Fuzz testing is a dynamic software testing technique that involves providing invalid, unexpected, or random data inputs to programs to uncover vulnerabilities and bugs. This method helps improve software security and stability by identifying issues that traditional testing might overlook. Explore the rest of the article to learn how fuzz testing can safeguard your applications and enhance their reliability.
Table of Comparison
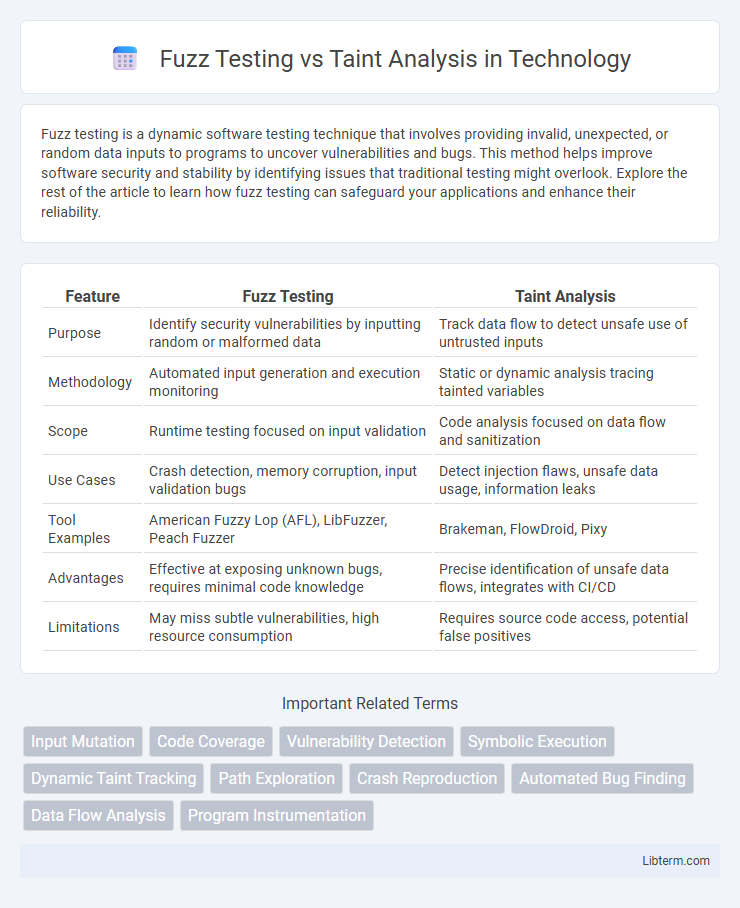
| Feature | Fuzz Testing | Taint Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Identify security vulnerabilities by inputting random or malformed data | Track data flow to detect unsafe use of untrusted inputs |
| Methodology | Automated input generation and execution monitoring | Static or dynamic analysis tracing tainted variables |
| Scope | Runtime testing focused on input validation | Code analysis focused on data flow and sanitization |
| Use Cases | Crash detection, memory corruption, input validation bugs | Detect injection flaws, unsafe data usage, information leaks |
| Tool Examples | American Fuzzy Lop (AFL), LibFuzzer, Peach Fuzzer | Brakeman, FlowDroid, Pixy |
| Advantages | Effective at exposing unknown bugs, requires minimal code knowledge | Precise identification of unsafe data flows, integrates with CI/CD |
| Limitations | May miss subtle vulnerabilities, high resource consumption | Requires source code access, potential false positives |
Introduction to Fuzz Testing and Taint Analysis
Fuzz testing is a dynamic analysis technique that inputs random or malformed data into software to uncover vulnerabilities, crashes, and security flaws by observing unexpected behavior. Taint analysis is a static or dynamic method that tracks the flow of untrusted input through a program to identify potential security risks, such as injection attacks or data leaks. Both techniques serve as complementary approaches for improving software security by detecting different types of vulnerabilities.
