Descriptive analytics transforms raw data into meaningful insights by summarizing historical information through metrics such as averages, totals, and trends. This approach helps you understand past performance and identify patterns that inform strategic decisions. Explore the rest of the article to discover how descriptive analytics can enhance your data-driven decision-making.
Table of Comparison
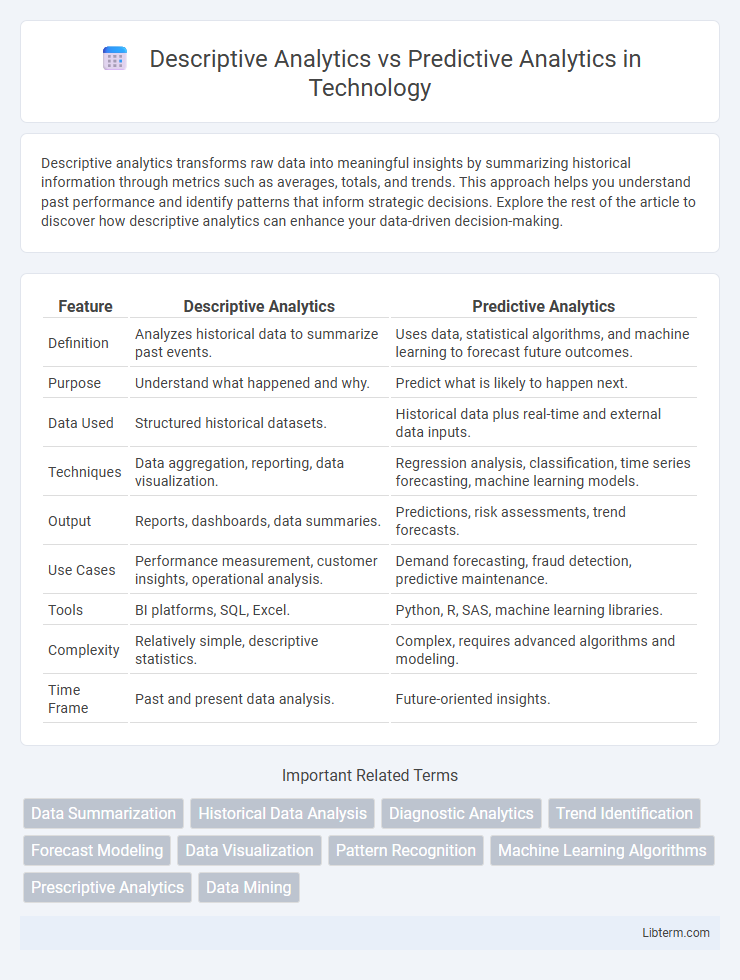
| Feature | Descriptive Analytics | Predictive Analytics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Analyzes historical data to summarize past events. | Uses data, statistical algorithms, and machine learning to forecast future outcomes. |
| Purpose | Understand what happened and why. | Predict what is likely to happen next. |
| Data Used | Structured historical datasets. | Historical data plus real-time and external data inputs. |
| Techniques | Data aggregation, reporting, data visualization. | Regression analysis, classification, time series forecasting, machine learning models. |
| Output | Reports, dashboards, data summaries. | Predictions, risk assessments, trend forecasts. |
| Use Cases | Performance measurement, customer insights, operational analysis. | Demand forecasting, fraud detection, predictive maintenance. |
| Tools | BI platforms, SQL, Excel. | Python, R, SAS, machine learning libraries. |
| Complexity | Relatively simple, descriptive statistics. | Complex, requires advanced algorithms and modeling. |
| Time Frame | Past and present data analysis. | Future-oriented insights. |
Introduction to Descriptive and Predictive Analytics
Descriptive analytics involves analyzing historical data to understand past performance and identify trends, patterns, and anomalies. Predictive analytics uses statistical models and machine learning algorithms to forecast future outcomes based on historical data. Both approaches are essential for data-driven decision-making, with descriptive analytics providing insights into what has happened and predictive analytics offering projections for informed strategic planning.
