Distributed innovation leverages diverse talents and resources across different locations to accelerate the development of new ideas and solutions. This approach enhances creativity and problem-solving by integrating multiple perspectives and expertise within a collaborative network. Explore the rest of the article to discover how distributed innovation can transform your organization's approach to growth and competitiveness.
Table of Comparison
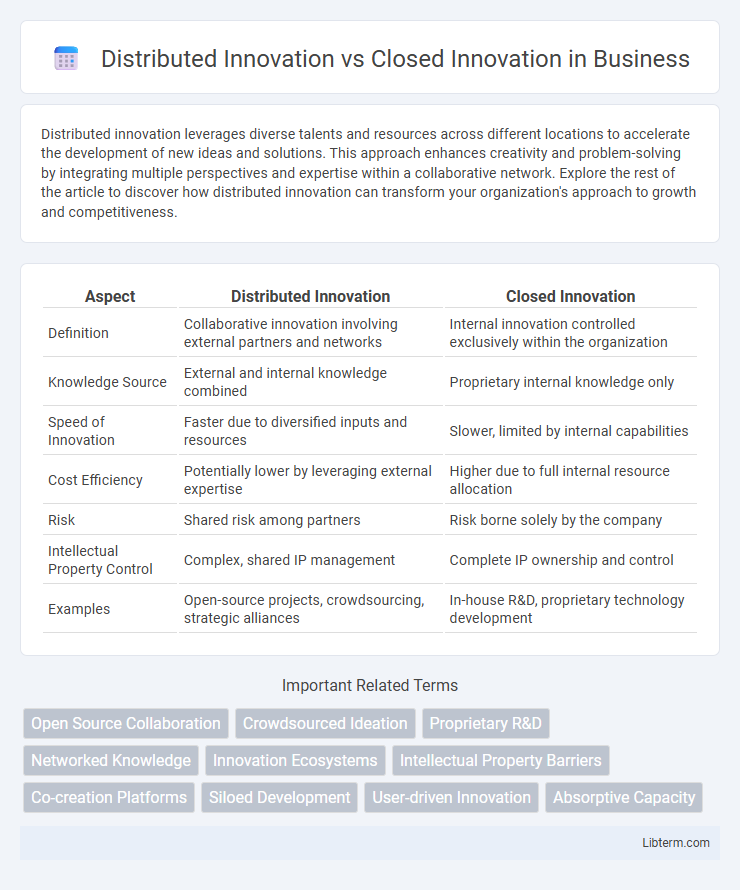
| Aspect | Distributed Innovation | Closed Innovation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Collaborative innovation involving external partners and networks | Internal innovation controlled exclusively within the organization |
| Knowledge Source | External and internal knowledge combined | Proprietary internal knowledge only |
| Speed of Innovation | Faster due to diversified inputs and resources | Slower, limited by internal capabilities |
| Cost Efficiency | Potentially lower by leveraging external expertise | Higher due to full internal resource allocation |
| Risk | Shared risk among partners | Risk borne solely by the company |
| Intellectual Property Control | Complex, shared IP management | Complete IP ownership and control |
| Examples | Open-source projects, crowdsourcing, strategic alliances | In-house R&D, proprietary technology development |
Introduction to Innovation Models
Distributed innovation leverages external and internal sources by enabling collaboration across organizational boundaries, enhancing creativity and accelerating product development. Closed innovation relies on proprietary knowledge and in-house resources to maintain control over intellectual property and internal R&D processes. Understanding these innovation models is crucial for businesses to align strategies with market dynamics and technological advancement.
Defining Distributed Innovation
Distributed innovation refers to a collaborative approach where multiple organizations, teams, or individuals across various locations contribute to the innovation process, leveraging diverse expertise and resources. Unlike closed innovation, which relies on internal R&D within a single company, distributed innovation enhances creativity by integrating external knowledge, partnerships, and open communication channels. This model accelerates problem-solving and product development by tapping into a broader network of ideas and technologies.
Understanding Closed Innovation
Closed Innovation relies on internal resources, expertise, and intellectual property within a company to develop new products or services. This traditional approach emphasizes secrecy and control over the innovation process to maintain competitive advantage. Companies practicing Closed Innovation often invest heavily in R&D departments and restrict external collaborations to protect proprietary knowledge.
Key Differences Between Distributed and Closed Innovation
Distributed innovation harnesses external ideas and collaboration across organizations, enabling faster problem-solving and access to diverse expertise, while closed innovation relies solely on internal research and development, maintaining strict intellectual property control. Distributed innovation fosters open networks that accelerate product development and market adaptation, contrasting with closed innovation's proprietary focus that limits knowledge sharing and external input. The key differences lie in knowledge flow, collaboration scope, and innovation speed, with distributed innovation promoting openness and agility compared to the insularity of closed innovation.
Advantages of Distributed Innovation
Distributed innovation leverages external knowledge sources and collaborative networks, accelerating product development cycles and reducing time-to-market. It enhances creativity through diverse perspectives, leading to more robust and market-relevant solutions compared to the limited scope of closed innovation. Access to global talent and resources lowers R&D costs and mitigates risks by sharing investment among multiple stakeholders.
Benefits of Closed Innovation
Closed Innovation offers businesses enhanced control over intellectual property, ensuring proprietary technologies remain protected from competitors. This approach enables streamlined decision-making processes, reducing risks associated with external collaboration and maintaining confidentiality. Companies benefit from focused resource allocation, promoting deep expertise development within internal teams and accelerating product development cycles.
Challenges and Risks of Each Approach
Distributed innovation faces challenges such as intellectual property risks, coordination complexity, and potential misalignment of goals among diverse contributors. Closed innovation encounters risks including limited idea diversity, slower development cycles, and vulnerability to external competition exploiting untapped market opportunities. Both approaches require strategic management of knowledge flow to balance innovation speed and protective measures effectively.
Real-World Examples: Distributed vs Closed Innovation
Distributed innovation thrives in companies like Procter & Gamble, where open collaboration with external partners accelerates product development by leveraging diverse expertise and global resources. In contrast, Apple exemplifies closed innovation by maintaining strict internal control over research and design processes to protect proprietary technology and ensure high-quality output. These real-world examples highlight how distributed innovation fosters rapid iteration through shared knowledge, while closed innovation emphasizes confidentiality and cohesive brand identity.
When to Choose Distributed or Closed Innovation
Distributed innovation is best chosen when organizations seek diverse expertise, rapid problem-solving, and access to global knowledge networks, enabling accelerated product development and reduced costs. Closed innovation suits firms aiming to protect intellectual property strictly, maintain full control over research processes, and leverage internal resources in highly regulated or competitive industries. Decision factors include the company's risk tolerance, need for collaboration, innovation speed requirements, and strategic priorities related to knowledge sharing and confidentiality.
Future Trends in Innovation Models
Distributed innovation leverages external networks, crowdsourcing, and open collaboration platforms to accelerate product development and reduce R&D costs, contrasting with closed innovation's reliance on internal resources and proprietary knowledge. Future trends highlight hybrid models combining open innovation ecosystems with internal capabilities, driven by advanced AI, blockchain for secure knowledge sharing, and increased cross-industry partnerships. Emphasis on agility, real-time data exchange, and global talent integration will define the evolution toward more dynamic and resilient innovation frameworks.
Distributed Innovation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com