T0 reduces counterparty risk by accelerating transaction finality, but demands higher operational efficiency and real-time processing capabilities. T2 is more traditional, allowing more time for funding and reconciliation, but increasing settlement risk due to the delay.
Advantages of T2
T2 offers significant advantages over T0, including enhanced scalability and faster transaction processing speeds, making it ideal for high-volume applications. Its improved security protocols reduce vulnerabilities, ensuring robust protection of sensitive data. T2's advanced interoperability supports seamless integration with various platforms, boosting overall system efficiency and user experience.
Advantages of T0
T0 offers real-time transaction processing, significantly reducing settlement times compared to T2's longer batch processing cycles. This instantaneous settlement enhances liquidity management and minimizes counterparty risk for financial institutions. The seamless integration of T0 with advanced blockchain technology further boosts transparency and security in financial markets.
Use Cases for T2
T2 instances offer enhanced CPU performance and burstable capability ideal for workloads with variable CPU demands such as web servers, development environments, and small databases. These instances provide a balance of compute, memory, and network resources, making them suitable for applications requiring consistent baseline performance with the ability to handle periodic spikes. In contrast, T0 refers to baseline performance with limited burst capacity, making T2 more appropriate for use cases needing reliable responsiveness under fluctuating workloads.
Use Cases for T0
T0 technology offers enhanced real-time data processing and analytics, making it ideal for high-frequency trading and rapid decision-making scenarios where milliseconds matter. Its low-latency architecture supports use cases in autonomous vehicles and industrial automation requiring immediate responsiveness. Compared to T2, T0 delivers superior performance in dynamic environments demanding instant data interpretation and action.
Performance Comparison: T2 vs T0
The T2 micro instances offer a baseline level of CPU performance with the ability to burst above the baseline, making them cost-effective for low to moderate workloads, while the T0 instances represent earlier generation burstable performance with more limited CPU credits and slower response times. T2 instances typically provide better sustained CPU performance, increased network throughput, and enhanced memory capacity compared to T0, resulting in improved application responsiveness and efficiency. Performance metrics show T2 achieves higher CPU utilization rates and faster scaling, making it more suitable for unpredictable workloads requiring flexible compute power.
Choosing Between T2 and T0
Choosing between T2 and T0 processors depends on the specific needs of the workload and performance requirements. T2 processors provide a baseline level of CPU performance with the ability to burst above the baseline for short durations, making them suitable for general-purpose applications with variable demand. T0 processors typically offer lower baseline performance and are more cost-effective for less demanding tasks, so evaluating workload intensity and budget constraints is essential for optimal decision-making.
Conclusion: T2 or T0?
T2 displays superior energy efficiency and enhanced processing power compared to T0, making it the preferred choice for high-performance computing tasks. Its advanced thermal management and faster data throughput significantly outperform T0 in real-world applications. Therefore, T2 is the optimal selection for users prioritizing speed and sustainability in their technology investments.
T2 Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com