Defining Descriptive Analytics
Descriptive Analytics involves the examination and interpretation of historical data to understand what has happened in a business or system, using techniques like data aggregation, data mining, and visualization. It provides insights through reports, dashboards, and basic statistical analysis that summarize past performance and trends. This type of analytics serves as the foundation for data-driven decision-making by highlighting patterns and anomalies within the dataset.
Defining Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics uses historical data, statistical algorithms, and machine learning techniques to forecast future events and trends, enabling proactive decision-making. Unlike descriptive analytics, which summarizes past data and highlights what has happened, predictive analytics focuses on predicting potential outcomes and identifying patterns that inform business strategies. Key tools in predictive analytics include regression analysis, neural networks, and time series forecasting, which help organizations anticipate customer behavior, market shifts, and operational risks.
Key Differences Between Descriptive and Predictive Analytics
Descriptive analytics focuses on analyzing historical data to identify patterns, trends, and insights, providing a clear summary of past performance through reports and dashboards. Predictive analytics uses statistical models, machine learning algorithms, and data mining techniques to forecast future outcomes and trends based on historical and current data. Key differences include the objective--descriptive analytics explains what has happened, while predictive analytics anticipates what is likely to happen--and their respective reliance on historical data analysis versus advanced forecasting models.
Core Techniques in Descriptive Analytics
Descriptive analytics primarily employs data aggregation, data mining, and statistical measures such as mean, median, and standard deviation to summarize historical data and identify patterns. Techniques like clustering, association rule mining, and data visualization tools enable businesses to gain insights into past performance and customer behavior. These core methods provide a foundation for understanding trends and anomalies without forecasting future outcomes, distinguishing descriptive analytics from predictive analytics.
Core Techniques in Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics primarily employs machine learning algorithms, regression analysis, and time series forecasting to analyze historical data and make informed predictions about future outcomes. Techniques such as decision trees, neural networks, and support vector machines enable the identification of patterns and trends that support predictive accuracy. Unlike descriptive analytics, which summarizes past data, predictive analytics leverages statistical models and data mining methods to forecast potential scenarios and inform decision-making.
Use Cases for Descriptive Analytics
Descriptive analytics excels in summarizing historical data to identify patterns and trends, making it essential for use cases like sales performance analysis, customer segmentation, and operational efficiency assessment. It helps businesses understand what has happened by processing large datasets through dashboards, reports, and data visualization tools. Retailers, financial institutions, and healthcare providers leverage descriptive analytics to track key performance indicators and support data-driven decision-making.
Use Cases for Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics leverages historical data, statistical algorithms, and machine learning techniques to forecast future outcomes, enabling businesses to anticipate customer behavior, optimize supply chain management, and improve risk assessment. Key use cases include fraud detection in financial services, demand forecasting in retail, and predictive maintenance in manufacturing, which minimize downtime and reduce operational costs. Organizations deploying predictive analytics gain actionable insights to make data-driven decisions that enhance performance and competitive advantage.
Benefits and Limitations of Each Approach
Descriptive analytics provides valuable insights by analyzing historical data to identify patterns and trends, enhancing decision-making accuracy but is limited by its reliance on past information without forecasting capabilities. Predictive analytics leverages statistical models and machine learning algorithms to forecast future outcomes, enabling proactive strategies and risk management, though its effectiveness depends on data quality and model assumptions. Both approaches complement each other by combining comprehensive data understanding with foresight, yet businesses must balance resource investment and analytical complexity to maximize benefits.
Choosing the Right Analytics Method for Your Business
Descriptive analytics summarizes historical data to reveal trends and patterns, providing a clear understanding of past performance essential for making informed business decisions. Predictive analytics utilizes advanced statistical models and machine learning algorithms to forecast future outcomes, enabling proactive strategies and risk management. Choosing the right analytics method involves assessing business goals, data availability, and resource capabilities to balance insight from historical analysis with actionable future predictions.
Descriptive Analytics Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com