Core Concepts and Definitions
Fuzz testing is an automated software testing technique that inputs random or unexpected data into programs to identify vulnerabilities and crashes by observing their responses. Taint analysis tracks the flow of untrusted or potentially harmful data through a program to detect security flaws like injection attacks by marking and monitoring tainted variables. Both methods enhance software security but differ in approach: fuzz testing proactively generates test cases to expose errors, while taint analysis statically or dynamically traces data propagation to highlight unsafe data use.
How Fuzz Testing Works
Fuzz testing works by automatically generating and inputting large volumes of randomized or malformed data into a program to identify security vulnerabilities, crashes, and unexpected behavior. This method monitors the application's response, detecting anomalies that indicate memory leaks, buffer overflows, or input validation flaws. By systematically exploring code paths through varied inputs, fuzz testing effectively uncovers bugs that traditional testing methods might miss.
How Taint Analysis Operates
Taint analysis operates by tracking the flow of untrusted or user-controlled data through a software program to identify potential security vulnerabilities. It marks data from external inputs as "tainted" and monitors how it propagates through variables, functions, and memory locations, flagging any unsafe use that could lead to exploits such as SQL injection or cross-site scripting. By leveraging static or dynamic code analysis techniques, taint analysis provides granular insights into data flow paths and vulnerability points without requiring extensive input generation like fuzz testing.
Strengths of Fuzz Testing
Fuzz testing excels at uncovering unknown security vulnerabilities by inputting large volumes of random or malformed data, which triggers unexpected behaviors and crashes. Its automated nature allows rapid identification of memory corruptions, buffer overflows, and input validation errors without needing detailed source code analysis. This makes fuzz testing particularly effective for discovering zero-day exploits and improving overall software robustness.
Advantages of Taint Analysis
Taint analysis excels at detecting intricate security vulnerabilities by tracking the flow of untrusted data through a program, identifying potential injection points and data leaks that fuzz testing might miss. It provides precise vulnerability localization by analyzing code paths without requiring extensive input generation, making it highly efficient for static code analysis. This method enables developers to prioritize remediation efforts by pinpointing exact sources and sinks of tainted data, thus improving overall software security.
Limitations and Challenges
Fuzz testing faces limitations such as difficulty in generating high-quality, domain-specific inputs and often missing deeper logical vulnerabilities due to its random nature. Taint analysis encounters challenges including high false positive rates and scalability issues when handling large codebases, especially in dynamic or complex taint propagation scenarios. Both techniques require significant computational resources and expert tuning to improve accuracy and practical applicability in real-world software security assessments.
Comparative Use Cases
Fuzz testing excels in identifying vulnerabilities by inputting vast amounts of random data to trigger unexpected behavior or crashes, making it ideal for discovering unknown bugs in software like web browsers and network protocols. Taint analysis tracks the flow of untrusted input through a program to detect vulnerabilities related to data corruption or injection attacks, which is especially effective for securing applications handling sensitive information, such as financial or healthcare software. Combining fuzz testing's broad fault detection with taint analysis's precise data flow tracking provides a comprehensive approach for enhancing software security across different development environments.
Integration in Modern Security Workflows
Fuzz testing and taint analysis both enhance modern security workflows by identifying vulnerabilities through different approaches; fuzz testing automates the discovery of input-related bugs by feeding random data to applications, while taint analysis traces the flow of untrusted data to detect security flaws such as injection vulnerabilities. Integrating fuzz testing with taint analysis tools enables security teams to cover a wider attack surface by combining dynamic input validation and static code examination, resulting in more comprehensive vulnerability detection. Modern DevSecOps pipelines leverage this integration to automate continuous security assessment, improve threat detection accuracy, and accelerate remediation processes.
Choosing the Right Approach
Choosing the right approach between fuzz testing and taint analysis depends on the specific security goals and software environment. Fuzz testing excels at uncovering unknown vulnerabilities by generating random inputs to trigger unexpected behaviors, making it ideal for identifying memory corruption or crash bugs in complex systems. Taint analysis, on the other hand, is best suited for tracking data flow and identifying injection attacks by marking and tracing untrusted input through the program, which is crucial for detecting security flaws in web applications and preventing data leaks.
Fuzz Testing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com