Augmentation enhances existing capabilities by integrating advanced technologies or methodologies, leading to improved performance and efficiency across various fields. This process allows for the seamless expansion of functionalities without the need for complete replacement, making it a cost-effective and adaptive solution. Explore the article to discover how augmentation can transform your approach and deliver substantial benefits.
Table of Comparison
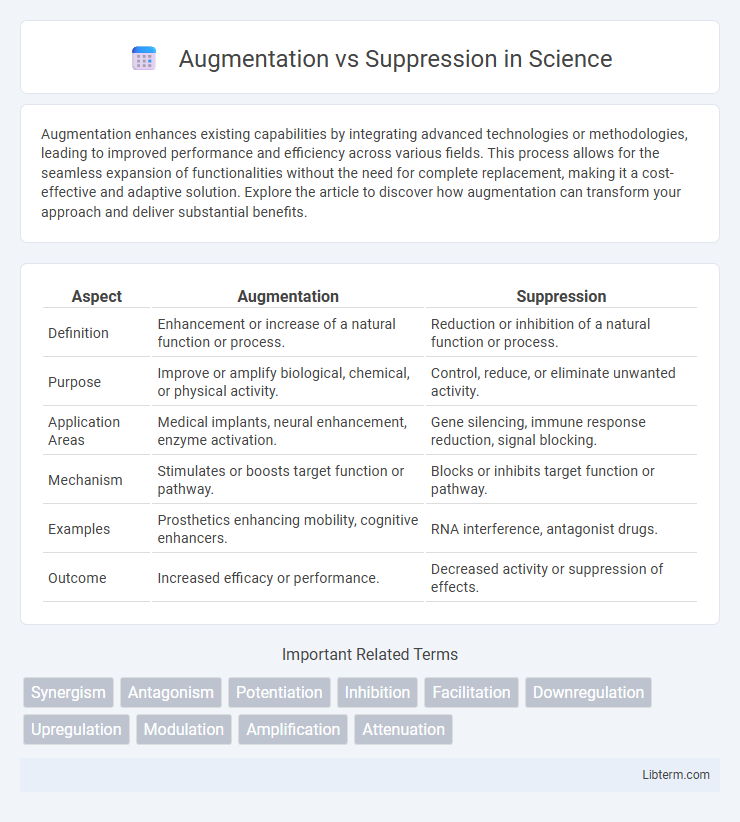
| Aspect | Augmentation | Suppression |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Enhancement or increase of a natural function or process. | Reduction or inhibition of a natural function or process. |
| Purpose | Improve or amplify biological, chemical, or physical activity. | Control, reduce, or eliminate unwanted activity. |
| Application Areas | Medical implants, neural enhancement, enzyme activation. | Gene silencing, immune response reduction, signal blocking. |
| Mechanism | Stimulates or boosts target function or pathway. | Blocks or inhibits target function or pathway. |
| Examples | Prosthetics enhancing mobility, cognitive enhancers. | RNA interference, antagonist drugs. |
| Outcome | Increased efficacy or performance. | Decreased activity or suppression of effects. |
Understanding Augmentation and Suppression
Augmentation involves enhancing or increasing specific responses, often used in psychological conditioning to strengthen a behavior's intensity or frequency. Suppression refers to the reduction or inhibition of certain responses, aiming to decrease unwanted behaviors or emotional reactions through various cognitive or behavioral techniques. Understanding augmentation and suppression is crucial in fields like neuroscience and behavioral therapy for designing effective intervention strategies.
Key Differences Between Augmentation and Suppression
Augmentation enhances or increases a specific function, response, or signal, whereas suppression decreases or inhibits it. In neuroscience, augmentation might amplify neural activity to promote a behavior, while suppression reduces activity to prevent it. These opposing mechanisms play critical roles in balancing physiological and behavioral responses.
Use Cases for Augmentation Strategies
Augmentation strategies enhance human capabilities by integrating AI to improve decision-making, automate repetitive tasks, and personalize customer experiences across industries like healthcare, finance, and retail. Use cases include diagnostic assistance in medical imaging, fraud detection in banking, and dynamic content recommendations in e-commerce platforms. These AI-driven augmentations increase efficiency, accuracy, and user engagement without replacing human judgment.
Applications of Suppression Techniques
Suppression techniques play a crucial role in applications such as noise reduction in speech processing, signal enhancement in biomedical engineering, and interference cancellation in wireless communication systems. These methods improve data quality by selectively minimizing unwanted signals or noise without compromising the integrity of the original information. Effective suppression enhances performance in environments with high signal contamination, leading to clearer audio, more accurate diagnostics, and stronger communication reliability.
Benefits of Augmentation in Modern Systems
Augmentation in modern systems enhances human capabilities by integrating advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and automation to improve decision-making speed and accuracy. It promotes productivity and innovation by enabling seamless collaboration between humans and machines, reducing errors and operational costs. These benefits position augmentation as a critical strategy for businesses aiming to sustain competitive advantage in rapidly evolving markets.
Limitations and Risks of Suppression
Suppression techniques can lead to incomplete or misleading data by masking critical behaviors or signals during analysis, reducing the reliability of findings. Overuse of suppression risks data integrity, potentially causing biased outcomes and hindering accurate decision-making in sensitive fields like cybersecurity or healthcare. Limitations also include the difficulty of reversing suppression effects, which can compromise transparency and auditability in complex systems.
Augmentation vs Suppression in Artificial Intelligence
Augmentation in Artificial Intelligence refers to enhancing human capabilities by integrating AI systems that assist with decision-making, data analysis, and problem-solving, thereby improving efficiency and accuracy. Suppression involves restricting or minimizing AI functions to prevent errors, biases, or undesired behaviors, often through regulatory measures or algorithmic constraints. Balancing augmentation and suppression is crucial for developing responsible AI technologies that maximize benefits while minimizing risks.
Ethical Considerations in Choosing Augmentation or Suppression
Ethical considerations in choosing augmentation or suppression revolve around autonomy, consent, and potential societal impact. Augmentation raises questions about fairness and accessibility, as enhanced abilities may create inequalities, while suppression poses risks of infringing on individual freedoms and suppressing diversity. Balancing the benefits and harms requires transparent policies and stakeholder engagement to ensure ethical implementation.
Future Trends: Integrating Augmentation and Suppression
Future trends in augmentation and suppression emphasize seamless integration to enhance human capabilities and cognitive functions. Advances in neural interface technologies and adaptive AI systems enable real-time balancing between augmenting desired skills and suppressing detrimental behaviors or distractions. This synergy promises personalized enhancement strategies across healthcare, education, and workplace productivity.
Making Strategic Decisions: When to Augment vs Suppress
Making strategic decisions between augmentation and suppression involves evaluating resource allocation to enhance or inhibit specific processes for optimal outcomes. Augmentation is effective when boosting capabilities or amplifying positive effects aligns with organizational goals, while suppression is preferred to mitigate risks, minimize undesired activities, or control negative impacts. Data-driven analysis of performance metrics, cost-efficiency, and potential long-term benefits guides the choice between augmenting strengths or suppressing weaknesses within a competitive strategy framework.
Augmentation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com