Direct Lease offers a streamlined vehicle leasing experience tailored to meet your specific needs, providing flexible terms and competitive rates. This approach eliminates the middleman, ensuring transparent pricing and personalized service. Discover how Direct Lease can simplify your vehicle acquisition by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
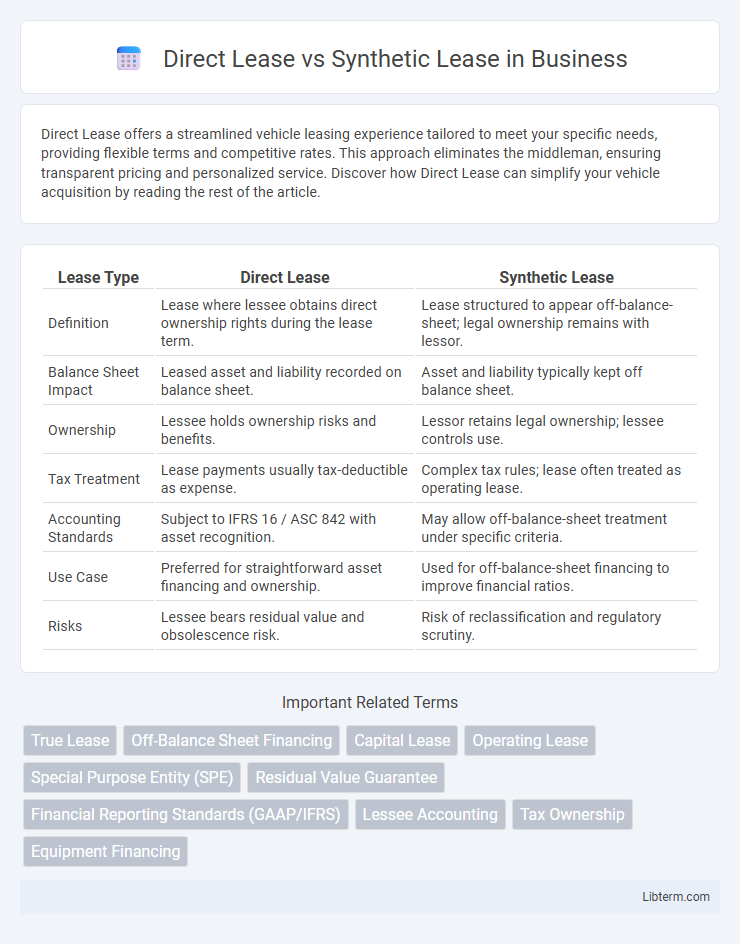
| Lease Type | Direct Lease | Synthetic Lease |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Lease where lessee obtains direct ownership rights during the lease term. | Lease structured to appear off-balance-sheet; legal ownership remains with lessor. |
| Balance Sheet Impact | Leased asset and liability recorded on balance sheet. | Asset and liability typically kept off balance sheet. |
| Ownership | Lessee holds ownership risks and benefits. | Lessor retains legal ownership; lessee controls use. |
| Tax Treatment | Lease payments usually tax-deductible as expense. | Complex tax rules; lease often treated as operating lease. |
| Accounting Standards | Subject to IFRS 16 / ASC 842 with asset recognition. | May allow off-balance-sheet treatment under specific criteria. |
| Use Case | Preferred for straightforward asset financing and ownership. | Used for off-balance-sheet financing to improve financial ratios. |
| Risks | Lessee bears residual value and obsolescence risk. | Risk of reclassification and regulatory scrutiny. |
Understanding Direct Lease: Definition and Key Features
Direct lease refers to a contractual agreement where the lessee obtains the right to use an asset from the lessor without transferring ownership, typically involving off-balance-sheet treatment for the lessee. Key features include fixed lease terms, predetermined payments, and maintenance responsibilities often borne by the lessor, allowing the lessee to conserve capital and improve financial ratios. This lease type is favored in sectors requiring operational flexibility and clear asset utilization without the burdens of ownership risks.
Exploring Synthetic Lease: Structure and Purpose
A synthetic lease is a hybrid financing structure that allows companies to keep leased assets and related liabilities off their balance sheets by combining elements of operating and capital leases. This arrangement typically involves a special purpose entity (SPE) that owns the asset, while the lessee retains operational control and benefits without recording the asset or debt, optimizing financial ratios and tax advantages. Designed primarily for asset-intensive businesses, synthetic leases provide balance sheet flexibility and tax deductions without triggering asset depreciation or full liability recognition.
