A promissory note is a legally binding document outlining a borrower's promise to repay a specific amount to a lender by a predetermined date. It includes key terms such as principal, interest rate, maturity date, and repayment schedule, offering both parties clarity and protection. Explore the rest of the article to understand how a promissory note can secure your financial agreements effectively.
Table of Comparison
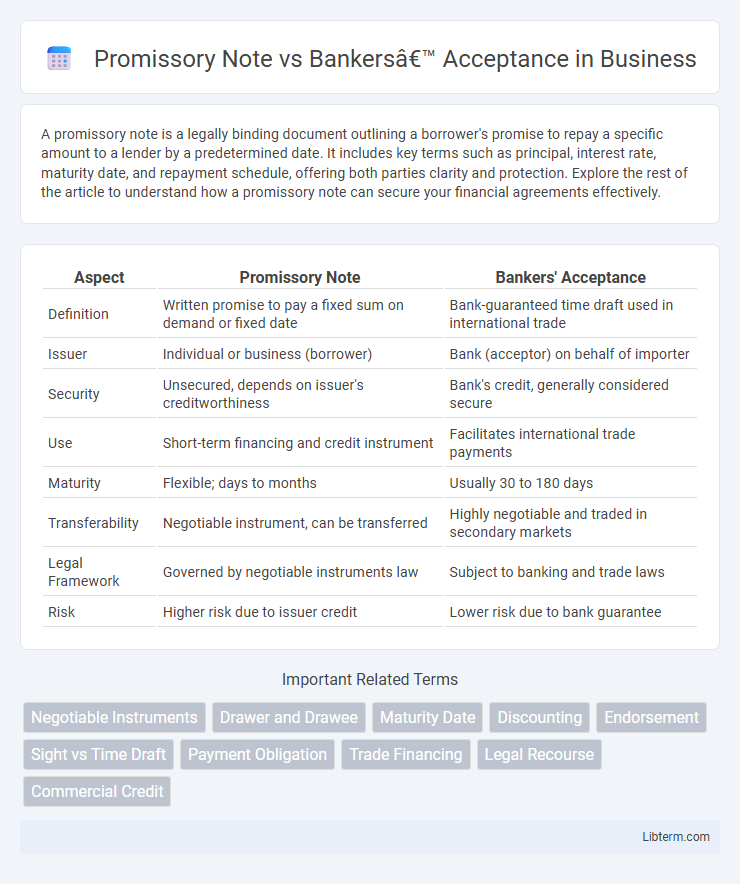
| Aspect | Promissory Note | Bankers' Acceptance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Written promise to pay a fixed sum on demand or fixed date | Bank-guaranteed time draft used in international trade |
| Issuer | Individual or business (borrower) | Bank (acceptor) on behalf of importer |
| Security | Unsecured, depends on issuer's creditworthiness | Bank's credit, generally considered secure |
| Use | Short-term financing and credit instrument | Facilitates international trade payments |
| Maturity | Flexible; days to months | Usually 30 to 180 days |
| Transferability | Negotiable instrument, can be transferred | Highly negotiable and traded in secondary markets |
| Legal Framework | Governed by negotiable instruments law | Subject to banking and trade laws |
| Risk | Higher risk due to issuer credit | Lower risk due to bank guarantee |
Introduction to Promissory Notes and Bankers’ Acceptances
Promissory notes are written financial instruments containing a promise by one party to pay a certain sum to another party at a specified future date, serving as evidence of debt. Bankers' acceptances are time drafts guaranteed by a bank, commonly used in international trade to facilitate secure payment by combining bank credit with the creditworthiness of the buyer. Both instruments play crucial roles in commercial finance, offering liquidity and reducing credit risk for businesses and financial institutions.
Definition and Key Features of Promissory Notes
A promissory note is a financial instrument in which one party promises in writing to pay a specific sum of money to another party at a predetermined date or on demand, serving as a legally binding debt instrument. Key features include the inclusion of the principal amount, interest rate, maturity date, and the signatures of the issuer, making it a negotiable instrument under the law. Unlike bankers' acceptances, promissory notes are primarily personal debt commitments and do not necessarily involve a bank guaranteeing payment.
