CAS, or Chemical Abstracts Service, provides a comprehensive database of chemical information essential for researchers and industry professionals. It offers detailed substance data, patent documents, and scientific literature to support your innovative projects and decision-making. Explore the full article to discover how CAS can enhance your research capabilities.
Table of Comparison
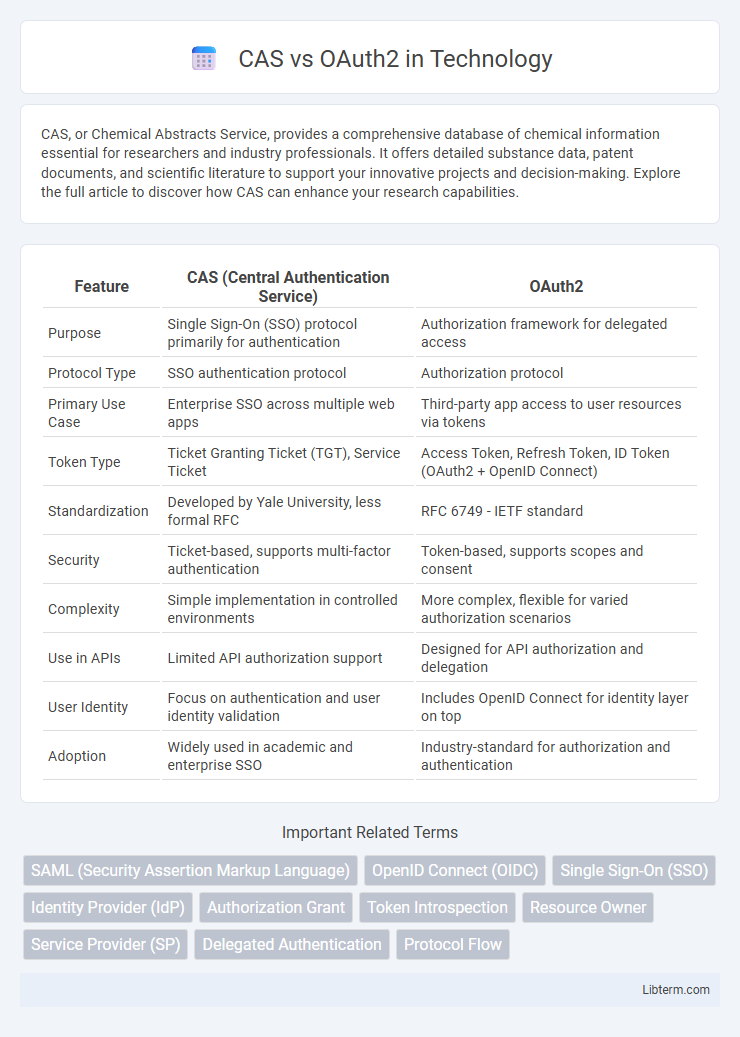
| Feature | CAS (Central Authentication Service) | OAuth2 |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Single Sign-On (SSO) protocol primarily for authentication | Authorization framework for delegated access |
| Protocol Type | SSO authentication protocol | Authorization protocol |
| Primary Use Case | Enterprise SSO across multiple web apps | Third-party app access to user resources via tokens |
| Token Type | Ticket Granting Ticket (TGT), Service Ticket | Access Token, Refresh Token, ID Token (OAuth2 + OpenID Connect) |
| Standardization | Developed by Yale University, less formal RFC | RFC 6749 - IETF standard |
| Security | Ticket-based, supports multi-factor authentication | Token-based, supports scopes and consent |
| Complexity | Simple implementation in controlled environments | More complex, flexible for varied authorization scenarios |
| Use in APIs | Limited API authorization support | Designed for API authorization and delegation |
| User Identity | Focus on authentication and user identity validation | Includes OpenID Connect for identity layer on top |
| Adoption | Widely used in academic and enterprise SSO | Industry-standard for authorization and authentication |
Introduction to CAS and OAuth2
CAS (Central Authentication Service) is a single sign-on protocol widely used in educational and enterprise environments to provide secure user authentication across multiple applications. OAuth2 is an open authorization framework designed for delegated access, enabling third-party applications to obtain limited access to user resources without exposing credentials. Both protocols enhance security but serve different purposes: CAS focuses on centralized authentication, while OAuth2 manages authorization and resource access control.
