The service plane is a crucial component in aircraft design, providing a stable surface that maintains lift during various flight maneuvers. Ensuring optimal aerodynamic performance, it directly impacts the efficiency and safety of the aircraft in operation. Explore the rest of the article to understand how the service plane enhances your aviation experience.
Table of Comparison
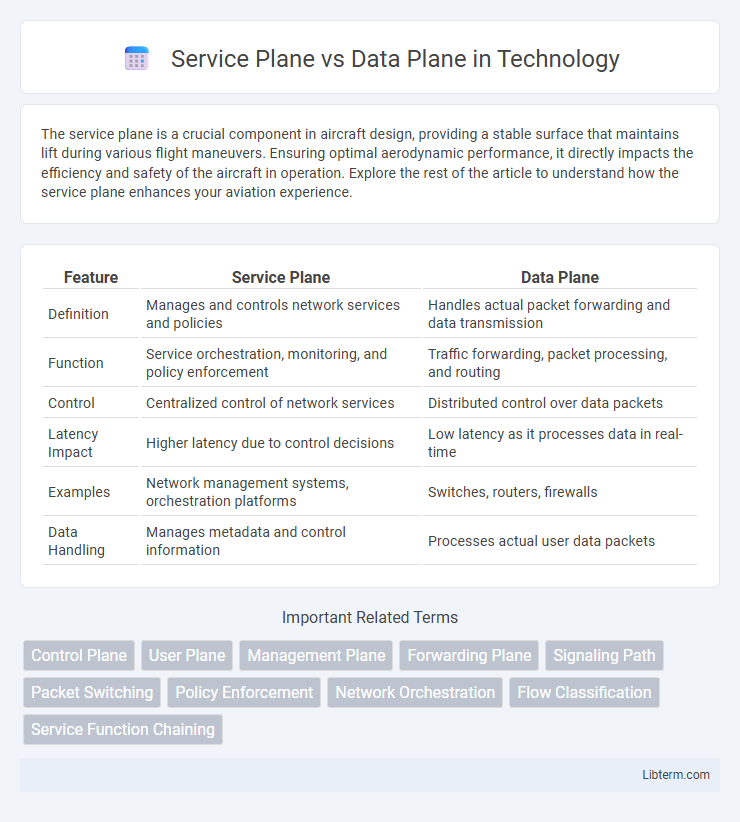
| Feature | Service Plane | Data Plane |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Manages and controls network services and policies | Handles actual packet forwarding and data transmission |
| Function | Service orchestration, monitoring, and policy enforcement | Traffic forwarding, packet processing, and routing |
| Control | Centralized control of network services | Distributed control over data packets |
| Latency Impact | Higher latency due to control decisions | Low latency as it processes data in real-time |
| Examples | Network management systems, orchestration platforms | Switches, routers, firewalls |
| Data Handling | Manages metadata and control information | Processes actual user data packets |
Introduction to Service Plane and Data Plane
Service Plane manages the control and orchestration of network services, enabling centralized policy enforcement and network automation. Data Plane handles the actual packet forwarding and processing, ensuring efficient data transmission across network devices. Together, these planes separate network management functions from traffic handling, optimizing overall network performance and scalability.
Defining the Service Plane
The Service Plane is the layer responsible for managing and orchestrating network services, ensuring seamless delivery and integration of applications. It handles tasks such as policy enforcement, service chaining, and service function virtualization, enabling dynamic and programmable network behavior. Unlike the Data Plane, which forwards packets based on established rules, the Service Plane provides the intelligent control necessary for sophisticated service management.
Defining the Data Plane
The Data Plane performs the core function of packet forwarding by processing and transferring user data through network devices like routers and switches. It handles tasks such as packet replication, filtering, and modification based on rules provided by the Control Plane. The efficiency and speed of the Data Plane directly impact network performance and latency in communication systems.
Core Functions of the Service Plane
The Service Plane manages network services by orchestrating functions such as authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA), along with policy enforcement and quality of service (QoS) management. It acts as the intermediary between the Data Plane and the control systems, ensuring that data forwarding follows predefined service rules. Core functions also include session management and service provisioning to maintain seamless user experience and network reliability.
Core Functions of the Data Plane
The Data Plane handles the core functions of packet forwarding, including switching, routing, and traffic filtering at wire speed to ensure efficient data transmission across the network. It processes packets based on predefined rules from the Control Plane, performing tasks such as encapsulation, decapsulation, and header rewriting, which are critical for maintaining low-latency communication. Designed for high-performance execution, the Data Plane operates within network devices like routers and switches, directly managing the flow of user data to optimize network throughput and reliability.
Key Differences Between Service Plane and Data Plane
The Service Plane handles control and management functions, orchestrating network services and policies, whereas the Data Plane is responsible for the actual forwarding of packets based on established rules. Key differences include the Service Plane's role in decision-making and configuration, contrasting with the Data Plane's real-time packet processing and traffic handling. This separation enhances network scalability, security, and performance by isolating control logic from data transmission.
Interaction Between Service Plane and Data Plane
The interaction between the Service Plane and Data Plane is crucial for network functionality, where the Service Plane dictates policies and controls, while the Data Plane manages actual packet forwarding based on those instructions. Effective communication protocols ensure that the Service Plane dynamically configures the Data Plane to optimize traffic flow and enforce security measures. This coordination enables scalable, responsive network operations by separating control logic from data processing tasks.
Use Cases in Modern Network Architectures
Service Plane manages application-level functions such as policy enforcement, routing decisions, and security services, crucial for network virtualization and software-defined networking (SDN). Data Plane handles the actual packet forwarding and routing based on rules set by the Service Plane, ensuring high-speed data transmission in physical and virtual environments. Use cases in modern network architectures include SD-WAN for dynamic path selection, cloud-native deployments optimizing microservices traffic, and IoT networks requiring efficient data processing and real-time analytics.
Impact on Network Security and Performance
Service Plane centralizes network functions like firewalls and intrusion detection, enhancing security through consistent policy enforcement but potentially adding latency. Data Plane handles actual packet forwarding, prioritizing speed and efficiency, which is critical for maintaining high network performance. Balancing the Service Plane's security benefits with the Data Plane's performance demands is essential for optimizing overall network security and throughput.
Choosing the Right Plane for Network Solutions
Choosing the right plane for network solutions depends on the specific operational requirements and performance goals of the network architecture. The Service Plane handles application-level services and management tasks, optimizing control and orchestration functions, whereas the Data Plane focuses on the fast, efficient forwarding of user traffic and packet processing. Prioritizing the Data Plane improves throughput and low-latency transmission, while emphasizing the Service Plane enables enhanced service flexibility, scalability, and centralized network control.
Service Plane Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com