Efficient file storage solutions are essential for organizing and securing your digital data, ensuring quick access and reliable backup. Modern storage options range from cloud-based services to local drives, each offering unique advantages for different needs. Explore the rest of the article to discover the best file storage methods tailored for your requirements.
Table of Comparison
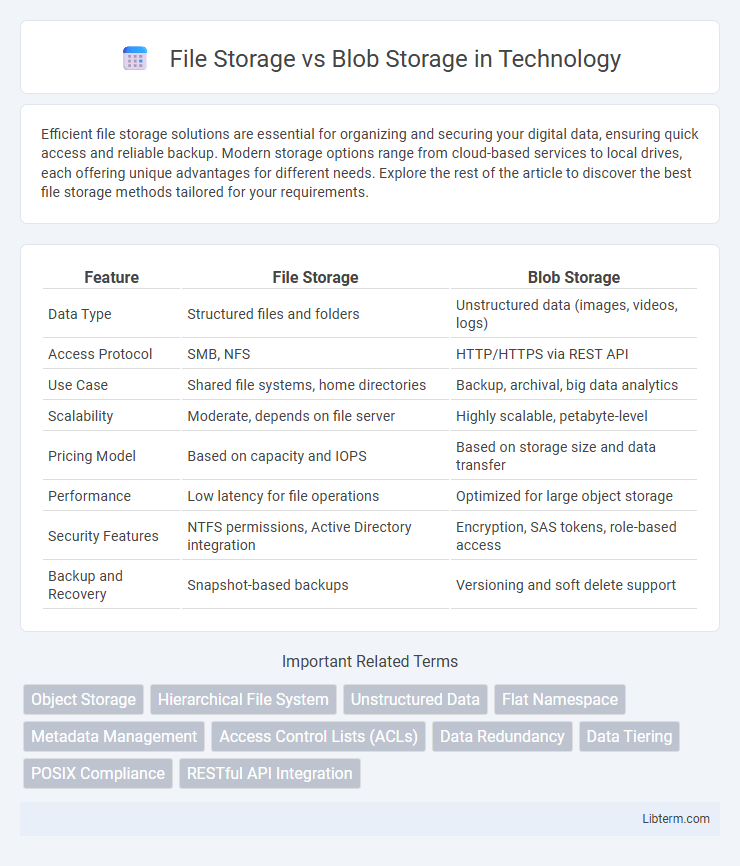
| Feature | File Storage | Blob Storage |
|---|---|---|
| Data Type | Structured files and folders | Unstructured data (images, videos, logs) |
| Access Protocol | SMB, NFS | HTTP/HTTPS via REST API |
| Use Case | Shared file systems, home directories | Backup, archival, big data analytics |
| Scalability | Moderate, depends on file server | Highly scalable, petabyte-level |
| Pricing Model | Based on capacity and IOPS | Based on storage size and data transfer |
| Performance | Low latency for file operations | Optimized for large object storage |
| Security Features | NTFS permissions, Active Directory integration | Encryption, SAS tokens, role-based access |
| Backup and Recovery | Snapshot-based backups | Versioning and soft delete support |
Introduction to File Storage vs Blob Storage
File Storage organizes data in a hierarchical structure with files and folders, making it ideal for scenarios requiring shared access and complex file management. Blob Storage stores unstructured data as binary large objects, optimized for scalable and cost-effective storage of massive amounts of unstructured data like images, videos, and backups. Both storage types serve distinct use cases, with File Storage suited for legacy applications and Blob Storage designed for cloud-native, scalable environments.
Understanding File Storage: Definition and Use Cases
File Storage is a data storage system that organizes information in a hierarchical structure using files and folders, similar to traditional computer file systems, making it ideal for storing and sharing files that require frequent access and modification. It is commonly used in scenarios such as collaboration on documents, development environments, and legacy applications that depend on standard file protocol support, including SMB and NFS. File Storage provides strong consistency, metadata management, and supports concurrent access, enhancing productivity for enterprises needing scalable and accessible data repository solutions.
What Is Blob Storage? Key Features and Benefits
Blob storage is a Microsoft Azure service designed to store large amounts of unstructured data such as images, videos, and backups. Key features include scalability, high availability, and support for diverse data types with tiered storage options like hot, cool, and archive. Benefits include cost-efficiency, seamless integration with Azure services, and optimized performance for storing massive binary objects.
File Storage Architecture Explained
File Storage architecture is built on a hierarchical system resembling traditional file systems, organizing data in directories and subdirectories accessible via protocols like SMB and NFS. It supports block-level storage ideal for applications requiring shared access and consistent low-latency performance, often used in enterprise environments for file sharing and collaborative workflows. The architecture enables features such as fine-grained permissions, file locking, and snapshot capabilities, ensuring data integrity and security in multi-user scenarios.
Blob Storage Architecture Overview
Blob Storage architecture organizes unstructured data as objects in containers within storage accounts on the cloud, enabling scalable and cost-effective management of massive amounts of data. Each blob is identified by a unique URL, ensuring easy access and integration with REST APIs for seamless data retrieval and manipulation. The architecture supports three types of blobs: block blobs for large text and binary data, append blobs for log files, and page blobs for random access files, optimizing performance based on specific storage needs.
Performance Comparison: File Storage vs Blob Storage
File Storage delivers high throughput and low latency for workloads requiring frequent file-level access, making it ideal for applications like databases and virtual machines. Blob Storage excels in scalability and cost-efficiency for massive unstructured data, offering optimized read/write speeds for large object storage and archival. Performance benchmarks highlight File Storage's advantage in random read/write operations, while Blob Storage outperforms in sequential access and large data streaming scenarios.
Security Differences Between File and Blob Storage
File Storage and Blob Storage differ significantly in security features tailored to their respective use cases; File Storage often integrates with traditional SMB protocol security and supports NTFS permissions for granular access control, making it ideal for lift-and-shift applications requiring SMB connectivity. Blob Storage employs advanced security mechanisms such as Azure Active Directory (AAD) integration, Shared Access Signatures (SAS), and encryption at rest with customer-managed keys, optimized for unstructured data and large-scale internet-facing applications. These security distinctions highlight Blob Storage's enhanced capabilities for controlling data access and protection in cloud-native environments, compared to File Storage's compatibility with legacy system security models.
Cost Analysis: File Storage vs Blob Storage
File Storage typically incurs higher costs due to its hierarchical structure and support for SMB/NFS protocols, leading to increased management overhead and storage fees. Blob Storage offers more cost-effective options by using flat namespace object storage optimized for unstructured data with pay-as-you-go pricing models, reducing total cost of ownership. Enterprises leveraging Blob Storage benefit from lower pricing tiers and automated tiering options, significantly optimizing expenses for large-scale data archives compared to traditional File Storage.
Scalability and Flexibility Considerations
File Storage offers structured hierarchy and strong consistency, making it suitable for legacy applications with fixed scalability needs, whereas Blob Storage provides massive scalability through flat namespace and is ideal for unstructured data like multimedia files. Blob Storage supports flexible data access models and seamless integration with modern cloud services, enhancing adaptability for growing workloads and diverse application requirements. When prioritizing scalability and flexibility, Blob Storage typically outperforms File Storage in handling vast, dynamic data environments with variable access patterns.
Choosing the Right Storage Solution for Your Needs
File Storage offers a hierarchical structure with file-level access ideal for shared file systems, while Blob Storage provides scalable object storage optimized for unstructured data like images and videos. Choosing the right storage solution depends on factors such as access patterns, performance requirements, and scalability needs. Evaluate workload characteristics and integration compatibility with applications to ensure optimal cost-efficiency and data management.
File Storage Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com