A Web Application Firewall (WAF) protects your website by filtering and monitoring HTTP traffic between a web application and the internet, blocking malicious requests that target vulnerabilities. It safeguards against common threats such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and other OWASP top 10 attacks to ensure your web applications remain secure and available. Discover how implementing a WAF can enhance your security strategy by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
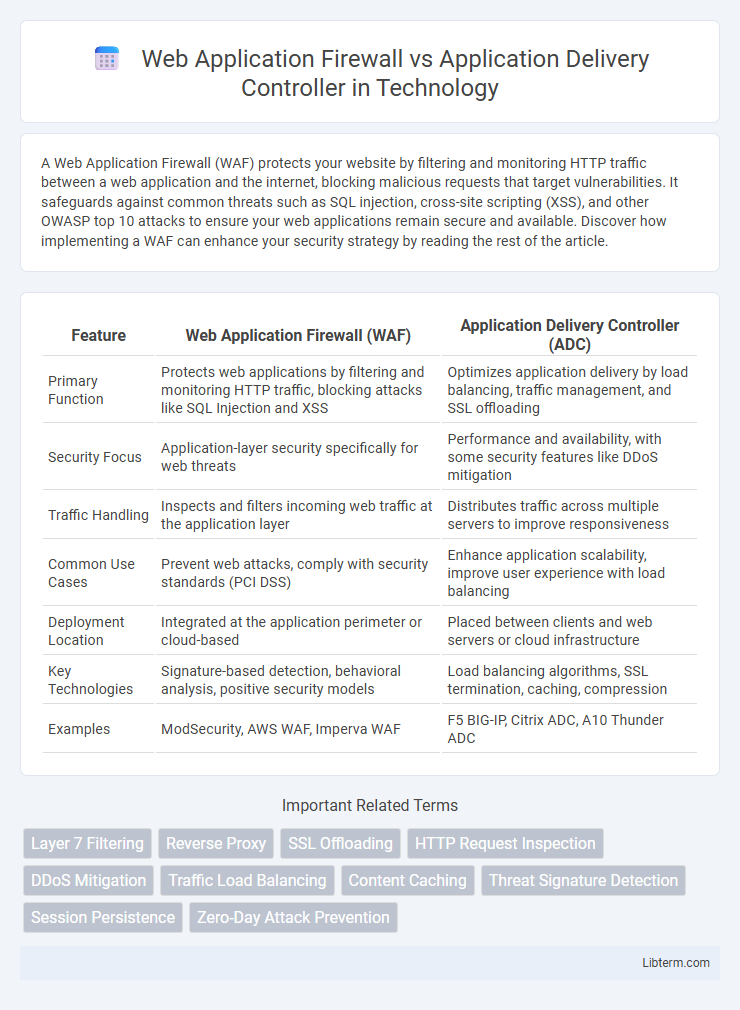
| Feature | Web Application Firewall (WAF) | Application Delivery Controller (ADC) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Protects web applications by filtering and monitoring HTTP traffic, blocking attacks like SQL Injection and XSS | Optimizes application delivery by load balancing, traffic management, and SSL offloading |
| Security Focus | Application-layer security specifically for web threats | Performance and availability, with some security features like DDoS mitigation |
| Traffic Handling | Inspects and filters incoming web traffic at the application layer | Distributes traffic across multiple servers to improve responsiveness |
| Common Use Cases | Prevent web attacks, comply with security standards (PCI DSS) | Enhance application scalability, improve user experience with load balancing |
| Deployment Location | Integrated at the application perimeter or cloud-based | Placed between clients and web servers or cloud infrastructure |
| Key Technologies | Signature-based detection, behavioral analysis, positive security models | Load balancing algorithms, SSL termination, caching, compression |
| Examples | ModSecurity, AWS WAF, Imperva WAF | F5 BIG-IP, Citrix ADC, A10 Thunder ADC |
Introduction to Web Application Firewalls (WAF)
Web Application Firewalls (WAF) protect web applications by filtering and monitoring HTTP traffic between a web application and the Internet, blocking malicious attacks such as SQL injection and cross-site scripting. Unlike Application Delivery Controllers (ADC), which optimize application performance and load balancing, WAFs focus specifically on application-layer security by inspecting traffic for threats and vulnerabilities. Deploying a WAF helps organizations safeguard sensitive data and ensure compliance with security standards like PCI DSS.