Core Concepts: CAS vs OAuth2
CAS (Central Authentication Service) operates primarily as a single sign-on protocol that authenticates users via a centralized server, issuing service tickets to grant access to multiple web applications. OAuth2 functions as an authorization framework that allows third-party applications to obtain limited access to user resources without exposing credentials, using tokens such as access and refresh tokens. While CAS centers on user authentication and ticket validation, OAuth2 emphasizes delegated authorization and token-based access control.
Authentication and Authorization Differences
CAS (Central Authentication Service) primarily focuses on authentication by providing single sign-on (SSO) capabilities, enabling users to authenticate once and gain access to multiple applications. OAuth2 is an authorization framework designed to grant third-party applications limited access to user resources without sharing credentials, using access tokens. CAS handles user identity verification, whereas OAuth2 manages delegated access control, making their core purposes distinct in authentication versus authorization.
Protocol Workflows: How CAS and OAuth2 Operate
CAS (Central Authentication Service) operates primarily through a ticket-based protocol workflow where a user authenticates once and obtains a Service Ticket (ST) to access multiple applications without re-entering credentials. OAuth2 uses an authorization code flow involving resource owners, clients, authorization servers, and resource servers, where tokens like access tokens and refresh tokens are exchanged to grant limited access to user resources. Both protocols facilitate single sign-on (SSO) but differ in mechanisms: CAS focuses on authentication with ticket validation, while OAuth2 emphasizes delegated authorization via token-based workflows.
Security Considerations in CAS and OAuth2
CAS (Central Authentication Service) employs a ticket-based system that limits exposure by issuing single-use tickets, reducing the risk of replay attacks, while OAuth2 relies on access tokens that require secure storage and management to prevent token theft or misuse. CAS centralizes user authentication in a trusted server, minimizing credential sharing, whereas OAuth2 delegates authorization through scopes but demands rigorous token validation and secure transport (e.g., HTTPS) to mitigate interception and token leakage risks. Implementing strong token expiration policies, refresh token management, and stringent client authentication methods are critical security considerations to maintain integrity in both CAS and OAuth2 protocols.
Use Cases: When to Use CAS or OAuth2
CAS is ideal for enterprise environments requiring centralized single sign-on (SSO) across multiple internal applications, emphasizing user authentication and session management within a trusted domain. OAuth2 excels in scenarios involving delegated access to third-party APIs, enabling secure authorization without sharing user credentials, commonly used for social logins and API integrations. Choose CAS for internal SSO solutions with strong authentication focus, and OAuth2 for external authorization and controlled resource access across diverse platforms.
Integration with Applications and Services
CAS (Central Authentication Service) integrates with web applications primarily through a ticket-based single sign-on (SSO) mechanism, enabling seamless authentication across multiple services within a unified ecosystem. OAuth2, designed as an authorization framework, facilitates delegated access by allowing applications to obtain limited access tokens for third-party APIs without exposing user credentials. The choice between CAS and OAuth2 depends on whether the integration requires centralized authentication management or secure authorization delegation for diverse applications and services.
Pros and Cons: CAS Compared to OAuth2
CAS offers centralized authentication with strong support for single sign-on (SSO) across multiple applications, providing seamless user experience and simplified credential management. OAuth2 specializes in delegated authorization, allowing third-party applications limited access to user resources without exposing credentials, enhancing security and control. However, CAS may be less flexible for API authorization tasks compared to OAuth2, which is widely adopted for modern mobile and web apps requiring granular permission scopes.
Migration Strategies Between CAS and OAuth2
Migration strategies between CAS (Central Authentication Service) and OAuth2 require careful planning to ensure seamless authentication transitions. Organizations should map CAS authentication flows to OAuth2 protocols, implementing OAuth2 authorization endpoints while phasing out CAS service tickets gradually. Utilizing middleware adapters or identity brokers facilitates interoperability during migration, minimizing downtime and preserving user sessions across both systems.
Choosing the Right Protocol for Your Organization
Choosing between CAS and OAuth2 depends on your organization's authentication and authorization needs. CAS excels in single sign-on (SSO) environments, particularly within academic and enterprise settings requiring centralized user authentication. OAuth2 offers granular access delegation, ideal for API security and third-party application integrations demanding scalable and flexible authorization mechanisms.
CAS Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com