The Lean Startup approach emphasizes iterative development, continuous feedback, and rapid experimentation to create products that better fit customer needs, contrasting with the Waterfall model's linear and sequential process. While Waterfall follows a set of predefined phases with little room for changes, Lean Startup embraces flexibility and pivoting based on validated learning. Discover how your project can benefit from choosing the right methodology by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
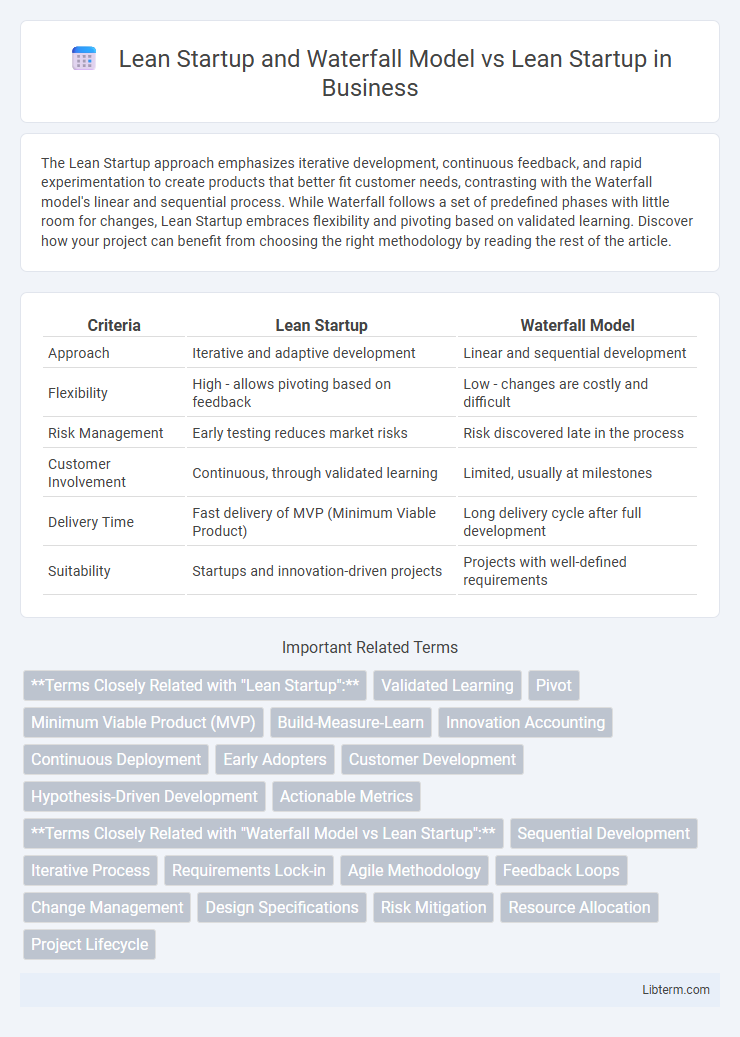
| Criteria | Lean Startup | Waterfall Model |
|---|---|---|
| Approach | Iterative and adaptive development | Linear and sequential development |
| Flexibility | High - allows pivoting based on feedback | Low - changes are costly and difficult |
| Risk Management | Early testing reduces market risks | Risk discovered late in the process |
| Customer Involvement | Continuous, through validated learning | Limited, usually at milestones |
| Delivery Time | Fast delivery of MVP (Minimum Viable Product) | Long delivery cycle after full development |
| Suitability | Startups and innovation-driven projects | Projects with well-defined requirements |
Introduction to Lean Startup
Lean Startup emphasizes rapid prototyping, validated learning, and iterative product releases to minimize waste and adapt quickly to market needs, contrasting with the Waterfall Model's linear, sequential phases that often delay feedback until project completion. This approach prioritizes customer feedback and data-driven decision-making to refine products throughout development. Lean Startup significantly reduces time-to-market and risk by enabling startups to pivot based on real user insights rather than adhering to a fixed plan.
