A password manager securely stores and organizes your passwords, helping you create strong, unique credentials for every account. It simplifies login processes and protects you from the risks of password reuse and data breaches. Discover how a password manager can enhance your online security by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
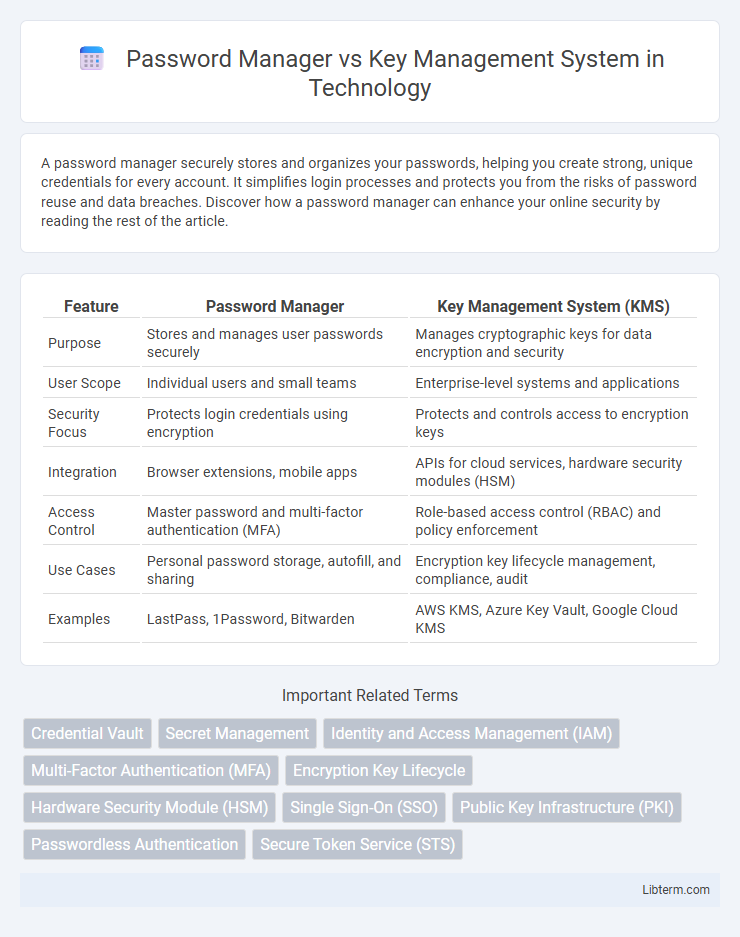
| Feature | Password Manager | Key Management System (KMS) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Stores and manages user passwords securely | Manages cryptographic keys for data encryption and security |
| User Scope | Individual users and small teams | Enterprise-level systems and applications |
| Security Focus | Protects login credentials using encryption | Protects and controls access to encryption keys |
| Integration | Browser extensions, mobile apps | APIs for cloud services, hardware security modules (HSM) |
| Access Control | Master password and multi-factor authentication (MFA) | Role-based access control (RBAC) and policy enforcement |
| Use Cases | Personal password storage, autofill, and sharing | Encryption key lifecycle management, compliance, audit |
| Examples | LastPass, 1Password, Bitwarden | AWS KMS, Azure Key Vault, Google Cloud KMS |
Understanding Password Managers
Password managers securely store and organize user credentials by encrypting passwords for easy retrieval and autofill across devices, enhancing both security and convenience. Unlike key management systems that handle cryptographic keys for enterprise-wide data protection, password managers are primarily designed for individual or small-scale use to simplify authentication processes. Effective password managers incorporate features such as multi-factor authentication, password generation, and breach alerts to safeguard against unauthorized access.
What is a Key Management System?
A Key Management System (KMS) is a security solution designed to generate, distribute, store, and track cryptographic keys used for data encryption and decryption. Unlike password managers that primarily store and manage user credentials, KMS focuses on securing encryption keys to protect sensitive data across applications and cloud environments. Enterprises utilize KMS to ensure compliance with data protection regulations and to maintain robust encryption key lifecycle management.
