Mastering translation involves not only converting words from one language to another but also capturing the intended meaning and cultural nuances. High-quality translation ensures your message resonates clearly across diverse audiences, enhancing communication and understanding. Read on to discover essential tips and strategies to improve your translation skills effectively.
Table of Comparison
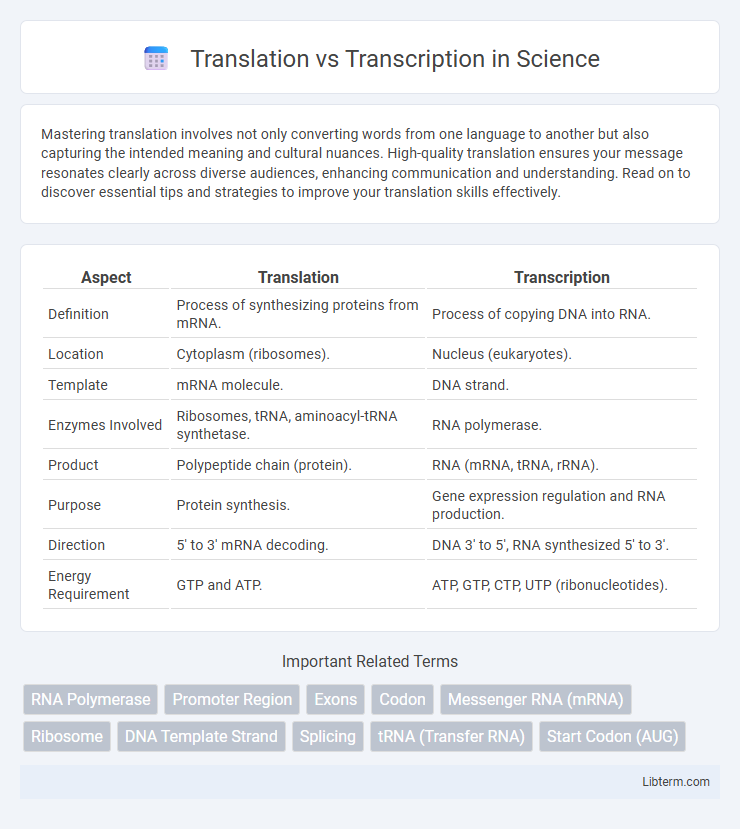
| Aspect | Translation | Transcription |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of synthesizing proteins from mRNA. | Process of copying DNA into RNA. |
| Location | Cytoplasm (ribosomes). | Nucleus (eukaryotes). |
| Template | mRNA molecule. | DNA strand. |
| Enzymes Involved | Ribosomes, tRNA, aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase. | RNA polymerase. |
| Product | Polypeptide chain (protein). | RNA (mRNA, tRNA, rRNA). |
| Purpose | Protein synthesis. | Gene expression regulation and RNA production. |
| Direction | 5' to 3' mRNA decoding. | DNA 3' to 5', RNA synthesized 5' to 3'. |
| Energy Requirement | GTP and ATP. | ATP, GTP, CTP, UTP (ribonucleotides). |
Introduction: Understanding Translation and Transcription
Translation converts text or speech from one language to another, preserving meaning and context for effective communication across cultures. Transcription involves converting spoken language into written text in the same language, capturing exact words and sounds for accurate documentation. Both processes serve distinct purposes: translation bridges linguistic gaps, while transcription creates textual records of audio content.
Defining Translation: What Does It Entail?
Translation entails converting written text from one language into another, preserving the original meaning, tone, and context. It requires deep linguistic expertise and cultural understanding to ensure accurate interpretation across languages. This process often involves specialized knowledge in fields like legal, medical, or technical domains to maintain terminology precision.
What is Transcription? Key Concepts Explained
Transcription is the process of converting spoken language into written text, capturing exact words, sounds, and nuances without altering the original meaning. Key concepts include verbatim transcription, which records speech word-for-word, and edited transcription, which refines text for readability while maintaining accuracy. This method is essential in fields like legal documentation, medical records, and media captioning to ensure precise communication and easy reference.
Core Differences Between Translation and Transcription
Translation involves converting written text from one language to another, ensuring the meaning and context are preserved for accurate communication. Transcription is the process of converting spoken language into written text, focusing on capturing exact words and speech details without altering content. The core difference lies in translation changing the language and transcription converting speech to text within the same language.
When to Use Translation vs. Transcription
Translation is essential when converting written content from one language to another to ensure accurate communication across linguistic barriers. Transcription is best used for converting spoken language into written text, capturing audio or video content verbatim for documentation or analysis. Use translation for localization of documents, websites, and marketing materials, while transcription suits situations requiring accurate record-keeping of interviews, meetings, or media.
Skills Required for Translators and Transcribers
Translators require advanced language proficiency, cultural knowledge, and strong writing skills to accurately interpret and convey meaning between source and target languages. Transcribers need excellent listening skills, attention to detail, and fast, accurate typing abilities to convert spoken language into written text. Both roles demand specialized training, but translators focus on linguistic nuance, while transcribers prioritize auditory comprehension and verbatim accuracy.
Tools and Technologies: Translation vs. Transcription
Translation tools utilize advanced neural machine translation (NMT) engines like Google Translate and DeepL, enabling real-time multilingual text conversion with high accuracy. Transcription technologies leverage automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems such as Otter.ai and Rev, which convert audio signals into precise text, supporting various dialects and specialized vocabularies. Both fields increasingly integrate AI-driven natural language processing (NLP) and cloud-based platforms to enhance scalability, efficiency, and contextual understanding.
Challenges Faced in Translation and Transcription
Translation faces challenges such as capturing cultural nuances, idiomatic expressions, and contextual meaning accurately across languages, which requires deep linguistic and cultural knowledge. Transcription struggles with audio quality issues, speaker accents, and overlapping dialogues that hinder precise conversion of spoken language into written text. Both processes demand specialized skills and tools to ensure fidelity and clarity in communication.
Industry Applications: Real-world Use Cases
Translation is essential in global business communications, enabling companies to localize marketing materials, legal documents, and technical manuals for diverse markets. Transcription plays a critical role in industries such as healthcare, legal, and media by converting audio and video content into accurate written records for compliance, accessibility, and content archiving. Both processes support multilingual customer service, international research collaboration, and multimedia localization, driving efficiency and market reach across various sectors.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Service for Your Needs
Selecting between translation and transcription depends on your project's goals: translation converts text between languages to reach a broader audience, while transcription transforms spoken language into written form for documentation or analysis. High accuracy in language and context is crucial for both services to ensure clarity and relevance. Consider your target audience, content purpose, and format requirements to choose the most effective solution.
Translation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com