NAT Gateway provides secure internet access for instances within a private subnet by translating private IP addresses to a public IP address. It ensures seamless communication without exposing your internal network, offering scalability and high availability for cloud environments. Discover how a NAT Gateway can optimize your network architecture in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
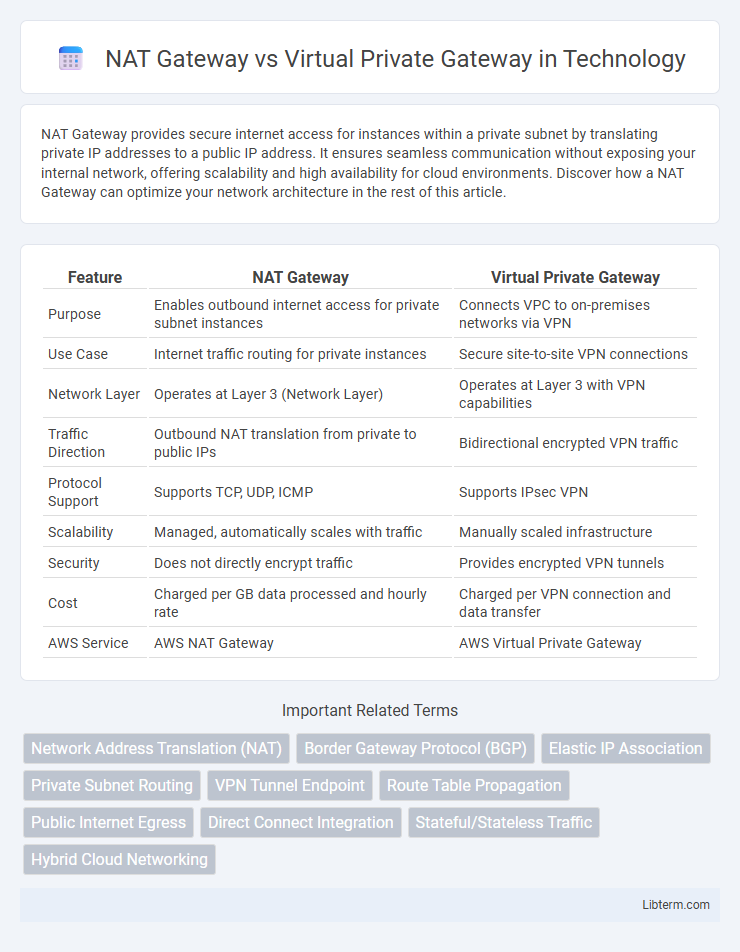
| Feature | NAT Gateway | Virtual Private Gateway |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Enables outbound internet access for private subnet instances | Connects VPC to on-premises networks via VPN |
| Use Case | Internet traffic routing for private instances | Secure site-to-site VPN connections |
| Network Layer | Operates at Layer 3 (Network Layer) | Operates at Layer 3 with VPN capabilities |
| Traffic Direction | Outbound NAT translation from private to public IPs | Bidirectional encrypted VPN traffic |
| Protocol Support | Supports TCP, UDP, ICMP | Supports IPsec VPN |
| Scalability | Managed, automatically scales with traffic | Manually scaled infrastructure |
| Security | Does not directly encrypt traffic | Provides encrypted VPN tunnels |
| Cost | Charged per GB data processed and hourly rate | Charged per VPN connection and data transfer |
| AWS Service | AWS NAT Gateway | AWS Virtual Private Gateway |
Introduction to Network Gateways
Network gateways serve as critical connection points between different networks, enabling data flow and communication. A NAT Gateway translates private IP addresses to public IP addresses, facilitating internet access for resources within a private subnet while maintaining security. In contrast, a Virtual Private Gateway provides a secure VPN connection between an on-premises network and a cloud Virtual Private Cloud (VPC), ensuring encrypted data transfer across environments.
What is a NAT Gateway?
A NAT Gateway is a managed network service that enables instances in a private subnet to connect to the internet or other AWS services while preventing inbound traffic from the internet. It translates private IP addresses to a public IP address, facilitating outbound internet access without exposing internal resources. NAT Gateways are highly available within an Availability Zone and support scalable traffic loads for secure internet connectivity in cloud environments.
