Behavioral analysis involves studying patterns in human actions to understand motivations and predict future behavior. This approach is widely used in psychology, marketing, and security to enhance decision-making and personal growth. Explore the rest of the article to discover how behavioral analysis can impact your life and work.
Table of Comparison
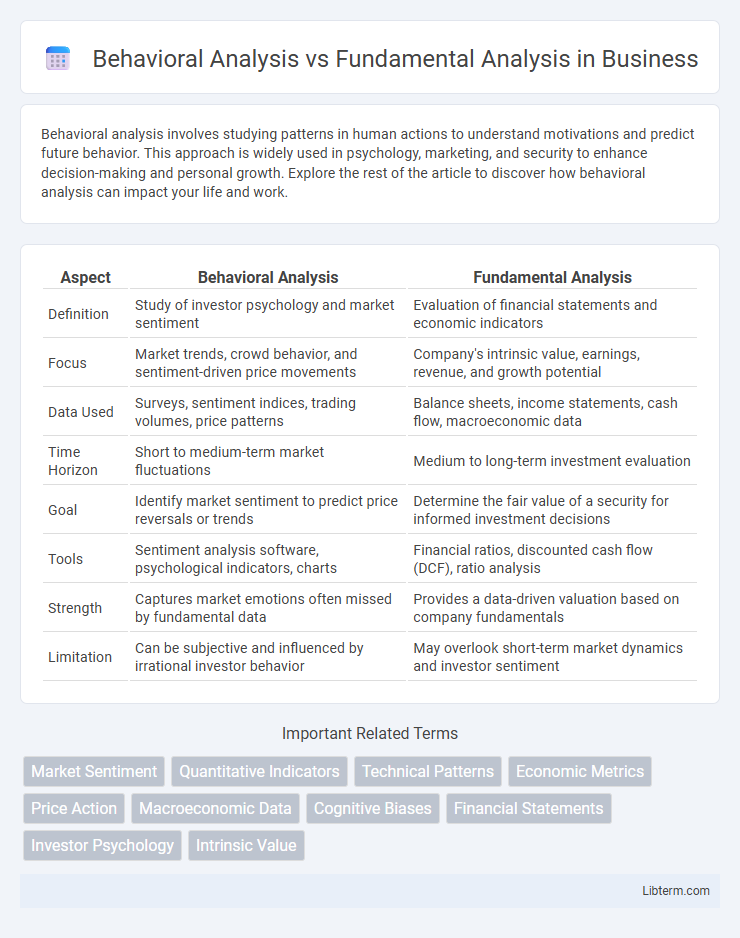
| Aspect | Behavioral Analysis | Fundamental Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study of investor psychology and market sentiment | Evaluation of financial statements and economic indicators |
| Focus | Market trends, crowd behavior, and sentiment-driven price movements | Company's intrinsic value, earnings, revenue, and growth potential |
| Data Used | Surveys, sentiment indices, trading volumes, price patterns | Balance sheets, income statements, cash flow, macroeconomic data |
| Time Horizon | Short to medium-term market fluctuations | Medium to long-term investment evaluation |
| Goal | Identify market sentiment to predict price reversals or trends | Determine the fair value of a security for informed investment decisions |
| Tools | Sentiment analysis software, psychological indicators, charts | Financial ratios, discounted cash flow (DCF), ratio analysis |
| Strength | Captures market emotions often missed by fundamental data | Provides a data-driven valuation based on company fundamentals |
| Limitation | Can be subjective and influenced by irrational investor behavior | May overlook short-term market dynamics and investor sentiment |
Introduction to Behavioral and Fundamental Analysis
Behavioral analysis examines investor psychology and market sentiment to understand price movements and market anomalies, while fundamental analysis evaluates a company's financial health, including earnings, assets, and liabilities, to determine intrinsic value. Key behavioral finance concepts include cognitive biases and emotional influences that affect decision-making, whereas fundamental analysis relies on quantitative data such as financial statements, ratios, and economic indicators. Both methods offer distinct perspectives for investment strategies, with behavioral analysis providing insights into market trends and fundamental analysis focusing on asset valuation.