Overview of the Waterfall Model
The Waterfall Model is a linear and sequential approach to software development characterized by distinct phases such as requirements, design, implementation, testing, deployment, and maintenance. It emphasizes thorough documentation and upfront planning, making each phase dependent on the completion of the previous one without returning to earlier stages. Compared to Lean Startup, which encourages iterative development and validated learning, the Waterfall Model is less flexible and more suited to projects with well-defined requirements.
Core Principles of Lean Startup
The Lean Startup methodology centers on rapid experimentation, validated learning, and iterative product releases to minimize waste and quickly respond to customer feedback. In contrast to the Waterfall model's linear and sequential phases, Lean Startup emphasizes building a minimum viable product (MVP), measuring user interaction, and learning from real market data to pivot or persevere. Core principles such as continuous innovation, customer development, and agile adaptation drive Lean Startup's approach to reduce risks and accelerate product-market fit.
Strengths of the Waterfall Model
The Waterfall Model offers a structured, linear approach to software development, ensuring clear project milestones and deliverables at each stage. Its well-defined phases such as requirements, design, implementation, and testing provide predictability and ease of management, especially for projects with fixed requirements. This model's strength lies in its emphasis on thorough documentation and sequential progression, minimizing scope creep and enabling straightforward progress tracking.
Lean Startup vs. Waterfall: Key Differences
Lean Startup emphasizes iterative development, rapid prototyping, and validated learning to quickly adapt to market feedback, while Waterfall Model follows a linear, sequential approach with distinct phases like requirement analysis, design, implementation, testing, and maintenance. Lean Startup promotes flexibility and customer involvement throughout the development process, contrasting with Waterfall's rigid structure and limited feedback loops until final stages. The key difference lies in Lean Startup's focus on experimentation and continuous improvement versus Waterfall's emphasis on upfront planning and fixed deliverables.
When to Use Lean Startup
Lean Startup is ideal for innovative projects with high uncertainty and rapidly changing markets where continuous customer feedback and iterative development drive product success. Unlike the Waterfall Model, which suits well-defined projects with clear requirements and fixed scopes, Lean Startup excels in early-stage ventures seeking to validate hypotheses quickly and pivot based on validated learning. Startups and product teams benefit from Lean Startup when the primary goal is to build a minimum viable product (MVP), test assumptions, and minimize waste before scaling.
When to Use the Waterfall Model
The Waterfall Model is best suited for projects with well-defined requirements, fixed scope, and minimal expected changes, such as in construction or manufacturing industries where sequential phases are critical. It provides a structured approach that facilitates thorough documentation and compliance with regulatory standards, making it ideal when predictability and stability are prioritized. Lean Startup, by contrast, excels in dynamic environments requiring rapid iteration and customer feedback, which are less feasible in highly regulated or rigid project settings where the Waterfall Model prevails.
Case Studies: Lean Startup in Action
Lean Startup methodology accelerates product development through iterative experimentation, validated learning, and customer feedback, contrasting sharply with the rigid, sequential Waterfall model. Case studies such as Dropbox and Airbnb illustrate Lean Startup's effectiveness by rapidly adapting to user needs and market changes, achieving scalability and reducing time-to-market. These successes underscore Lean Startup's advantage over Waterfall in dynamic industries requiring flexibility and continuous innovation.
Waterfall Model Success Stories
The Waterfall Model has demonstrated success in large-scale projects with well-defined requirements, such as NASA's space missions and aerospace engineering, where predictability and thorough documentation are critical. Its linear, sequential approach ensures disciplined progress through each development phase, minimizing risks in highly regulated industries. Compared to Lean Startup's iterative experimentation, Waterfall excels in environments demanding strict compliance, fixed budgets, and extensive upfront planning.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Project
Choosing the right approach for your project depends on factors like project complexity, customer involvement, and risk tolerance. The Lean Startup methodology emphasizes iterative development, rapid prototyping, and validated learning, making it ideal for innovation-driven projects with high uncertainty. In contrast, the Waterfall Model follows a linear, sequential process suitable for projects with well-defined requirements and low ambiguity, ensuring structured progress and predictable outcomes.
Lean Startup and Waterfall Model Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com