Core Features: Password Manager vs Key Management System
Password Managers primarily focus on securely storing, generating, and autofilling user passwords across multiple devices, enhancing personal and organizational credential management with encryption and easy access. Key Management Systems (KMS) specialize in the lifecycle management of cryptographic keys, including key generation, distribution, rotation, and policy enforcement for data encryption and digital signatures within enterprise environments. While Password Managers optimize user authentication security, KMS ensures robust cryptographic key control crucial for data protection and compliance in complex IT infrastructures.
Security Protocols and Encryption Standards
Password managers typically utilize AES-256 encryption and enforce multi-factor authentication (MFA) to safeguard user credentials, ensuring secure storage and retrieval of passwords. Key management systems (KMS) implement advanced encryption standards such as FIPS 140-2 validated cryptographic modules and support hardware security modules (HSM) for generating, storing, and controlling cryptographic keys with strong access controls and audit logging. While password managers focus on protecting individual user passwords, KMS provide robust, enterprise-grade security protocols designed for cryptographic key lifecycle management and compliance with regulatory standards like NIST and GDPR.
Use Cases: Individuals vs Enterprises
Password managers primarily serve individuals by securely storing and autofilling personal login credentials across multiple devices, enhancing convenience and preventing password reuse. Key management systems are designed for enterprises to centrally generate, store, and control cryptographic keys, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards and enabling secure data encryption across complex IT infrastructures. While password managers optimize personal security hygiene, enterprise key management systems address scalable encryption needs, secure API access, and data protection in cloud environments.
Centralized vs Decentralized Access Control
Password managers centralize access control by storing and encrypting user credentials in a single repository, simplifying user authentication while enhancing security through master passwords and multi-factor authentication. Key Management Systems (KMS) implement decentralized access control by distributing cryptographic keys across multiple nodes or hardware security modules, enabling fine-grained permissions and reducing single points of failure. Centralized password management suits individual and small team environments, whereas decentralized KMS ensures robust security and compliance in large-scale enterprise and cloud infrastructures.
Integration with Other Security Tools
Password managers seamlessly integrate with multi-factor authentication systems and single sign-on solutions to enhance user access security. Key management systems offer centralized control and compatibility with hardware security modules and encryption platforms, providing robust cryptographic key governance. Both solutions support API integration for streamlined workflows within broader cybersecurity infrastructures.
Compliance and Regulatory Considerations
Password Managers streamline compliance with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS by securing user credentials through encryption, audit trails, and multi-factor authentication. Key Management Systems (KMS) are essential for meeting stringent data protection standards such as FIPS 140-2 and NIST SP 800-57 by securely generating, storing, and rotating cryptographic keys that protect sensitive data. Both tools play critical roles in regulatory adherence, but KMS offers deeper control over encryption keys crucial for high-security environments and compliance mandates.
Scalability and Performance Differences
Password managers are designed primarily for individual or small team use, offering efficient credential storage with moderate scalability, whereas key management systems (KMS) handle vast volumes of cryptographic keys across distributed environments, ensuring high scalability and low latency for enterprise-level applications. KMS solutions leverage advanced hardware security modules (HSMs) and automated key lifecycle management to optimize performance under heavy load, contrasting with password managers that emphasize user-friendly interfaces over scalability. The performance difference hinges on KMS's ability to support large-scale encryption processes and strict compliance requirements, making them essential for cloud services and large infrastructures.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
Password managers streamline personal and team credential storage with features like autofill and secure sharing, ideal for individuals and small businesses needing straightforward access control. Key Management Systems (KMS) provide advanced encryption key lifecycle management, integrating with cloud environments and enterprise applications for robust data protection and regulatory compliance. Selecting the right solution depends on your security requirements, scale of operations, and whether you prioritize managing user credentials or cryptographic keys.
Password Manager Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com