Defining Behavioral Analysis in Finance
Behavioral Analysis in finance examines psychological influences and cognitive biases affecting investor decisions, deviating from traditional models that assume rational behavior. It incorporates concepts like herd behavior, overconfidence, and loss aversion to explain market anomalies and price movements. This approach contrasts with Fundamental Analysis, which evaluates financial statements, economic indicators, and intrinsic asset values to guide investment choices.
Key Principles of Fundamental Analysis
Fundamental analysis centers on evaluating a company's intrinsic value through financial statements, earnings reports, and economic indicators to determine its long-term growth potential. Key principles include analyzing revenue trends, profit margins, cash flow stability, and management effectiveness to assess overall financial health. This method contrasts with behavioral analysis, which examines market psychology and investor sentiment rather than objective financial data.
Core Differences Between Behavioral and Fundamental Approaches
Behavioral analysis examines investor psychology and market sentiment to explain price movements, focusing on cognitive biases and emotional decision-making. Fundamental analysis evaluates a company's intrinsic value through financial statements, economic indicators, and industry conditions to determine long-term investment potential. Key differences center on behavioral analysis's emphasis on market psychology versus fundamental analysis's reliance on quantitative financial data and economic fundamentals.
Psychological Factors Impacting Investment Decisions
Behavioral analysis examines psychological biases such as overconfidence, herd behavior, and loss aversion that influence investor decisions, often leading to market anomalies. Fundamental analysis focuses on quantifiable data like company earnings, financial ratios, and economic indicators to evaluate asset value, largely ignoring emotional factors. Understanding psychological influences through behavioral analysis helps investors recognize irrational market movements and improve decision-making beyond traditional fundamental metrics.
Valuation Techniques in Fundamental Analysis
Fundamental analysis employs valuation techniques such as discounted cash flow (DCF), comparable company analysis (CCA), and precedent transactions to estimate an asset's intrinsic value. These methods rely on financial metrics like earnings, revenue growth, and cash flow projections to assess long-term investment potential. Behavioral analysis, in contrast, focuses on market sentiment and investor psychology, often overlooking these quantitative valuation frameworks.
Case Studies: Behavioral Biases vs. Financial Data
Behavioral analysis reveals how cognitive biases like overconfidence and herd mentality can lead to market anomalies, as demonstrated in case studies during the Dotcom Bubble and 2008 Financial Crisis. Fundamental analysis relies on financial data such as earnings reports, cash flow, and balance sheets to assess a company's intrinsic value, often contrasting with market behavior influenced by investor psychology. Integrating these approaches helps identify discrepancies between market prices driven by biases and underlying financial performance, enhancing investment decision accuracy.
Strengths and Weaknesses of Each Analysis Method
Behavioral analysis excels in identifying market sentiment and psychological trends, offering insights into investor emotions and potential market reversals but often lacks data consistency and can be subjective. Fundamental analysis provides a rigorous evaluation of a company's financial health, valuation metrics, and macroeconomic factors, enabling long-term investment decisions, yet it may miss short-term market momentum and sentiment shifts. Combining both methods enhances decision-making by balancing quantitative financial data with qualitative market psychology.
Integrating Behavioral and Fundamental Insights
Integrating behavioral and fundamental insights enhances investment strategies by combining market psychology with intrinsic asset values. Behavioral analysis identifies investor sentiment trends, cognitive biases, and herd behavior that influence price fluctuations, while fundamental analysis assesses financial health, earnings potential, and economic indicators. This integrated approach enables more comprehensive risk assessment and improved timing for entry and exit points in equities and other asset classes.
Choosing the Right Analysis for Investment Strategy
Behavioral analysis examines investor psychology and market sentiment to identify irrational behaviors influencing stock prices, while fundamental analysis evaluates a company's financial health and intrinsic value through metrics like earnings, revenue, and cash flow. Choosing the right analysis depends on the investment strategy: behavioral analysis suits traders seeking to capitalize on market anomalies and short-term trends, whereas fundamental analysis aligns with long-term investors focused on sound financial performance and growth potential. Integrating both approaches can enhance decision-making by combining market sentiment insights with solid company valuation.
Behavioral Analysis Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com