Understanding Application Delivery Controllers (ADC)
Application Delivery Controllers (ADCs) optimize and manage web application performance by distributing incoming network traffic across multiple servers, ensuring high availability and scalability. Unlike Web Application Firewalls (WAFs), which primarily provide security by filtering malicious HTTP traffic and preventing attacks, ADCs focus on load balancing, SSL offloading, and application acceleration. Integrating ADCs enhances user experience by reducing latency and improving resource utilization in complex web environments.
Key Functions of Web Application Firewalls
Web Application Firewalls (WAFs) protect web applications by filtering and monitoring HTTP traffic to prevent attacks such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting, and other OWASP Top 10 threats. WAFs analyze application-layer traffic, enforce security policies, and provide real-time threat detection and mitigation to safeguard sensitive data and maintain application availability. Unlike Application Delivery Controllers (ADCs) that primarily optimize load balancing and application performance, WAFs specifically focus on security by blocking malicious requests before they reach the web server.
Core Capabilities of Application Delivery Controllers
Application Delivery Controllers (ADCs) optimize application performance, load balancing, and traffic management to ensure high availability and scalability of web services. Core capabilities include SSL offloading, content switching, and health monitoring, which enhance security and user experience without directly filtering malicious traffic like Web Application Firewalls (WAFs). ADCs also provide application acceleration and compression, reducing latency and enabling efficient resource utilization across distributed environments.
WAF vs ADC: Security Features Comparison
Web Application Firewalls (WAFs) specialize in protecting web applications by detecting and blocking threats such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks using deep packet inspection and behavioral analysis. Application Delivery Controllers (ADCs) primarily focus on optimizing application performance, load balancing, and SSL offloading, but also include some security features like basic firewalling and traffic filtering. When comparing security features, WAFs provide more granular, application-specific protection, while ADCs offer broader network-level security with less emphasis on detailed web threat management.
Performance Optimization: WAF vs ADC
Web Application Firewalls (WAF) enhance security by inspecting and filtering HTTP traffic to block malicious attacks, which can introduce latency impacting application load times. Application Delivery Controllers (ADC) optimize performance by managing traffic loads, performing SSL offloading, and enabling caching to accelerate response times and improve scalability. Combining WAF with ADC allows organizations to balance robust application security with efficient traffic management and performance optimization.
Scalability and Load Balancing Differences
Web Application Firewalls (WAFs) primarily focus on protecting web applications from security threats by filtering and monitoring HTTP traffic, with limited inherent scalability features. Application Delivery Controllers (ADCs) enhance scalability by efficiently distributing incoming traffic across multiple servers, ensuring optimal load balancing and application performance. Unlike WAFs, ADCs provide advanced load balancing algorithms, session persistence, and SSL offloading, which significantly improve application availability and resource utilization.
Deployment Options: WAF and ADC
Web Application Firewalls (WAFs) are typically deployed inline as reverse proxies, allowing them to inspect and filter HTTP/HTTPS traffic between users and web applications to protect against attacks such as SQL injection and cross-site scripting. Application Delivery Controllers (ADCs) are usually positioned in front of web servers, acting as load balancers and delivering optimized, secure application performance with deployment options including hardware appliances, virtual appliances, or cloud-based solutions. Both WAFs and ADCs support flexible deployment models, but WAFs emphasize security-focused traffic inspection, while ADCs prioritize application availability and acceleration.
Use Cases: When to Choose WAF or ADC
Web Application Firewalls (WAFs) are ideal for protecting web applications from common threats such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting, and OWASP Top 10 vulnerabilities, making them essential for organizations prioritizing security and compliance. Application Delivery Controllers (ADCs) excel in optimizing application performance, load balancing, SSL offloading, and ensuring high availability, suited for environments requiring efficient traffic management and scalability. Choose WAF for robust security in application layer filtering and ADC for enhancing application delivery and network resilience.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Solution for Your Web Applications
Choosing between a Web Application Firewall (WAF) and an Application Delivery Controller (ADC) depends on your web application's primary needs: security or performance optimization. A WAF is essential for protecting against web threats like SQL injection, cross-site scripting, and DDoS attacks, ensuring robust security compliance. In contrast, an ADC enhances application availability, load balancing, and acceleration, improving user experience through faster and more reliable delivery.
Web Application Firewall Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com