Key Differences Between Direct Lease and Synthetic Lease
Direct lease involves a straightforward rental agreement where the lessee records the leased asset and liability on their balance sheet, directly impacting financial statements and credit metrics. Synthetic lease, structured as an off-balance-sheet financing arrangement, allows the lessee to control and use the asset without reflecting the asset or liability on the balance sheet, enhancing financial ratios and potentially lowering reported debt. Key differences lie in balance sheet presentation, financial statement impact, and tax treatment, with synthetic leases offering off-balance-sheet benefits while direct leases provide clear ownership and accounting transparency.
Financial Implications of Direct vs. Synthetic Lease
Direct lease impacts financial statements by recording both the asset and liability on the balance sheet, increasing reported debt and affecting key ratios such as debt-to-equity and return on assets. Synthetic lease structures keep the leased asset off the lessee's balance sheet, preserving borrowing capacity and improving financial ratios while still allowing the company to use the asset operationally. Tax treatment differs as well; direct leases often allow depreciation and interest expense deductions, whereas synthetic leases typically provide operating lease treatment for accounting purposes but may qualify for capital lease benefits for tax purposes.
Tax Treatment: Direct Lease vs. Synthetic Lease
Direct lease transactions typically do not appear on the lessee's balance sheet, allowing for off-balance-sheet financing and enabling the lessee to deduct lease payments as operating expenses for tax purposes. Synthetic leases are structured to achieve off-balance-sheet treatment while the lessee maintains ownership for tax purposes, allowing depreciation deductions and interest expense benefits, providing a tax advantage over direct leases. This dual benefit in synthetic leases results in more favorable tax treatment compared to direct leases, influencing companies' preferences when managing asset financing and tax liabilities.
Accounting Impact: Balance Sheet and Income Statement Effects
Direct leases record both the leased asset and corresponding liability directly on the balance sheet, increasing reported assets and liabilities, while lease payments are recognized as rent expense on the income statement. Synthetic leases keep the leased asset and liability off the balance sheet, presenting lease payments as operating expenses, thus improving financial ratios by avoiding debt recognition. The choice between direct and synthetic lease structures fundamentally affects key financial metrics such as debt-to-equity ratio, EBITDA, and net income reported.
Risks and Benefits of Direct Lease Arrangements
Direct lease arrangements offer clear ownership benefits, including straightforward tax deductions through rental expenses and asset control without capital outlay. The primary risks involve potential long-term financial commitments and limited flexibility in modifying lease terms, which may affect cash flow stability. However, direct leases mitigate off-balance-sheet risks seen in synthetic leases by ensuring transparent accounting and regulatory compliance under standard lease classifications.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Synthetic Leases
Synthetic leases offer off-balance-sheet financing, enabling companies to maintain asset control without increasing reported debt, which improves financial ratios and shareholder appeal. They often provide tax benefits by allowing the lessee to claim depreciation deductions while treating the lease as an operating lease for accounting purposes. However, synthetic leases come with increased complexity, stricter regulatory scrutiny, and potential risks if accounting standards change, potentially leading to unexpected liabilities or loss of off-balance-sheet status.
Suitability: Which Lease Type Fits Your Business Needs?
Direct Lease suits businesses seeking straightforward asset ownership with clear tax benefits and simplified accounting, ideal for companies prioritizing long-term control and asset management. Synthetic Lease benefits organizations aiming to keep leased assets off their balance sheets, enhancing financial ratios while still maintaining operational control, making it suitable for firms focused on balance sheet optimization and flexible lease structuring. Choosing between Direct Lease and Synthetic Lease depends on the company's financial strategy, tax considerations, and reporting requirements.
Regulatory and Compliance Considerations
Direct leases are fully reflected on the balance sheet, requiring compliance with accounting standards such as ASC 842 and IFRS 16, ensuring transparency and regulatory adherence. Synthetic leases, structured to keep assets off the balance sheet, involve complex legal and tax considerations to meet criteria established by the IRS and GAAP without violating consolidation rules. Both lease types demand rigorous documentation and ongoing compliance monitoring to mitigate risks of regulatory scrutiny and financial misrepresentation.
Direct Lease Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com