Definition and Key Features of Bankers’ Acceptances
A Bankers' Acceptance is a short-term, negotiable financial instrument guaranteed by a bank that promises payment at a future date, typically used in international trade to facilitate transactions. Unlike promissory notes, which are unconditional written promises from one party to pay another, Bankers' Acceptances involve a bank's explicit assumption of payment responsibility, enhancing creditworthiness and liquidity. Key features include government or bank backing, fixed maturity dates, negotiability in secondary markets, and use as a secure medium of exchange between exporters and importers.
Legal Framework and Regulatory Differences
Promissory Notes are governed primarily by the Uniform Commercial Code (UCC) in the United States, establishing clear obligations between the maker and payee, while Bankers' Acceptances fall under both banking regulations and international trade laws, involving a bank's guarantee of payment. Regulatory oversight for Promissory Notes is less stringent, typically involving contract law enforcement, whereas Bankers' Acceptances require compliance with banking regulatory bodies such as the Federal Reserve and must adhere to specific standards for negotiability and trade finance. The legal framework for Bankers' Acceptances also incorporates risk management protocols to ensure creditworthiness and mitigate default risk, reflecting their use in commercial transactions with higher regulatory scrutiny compared to Promissory Notes.
Use Cases in Trade and Commercial Transactions
Promissory notes serve as written promises for payment between businesses, commonly used in short-term financing and credit arrangements in commercial transactions. Bankers' acceptances act as guaranteed payment instruments issued by banks, facilitating international trade by reducing credit risk and ensuring timely settlement between importers and exporters. Both instruments enhance liquidity and trust in trade finance but differ in their risk profiles and acceptance within financial markets.
Credit Risk and Financial Security
A promissory note represents a direct credit obligation from the issuer to the payee, inherently bearing higher credit risk due to the issuer's creditworthiness and lack of financial institution backing. In contrast, a bankers' acceptance is a time draft guaranteed by a bank, significantly reducing credit risk and enhancing financial security by substituting the bank's credit for that of the original drawer. The involvement of the bank in bankers' acceptances provides stronger assurance of payment, making them more secure instruments in trade finance.
Process of Issuance and Endorsement
A promissory note is a written, unconditional promise by one party to pay a specific sum to another, issued and signed directly by the borrower with endorsements involving simple signature transfers. Bankers' acceptance originates from a time draft drawn on and accepted by a bank, transforming it into a negotiable instrument guaranteed by the bank, with endorsements required to transfer ownership and ensure bank liability. The issuance of a promissory note involves borrower-driven creation, while bankers' acceptance requires bank acceptance and stamping, reflecting a formalized credit instrument backed by the bank's commitment.
Liquidity and Secondary Market Trading
A promissory note is a financial instrument that represents a written promise to pay a specific amount on a certain date, offering moderate liquidity with limited secondary market trading primarily among banks and financial institutions. Bankers' acceptances are time drafts guaranteed by a bank, providing higher liquidity due to their bank backing and active secondary market trading, making them preferable for short-term financing and trade transactions. The enhanced trust and creditworthiness of bankers' acceptances facilitate easier transferability and better pricing in secondary markets compared to promissory notes.
Advantages and Disadvantages Compared
A Promissory Note offers simplicity and directness, providing a clear, written promise to pay a specified sum, which benefits small businesses and individuals seeking straightforward credit arrangements; however, it carries higher risk due to lack of third-party guarantee and limited liquidity. Bankers' Acceptance provides enhanced security as it is a time draft guaranteed by a bank, improving creditworthiness and facilitating international trade with greater liquidity and negotiability, but it often involves higher costs and stricter eligibility criteria, limiting accessibility for smaller entities. Choosing between the two depends on factors like transaction size, risk tolerance, and need for liquidity in short-term financing.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Promissory Notes and Bankers’ Acceptances
Choosing between promissory notes and bankers' acceptances depends on the level of credit risk and liquidity required in a transaction. Promissory notes are ideal for direct borrower-lender agreements with moderate risk, while bankers' acceptances offer enhanced security by involving a bank's guarantee, making them preferable for international trade and high-credit environments. Assessing factors such as creditworthiness, transferability, and market acceptance ensures the optimal financing instrument aligns with business needs and risk tolerance.
Promissory Note Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com