Add-on selling boosts your average transaction value by encouraging customers to purchase complementary products or services alongside their initial choice. This technique enhances customer satisfaction by offering tailored suggestions that meet their needs more completely. Discover effective strategies to master add-on selling and increase your revenue in the full article.
Table of Comparison
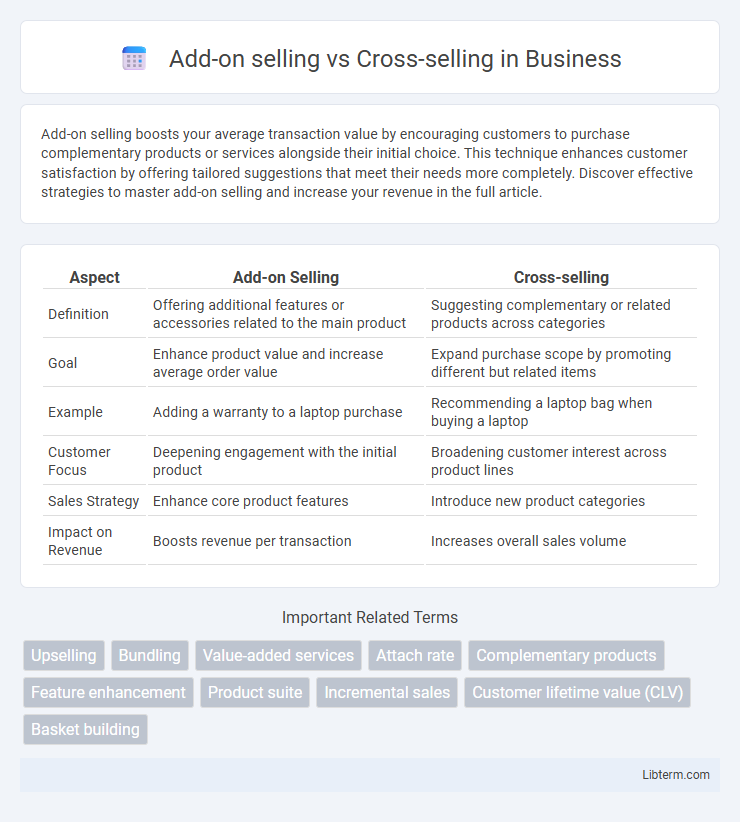
| Aspect | Add-on Selling | Cross-selling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Offering additional features or accessories related to the main product | Suggesting complementary or related products across categories |
| Goal | Enhance product value and increase average order value | Expand purchase scope by promoting different but related items |
| Example | Adding a warranty to a laptop purchase | Recommending a laptop bag when buying a laptop |
| Customer Focus | Deepening engagement with the initial product | Broadening customer interest across product lines |
| Sales Strategy | Enhance core product features | Introduce new product categories |
| Impact on Revenue | Boosts revenue per transaction | Increases overall sales volume |
Understanding Add-on Selling
Add-on selling involves encouraging customers to purchase additional products or services that complement the primary item, enhancing their overall experience and satisfaction. This strategy targets the immediate transaction, offering relevant enhancements such as accessories or extended warranties to increase order value. Effective add-on selling requires understanding customer needs and preferences to suggest timely, personalized options that add genuine value.
What is Cross-selling?
Cross-selling is a sales technique that encourages customers to purchase complementary or related products alongside their primary purchase, increasing overall transaction value. It involves identifying items that enhance or supplement the main product, such as offering phone cases or screen protectors when selling smartphones. Effective cross-selling enhances customer satisfaction by providing relevant solutions that meet broader needs while boosting revenue for businesses.
Key Differences Between Add-on and Cross-selling
Add-on selling involves offering customers complementary products or accessories directly related to their original purchase, such as a phone case with a smartphone, whereas cross-selling promotes entirely different but relevant products that fulfill additional needs, like selling a laptop alongside office software. Add-on selling typically aims to enhance the primary product's functionality and customer experience, while cross-selling broadens the customer's overall purchase scope by introducing related categories. Both strategies increase average transaction value but differ in product relevance and customer intent targeting.
Benefits of Add-on Selling
Add-on selling increases average transaction value by encouraging customers to purchase supplementary products that enhance the primary purchase, such as accessories or extended warranties. It improves customer satisfaction through personalized recommendations tailored to the buyer's needs, creating a more complete and convenient shopping experience. This strategy leverages existing buyer intent, making it easier to close sales without extensive additional marketing efforts, resulting in higher profitability for businesses.
Advantages of Cross-selling
Cross-selling enhances customer lifetime value by promoting complementary products that meet broader customer needs, leading to increased average order value and stronger brand loyalty. It leverages customer purchase history and preferences to suggest relevant items, improving the shopping experience and boosting conversion rates. Businesses benefit from higher revenue without significant additional marketing costs, making cross-selling a cost-effective strategy compared to add-on selling.
Common Add-on Selling Techniques
Common add-on selling techniques include suggesting complementary products that enhance the primary purchase, such as offering phone cases or screen protectors when selling smartphones. Sales representatives often use bundling strategies by grouping related items at a discounted price to encourage customers to buy more. Personalized recommendations based on customer preferences and purchase history also boost add-on sales effectiveness by increasing relevance.
Effective Cross-selling Strategies
Effective cross-selling strategies leverage customer purchase history and preferences to offer complementary products that enhance the original purchase experience. Utilizing personalized recommendations and bundling options increases customer satisfaction and boosts average transaction value. Data-driven insights and timely offers during the buying journey maximize cross-selling success and long-term customer loyalty.
When to Use Add-on Selling vs Cross-selling
Add-on selling is most effective when customers have already decided on a primary product and are open to enhancing their purchase with complementary accessories or services. Cross-selling works best when customers need related products that fulfill a broader need, often in a different category or function. Use add-on selling to increase average order value during the checkout process, and opt for cross-selling to expand customer solutions and deepen engagement across multiple product lines.
Mistakes to Avoid in Add-on and Cross-selling
Avoid overwhelming customers with irrelevant or excessive add-on offers, which can create frustration and reduce purchase likelihood. In cross-selling, steer clear of suggesting unrelated or low-value products that do not complement the original purchase, as this undermines trust and decreases conversion rates. Both strategies require personalized recommendations based on customer behavior and preferences to maximize effectiveness and maintain a positive shopping experience.
Optimizing Sales with Both Approaches
Add-on selling maximizes revenue by encouraging customers to purchase complementary products that enhance their primary purchase, while cross-selling broadens sales opportunities by offering related items from different categories. Integrating these approaches leverages customer insights and purchase behavior, boosting average order value and customer lifetime value. Strategic implementation involves personalized recommendations and timing, ensuring relevance and increasing the likelihood of successful conversions.
Add-on selling Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com