Materialize offers a powerful platform for building real-time data applications with ease and scalability. It integrates seamlessly with existing data infrastructure, enabling you to transform, analyze, and visualize streaming data instantly. Explore this article to discover how Materialize can revolutionize your data processing workflow.
Table of Comparison
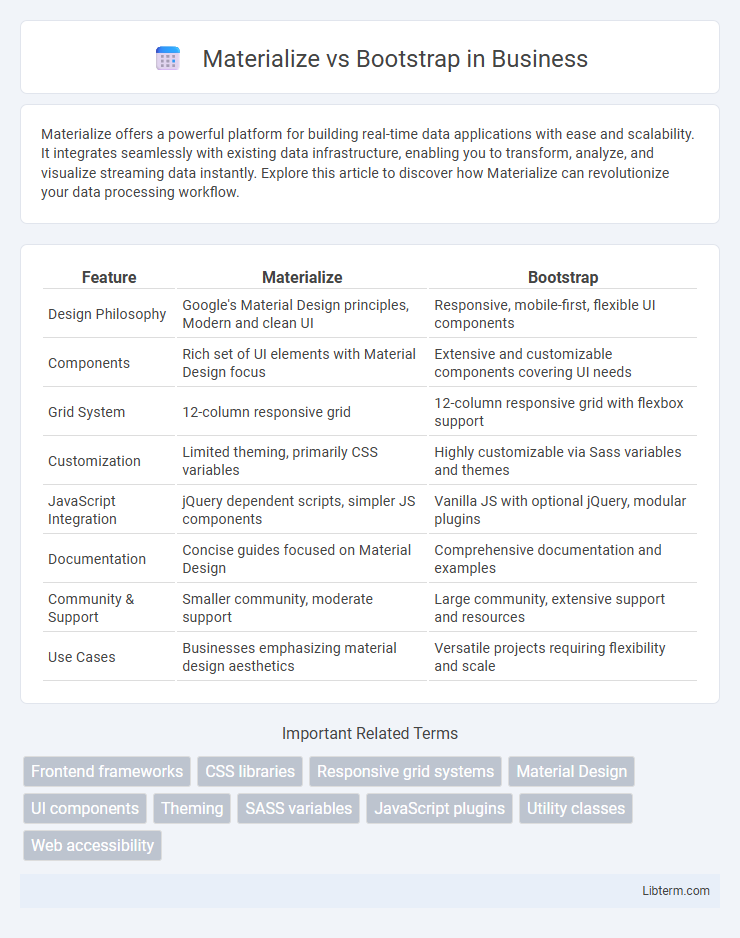
| Feature | Materialize | Bootstrap |
|---|---|---|
| Design Philosophy | Google's Material Design principles, Modern and clean UI | Responsive, mobile-first, flexible UI components |
| Components | Rich set of UI elements with Material Design focus | Extensive and customizable components covering UI needs |
| Grid System | 12-column responsive grid | 12-column responsive grid with flexbox support |
| Customization | Limited theming, primarily CSS variables | Highly customizable via Sass variables and themes |
| JavaScript Integration | jQuery dependent scripts, simpler JS components | Vanilla JS with optional jQuery, modular plugins |
| Documentation | Concise guides focused on Material Design | Comprehensive documentation and examples |
| Community & Support | Smaller community, moderate support | Large community, extensive support and resources |
| Use Cases | Businesses emphasizing material design aesthetics | Versatile projects requiring flexibility and scale |
Introduction to Materialize and Bootstrap
Materialize is a modern responsive CSS framework based on Google's Material Design principles, offering components like cards, buttons, and forms tailored for sleek, mobile-first web interfaces. Bootstrap, developed by Twitter, is one of the most popular front-end frameworks featuring a vast collection of pre-built responsive components, grid systems, and JavaScript plugins that streamline web development. Both frameworks prioritize consistency and responsiveness but differ in design aesthetics and component customization options.
Core Philosophy and Design Principles
Materialize embraces Google's Material Design philosophy, aiming for a unified and tactile user experience with dynamic grid systems, responsive animations, and depth effects linked to real-world physics. Bootstrap prioritizes a mobile-first approach with a strong emphasis on simplicity, responsive grids, and extensive UI components designed for rapid development across diverse devices. Materialize focuses on visual consistency and motion, while Bootstrap centers on flexibility and broad compatibility.