What is a Virtual Private Gateway?
A Virtual Private Gateway (VPG) is a critical component in AWS that enables secure communication between a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) and external networks, such as corporate data centers or other VPNs, via IPsec VPN connections or AWS Direct Connect. Unlike a NAT Gateway, which provides outbound internet access for private subnets, the VPG facilitates private, encrypted tunnels for hybrid cloud architectures. It supports highly available, scalable connectivity solutions essential for enterprise-grade network security and integration.
Key Differences Between NAT Gateway and Virtual Private Gateway
NAT Gateway enables private subnet instances to access the internet for outbound traffic while preventing inbound internet traffic, ensuring secure communication without exposing internal resources directly. Virtual Private Gateway allows secure, encrypted VPN connections between a VPC and on-premises networks or other AWS regions, supporting hybrid cloud architectures and cross-region access. The key difference lies in NAT Gateway facilitating internet-bound traffic for private subnets, whereas Virtual Private Gateway manages site-to-site VPN connectivity for secure, private network integration.
Use Cases for NAT Gateway
NAT Gateway is primarily used to enable instances in a private subnet to access the internet for updates, patches, and external services without exposing those instances to inbound internet traffic. It is ideal for workloads requiring outbound internet connectivity while maintaining secure private subnet isolation. In contrast, a Virtual Private Gateway is designed for establishing VPN connections between an on-premises network and an AWS VPC, enabling private communication rather than providing internet access.
Use Cases for Virtual Private Gateway
Virtual Private Gateway (VPG) is primarily used to establish secure VPN connections between an on-premises network and an Amazon VPC, enabling seamless hybrid cloud architectures. It supports private, encrypted communication for data transfer, making it ideal for enterprises requiring secure, persistent connectivity for compliance and sensitive workloads. Unlike NAT Gateways, which manage outbound internet traffic for private subnets, VPG facilitates site-to-site VPNs and AWS Direct Connect integration for robust enterprise networking solutions.
Security Implications: NAT vs. Virtual Private Gateway
NAT Gateways enhance security by allowing instances in private subnets to initiate outbound internet traffic while preventing unsolicited inbound connections, effectively masking internal IP addresses. Virtual Private Gateways provide secure, encrypted VPN connections between your VPC and on-premises networks, ensuring confidential data transmission over public networks. The choice between NAT and Virtual Private Gateways depends on whether secure internet access or private network connectivity is the primary security requirement.
Performance and Scalability Considerations
NAT Gateway offers high scalability by automatically handling bursts of traffic without manual intervention, making it ideal for outbound internet traffic in large-scale AWS environments. Virtual Private Gateway supports VPN connections for secure site-to-site communication but may introduce latency and throughput limitations depending on the VPN appliance and network configuration. Performance-wise, NAT Gateway provides consistent high throughput for NAT operations, whereas Virtual Private Gateway performance is influenced by encryption overhead and tunnel management complexities.
Cost Comparison: NAT Gateway vs Virtual Private Gateway
NAT Gateway typically incurs higher hourly and data processing costs compared to Virtual Private Gateway, making it more expensive for large volumes of outbound internet traffic. Virtual Private Gateway, used primarily for VPN connections to on-premises networks, involves lower data transfer fees but may include additional costs related to VPN connection hours and endpoints. For cost efficiency, Virtual Private Gateway is preferred in hybrid cloud scenarios, while NAT Gateway suits internet-bound traffic despite its higher operational expenses.
Choosing the Right Gateway for Your Cloud Architecture
Choosing the right gateway for your cloud architecture depends on specific use cases: NAT Gateway provides outbound internet access for instances in private subnets, enabling secure communication without exposing resources to inbound traffic. Virtual Private Gateway connects your VPC to on-premises networks via VPN or AWS Direct Connect, facilitating hybrid cloud deployments and secure remote access. Assess your security requirements, network traffic flows, and hybrid connectivity needs to determine which gateway aligns with your architecture goals.
NAT Gateway Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com