Quality assurance ensures products and services meet specific standards through systematic processes and thorough testing, minimizing defects and enhancing customer satisfaction. Implementing effective quality assurance strategies boosts reliability and operational efficiency within your organization. Explore the rest of the article to learn how quality assurance can transform your business outcomes.
Table of Comparison
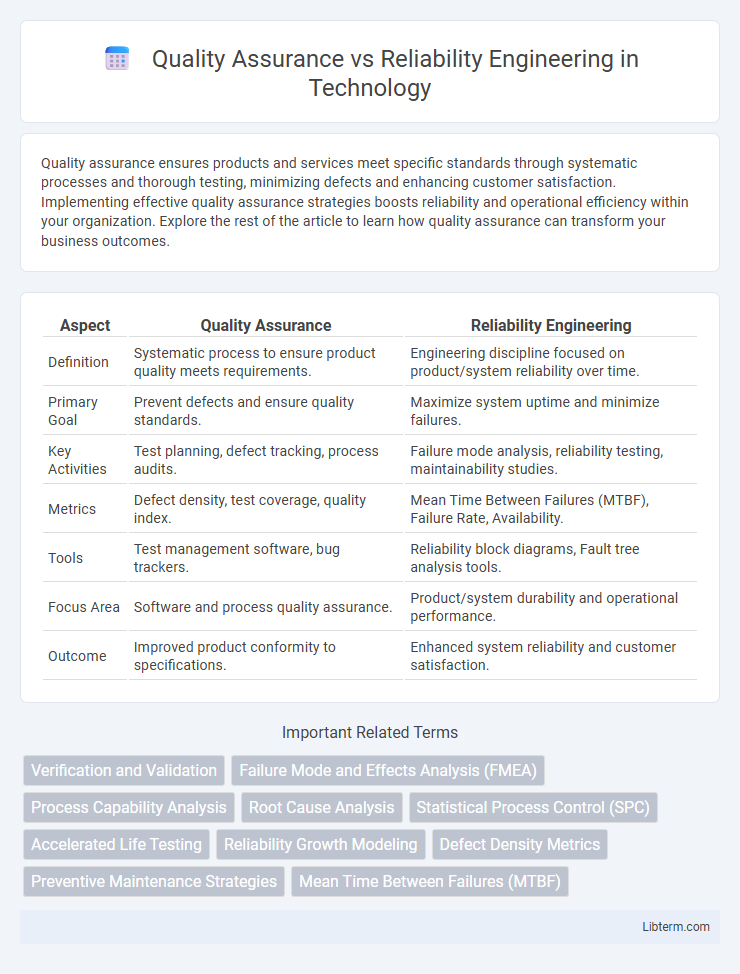
| Aspect | Quality Assurance | Reliability Engineering |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Systematic process to ensure product quality meets requirements. | Engineering discipline focused on product/system reliability over time. |
| Primary Goal | Prevent defects and ensure quality standards. | Maximize system uptime and minimize failures. |
| Key Activities | Test planning, defect tracking, process audits. | Failure mode analysis, reliability testing, maintainability studies. |
| Metrics | Defect density, test coverage, quality index. | Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF), Failure Rate, Availability. |
| Tools | Test management software, bug trackers. | Reliability block diagrams, Fault tree analysis tools. |
| Focus Area | Software and process quality assurance. | Product/system durability and operational performance. |
| Outcome | Improved product conformity to specifications. | Enhanced system reliability and customer satisfaction. |
Introduction to Quality Assurance and Reliability Engineering
Quality Assurance (QA) involves systematic processes and standards designed to ensure products meet specified quality criteria through continuous monitoring and improvement. Reliability Engineering focuses on predicting, analyzing, and enhancing product performance over time to minimize failures and maximize operational lifespan. Both disciplines are essential in product development, with QA emphasizing process quality and compliance, while Reliability Engineering targets durability and long-term dependability.