Key Features and Components Comparison
Materialize offers a modern design system based on Google's Material Design, featuring responsive grid layouts, interactive components like cards, sliders, and modals, and built-in animations for enhanced user experience. Bootstrap emphasizes a robust and flexible framework with a comprehensive set of pre-styled UI components including buttons, forms, navbars, and extensive utility classes, promoting rapid development and consistent design across browsers. Both frameworks provide grid systems and responsive design capabilities, but Materialize focuses more on aesthetic material design principles, while Bootstrap prioritizes versatility and broad compatibility.
User Interface and Customization Options
Materialize offers a sleek, material design-inspired user interface emphasizing consistency and depth effects, ideal for creating modern, visually appealing web apps. Bootstrap provides a robust, grid-based system with a wide range of prebuilt components, focusing on responsive design and ease of customization using Sass variables and utility classes. Both frameworks support extensive customization, but Materialize leans towards predefined material design aesthetics while Bootstrap offers greater flexibility for personalized UI development.
Responsiveness and Mobile-First Approach
Materialize and Bootstrap both prioritize responsiveness and a mobile-first approach, but Materialize leverages Google's Material Design principles for a more modern, touch-friendly interface, optimized for seamless user experience on mobile devices. Bootstrap, with its extensive grid system and utility classes, offers robust responsiveness and flexibility across various screen sizes, making it ideal for rapid development and compatibility. Developers often choose Materialize for its aesthetic consistency and mobile gesture support, while Bootstrap excels in scalability and broad browser support.
Documentation and Community Support
Materialize offers comprehensive documentation with clear examples and a responsive design focus, catering well to developers seeking modern UI components based on Material Design principles. Bootstrap provides extensive, well-organized documentation supported by one of the largest developer communities, ensuring abundant resources, tutorials, and third-party plugins. The robust community around Bootstrap facilitates faster issue resolution and continuous updates, making it ideal for projects requiring strong support and ecosystem integration.
Performance and Load Times
Materialize, built on the latest CSS and JavaScript standards, typically offers faster load times due to its optimized modular structure and streamlined components, resulting in reduced file sizes. Bootstrap, widely used and feature-rich, may experience slower initial load speeds because of its comprehensive CSS and JavaScript libraries, though tools like tree shaking can mitigate this impact. Performance benchmarks highlight that Materialize often delivers quicker rendering and responsiveness on mobile devices, making it more suitable for projects where fast load times are critical.
Integration with Other Frameworks
Materialize seamlessly integrates with popular JavaScript frameworks like Angular, React, and Vue through dedicated wrapper libraries and components, enhancing the development of responsive and interactive web applications. Bootstrap offers broad compatibility with numerous front-end frameworks and can be easily customized via its extensive Sass variables and modular structure, making it adaptable for complex, multi-framework projects. Both frameworks provide robust support for third-party plugins and tools, enabling developers to incorporate advanced functionalities without compromising design consistency.
Use Cases and Best Suitability
Materialize is best suited for projects aiming to implement Google's Material Design principles, providing a modern, visually consistent UI ideal for mobile-first applications and interactive interfaces. Bootstrap excels in building responsive, grid-based layouts with extensive support for customization and a wide range of UI components, making it the preferred choice for enterprise-level dashboards and traditional websites. Use Materialize when aiming for a sleek, modern aesthetic with ready-to-use animations, while Bootstrap is better for flexibility, broader community support, and faster prototyping across diverse device sizes.
Conclusion: Which Framework Should You Choose?
Materialize offers a modern, Material Design-based aesthetic ideal for visually rich, interactive web projects, while Bootstrap excels in versatility and extensive component support, making it suitable for diverse application needs. Developers seeking a sleek, mobile-first interface with predefined animations often prefer Materialize, whereas those requiring comprehensive customization and a larger community benefit more from Bootstrap. Choosing between the two depends on project goals, design preferences, and the desired balance between innovation and stability.
Materialize Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com