Triggered emotions can often disrupt your ability to think clearly and respond calmly in difficult situations. Understanding the root causes of these triggers helps you develop healthier coping mechanisms and maintain emotional balance. Explore the rest of this article to learn how to identify and manage your emotional triggers effectively.
Table of Comparison
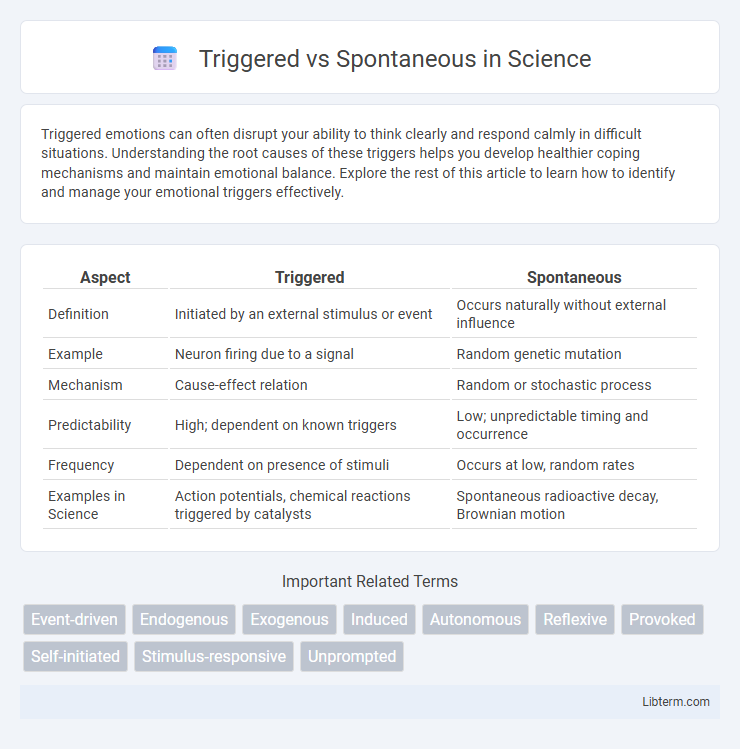
| Aspect | Triggered | Spontaneous |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Initiated by an external stimulus or event | Occurs naturally without external influence |
| Example | Neuron firing due to a signal | Random genetic mutation |
| Mechanism | Cause-effect relation | Random or stochastic process |
| Predictability | High; dependent on known triggers | Low; unpredictable timing and occurrence |
| Frequency | Dependent on presence of stimuli | Occurs at low, random rates |
| Examples in Science | Action potentials, chemical reactions triggered by catalysts | Spontaneous radioactive decay, Brownian motion |
Understanding Triggered vs Spontaneous Responses
Triggered responses occur as automatic reactions to specific stimuli, often rooted in past experiences or conditioned behavior, leading to immediate and involuntary actions. Spontaneous responses arise without external prompts, reflecting genuine, moment-to-moment decision-making and creativity that are less constrained by prior conditioning. Understanding the distinction between triggered and spontaneous responses is crucial for emotional regulation, cognitive flexibility, and improving interpersonal communication.
Defining Triggered Reactions
Triggered reactions occur when specific external stimuli provoke an immediate and often intense emotional or physical response, distinguishing them from spontaneous reactions that arise without an obvious cause. These responses are typically linked to past experiences, memories, or conditioned triggers that activate a predictable pattern of behavior or feelings. Understanding triggered reactions is essential for developing effective coping strategies and therapeutic interventions in mental health contexts.
Exploring Spontaneous Behaviors
Spontaneous behaviors emerge without external prompts, driven by internal motivations or sudden impulses that reflect genuine emotional responses. These actions often reveal true personality traits and can enhance creativity and adaptability in dynamic environments. Understanding spontaneous behaviors helps in recognizing authentic human interactions beyond triggered reactions caused by specific stimuli.
Key Differences Between Triggered and Spontaneous
Triggered events occur as a direct response to a specific external stimulus, while spontaneous events arise internally without any apparent cause. The key differences between triggered and spontaneous processes include the presence of identifiable catalysts in triggered events versus the inherently unpredictable nature of spontaneous occurrences. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for analyzing behavioral patterns, chemical reactions, and neurological responses in various scientific fields.
Psychological Mechanisms at Play
Triggered responses arise from specific external stimuli activating neural pathways linked to past experiences, often engaging the amygdala and hippocampus to process emotional memories. Spontaneous reactions emerge without identifiable triggers, driven by intrinsic neural fluctuations or subconscious processes within the prefrontal cortex and limbic system. Understanding these differing psychological mechanisms highlights how conditioned responses contrast with internally generated cognitive and emotional states.
Common Examples in Everyday Life
Triggered reactions often occur in response to specific stimuli such as a loud noise causing someone to jump or a person feeling anxious when entering a crowded room. Spontaneous behaviors emerge without obvious external prompts, like laughing suddenly at a funny thought or deciding to take a walk on an unplanned whim. Common examples in everyday life show that triggered actions are reflexive and situational, while spontaneous responses reflect internal moods or desires.
Impact on Decision-Making Processes
Triggered decision-making involves predetermined stimuli that activate a specific response, leading to faster but sometimes less flexible outcomes. Spontaneous decision-making relies on real-time intuition and situational awareness, enhancing adaptability but potentially increasing risk due to lack of prior analysis. Understanding the balance between triggered and spontaneous decisions is crucial for optimizing performance in high-pressure environments such as emergency response or strategic business management.
Managing Triggered vs Spontaneous Actions
Managing triggered actions requires immediate recognition of emotional or environmental cues that prompt automatic responses, enabling individuals to implement coping strategies such as mindfulness or cognitive restructuring to prevent impulsive behavior. In contrast, managing spontaneous actions involves balancing spontaneity with thoughtful decision-making to ensure actions align with long-term goals while maintaining flexibility and creativity. Effective management of both triggered and spontaneous actions enhances emotional regulation, improves interpersonal relationships, and promotes adaptive behavior in dynamic situations.
Relevance in Mental Health and Wellbeing
Triggered emotional responses arise from specific stimuli linked to past trauma or stress, often causing intense distress and impacting mental health stability. Spontaneous reactions occur naturally without identifiable external triggers, reflecting immediate psychological states or moods. Understanding the relevance of these distinctions aids mental health professionals in tailoring interventions to improve emotional regulation and overall wellbeing.
Practical Tips for Awareness and Control
Triggered behaviors often arise from specific stimuli linked to past experiences, while spontaneous actions emerge without clear external prompts. Practicing mindfulness and keeping a journal to record situations and emotional responses cultivates awareness of triggers and patterns. Establishing grounding techniques, such as deep breathing or pausing before reacting, empowers control over both triggered and spontaneous impulses for better emotional regulation.
Triggered Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com