Defining Quality Assurance
Quality Assurance (QA) is a systematic process that ensures products or services meet specified requirements and standards through planned and procedural activities. It involves defining quality policies, creating test plans, and implementing process improvements to prevent defects and enhance product quality. Emphasizing proactive measures, QA focuses on verifying that development processes consistently produce reliable outcomes before the product reaches the customer.
Defining Reliability Engineering
Reliability Engineering focuses on ensuring products perform consistently over time under specified conditions by analyzing failure modes, conducting reliability testing, and implementing design improvements. It uses statistical methods and predictive models like Weibull analysis and Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA) to enhance system durability and minimize downtime. Unlike Quality Assurance, which emphasizes meeting project standards and defect prevention, Reliability Engineering drives long-term product dependability and lifecycle optimization.
Key Objectives: QA vs Reliability Engineering
Quality Assurance focuses on systematically monitoring and improving product development processes to ensure compliance with standards and customer satisfaction. Reliability Engineering emphasizes predicting, analyzing, and enhancing product performance to minimize failures and extend operational life. Both disciplines aim to deliver high-quality products but differ in their key objectives: QA targets defect prevention and process improvement, while Reliability Engineering concentrates on durability and failure mitigation.
Core Processes and Methodologies
Quality Assurance focuses on systematic processes such as inspection, testing, and process audits to ensure that products meet predefined standards and customer requirements. Reliability Engineering emphasizes statistical analysis, failure modes and effects analysis (FMEA), and predictive maintenance to enhance system dependability and lifespan. Both methodologies integrate continuous improvement techniques like Six Sigma and root cause analysis but target different aspects of product excellence and operational stability.
Role in Product Development Lifecycle
Quality Assurance ensures that products meet predefined standards through systematic testing and process validation during the product development lifecycle, preventing defects and enhancing usability. Reliability Engineering focuses on predicting, analyzing, and improving product longevity and performance under real-world conditions to minimize failures and maintenance costs. Together, they work synergistically to deliver robust, high-quality products that satisfy customer expectations and regulatory requirements.
Tools and Techniques Used
Quality Assurance employs tools such as statistical process control, Six Sigma, and automated testing frameworks like Selenium to ensure product conformity and defect prevention. Reliability Engineering focuses on failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA), reliability block diagrams, and accelerated life testing to predict and enhance system durability. Both disciplines leverage data analytics and root cause analysis software to continuously improve performance and minimize downtime.
Metrics for Success: QA vs Reliability Engineering
Quality Assurance metrics emphasize defect detection rate, test coverage, and customer satisfaction scores to ensure software meets predefined standards. Reliability Engineering metrics focus on Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF), Failure Rate, and system availability to measure long-term system performance and dependability. Both disciplines require data-driven insights but differ in evaluating product quality versus operational stability.
Industry Applications and Case Studies
Quality Assurance (QA) in industry applications ensures product conformity through systematic process audits and defect prevention, commonly demonstrated in automotive manufacturing where compliance with ISO/TS 16949 reduces recalls. Reliability Engineering focuses on predicting and improving product lifespan and performance using failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA), exemplified by aerospace case studies that enhance aircraft system durability and reduce maintenance costs. Both disciplines integrate to optimize operational efficiency, with electronics industry case studies showing improved yield and decreased warranty claims via combined QA and reliability protocols.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Organization
Quality Assurance (QA) focuses on preventing defects through systematic processes and testing to ensure product standards, while Reliability Engineering emphasizes predicting, measuring, and enhancing the product's long-term performance and durability. Choosing the right approach depends on the organization's objectives, product complexity, and customer expectations, where QA suits environments prioritizing defect reduction and process improvements, and Reliability Engineering fits industries requiring consistent product uptime and failure minimization. Combining both methodologies can create a comprehensive strategy for delivering high-quality, dependable products tailored to specific operational needs.
Quality Assurance Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com