Franchising offers a proven business model that allows entrepreneurs to leverage brand recognition and established operational systems for faster growth. By investing in a franchise, your risk is reduced through support in marketing, training, and ongoing assistance from the franchisor. Explore the full article to discover how franchising can accelerate your path to business success.
Table of Comparison
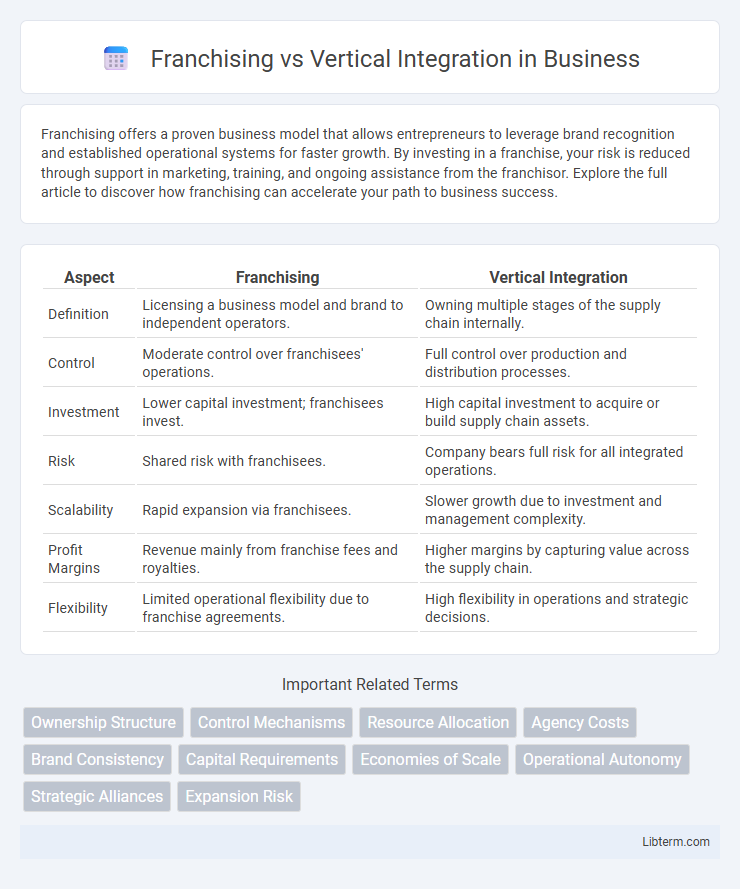
| Aspect | Franchising | Vertical Integration |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Licensing a business model and brand to independent operators. | Owning multiple stages of the supply chain internally. |
| Control | Moderate control over franchisees' operations. | Full control over production and distribution processes. |
| Investment | Lower capital investment; franchisees invest. | High capital investment to acquire or build supply chain assets. |
| Risk | Shared risk with franchisees. | Company bears full risk for all integrated operations. |
| Scalability | Rapid expansion via franchisees. | Slower growth due to investment and management complexity. |
| Profit Margins | Revenue mainly from franchise fees and royalties. | Higher margins by capturing value across the supply chain. |
| Flexibility | Limited operational flexibility due to franchise agreements. | High flexibility in operations and strategic decisions. |
Introduction to Franchising and Vertical Integration
Franchising involves a business model where a franchisor licenses trademarks and processes to franchisees, enabling rapid expansion with reduced capital investment. Vertical integration occurs when a company controls multiple stages of production or distribution within the same industry, enhancing supply chain efficiency and reducing costs. Both strategies optimize market reach and operational control but differ in ownership structure and resource allocation.
Definitions and Key Concepts
Franchising is a business model where a franchisor licenses its brand, products, and operational methods to a franchisee in exchange for fees or royalties, enabling rapid expansion with lower capital investment. Vertical integration involves a company controlling multiple stages of its supply chain, from production to distribution, to increase efficiency and reduce dependency on external suppliers. Both strategies offer distinct approaches to growth and control, with franchising emphasizing brand replication and vertical integration focusing on supply chain consolidation.
Historical Evolution of Business Expansion Models
Franchising emerged in the mid-19th century as a scalable business expansion model, notably popularized by companies like Singer and later McDonald's, allowing rapid market penetration with reduced capital investment by leveraging local entrepreneurs. Vertical integration dates back to the late 19th and early 20th centuries, exemplified by industrial giants such as Carnegie Steel, which controlled multiple stages of production to reduce costs and increase control over the supply chain. These two models have historically reflected differing strategies: franchising emphasizes decentralized growth through licensing agreements, while vertical integration seeks centralized control over production and distribution.
Advantages of Franchising
Franchising offers significant advantages such as rapid market expansion with lower capital investment compared to vertical integration. It leverages the entrepreneurial drive of franchisees, leading to enhanced local market knowledge and operational efficiency. This model also reduces business risk for the franchisor by distributing it across multiple independent owners.
Benefits of Vertical Integration
Vertical integration enhances operational control by allowing companies to oversee multiple stages of production and distribution, leading to improved quality consistency and efficiency. It reduces dependency on external suppliers, lowering costs and minimizing supply chain disruptions. Companies gain greater market power and the ability to capture higher profit margins through streamlined processes and direct access to resources.
Challenges and Risks of Franchising
Franchising presents challenges such as maintaining consistent brand standards across diverse locations due to varying franchisee management styles and operational capabilities. Risks also include potential conflicts between franchisors and franchisees over control, royalties, and marketing strategies, which can dilute brand reputation. Legal complications and the high cost of supporting franchisees in training, compliance, and quality control further increase operational complexity and financial exposure.
Drawbacks and Limitations of Vertical Integration
Vertical integration often leads to significant capital investment and increased operational complexity, burdening companies with substantial fixed costs and reduced financial flexibility. This strategy can result in slower response times to market changes due to less external supplier competition and potential inefficiencies in managing diverse business units. Furthermore, vertical integration may limit innovation by reducing exposure to external partners and suppressing competitive pressures essential for continuous improvement.
Financial Implications and Investment Considerations
Franchising requires lower capital investment compared to vertical integration, as franchisees bear the financial burden of expansion, reducing risk for the franchisor. Vertical integration demands significant upfront investment in assets and operations but offers greater control over supply chains and profit margins. Financially, franchising provides steady royalty income streams, while vertical integration can yield higher long-term returns through cost efficiencies and market control.
Choosing the Right Expansion Strategy
Selecting the ideal expansion strategy depends on factors such as control, capital investment, and market adaptation. Franchising offers rapid growth with lower capital risk by leveraging local entrepreneurs, while vertical integration demands significant investment but ensures full control over production and distribution. Businesses must evaluate operational expertise, scalability, and long-term strategic goals to determine whether franchising or vertical integration aligns best with their growth objectives.
Future Trends in Business Expansion Models
Future trends in business expansion models highlight a growing preference for franchising due to its scalability and reduced capital investment requirements. Vertical integration remains vital for companies seeking tighter control over supply chains and product quality, especially in technology-driven industries. Advances in digital platforms and data analytics are transforming both models, enabling enhanced operational efficiencies and customer engagement.
Franchising Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com