Core assets are the fundamental resources essential to a company's operations and competitive advantage, often including intellectual property and key technologies. Intangible assets refer to non-physical assets such as patents, trademarks, brand reputation, and customer relationships that add value to a business. Discover how understanding these assets can enhance your business strategy by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
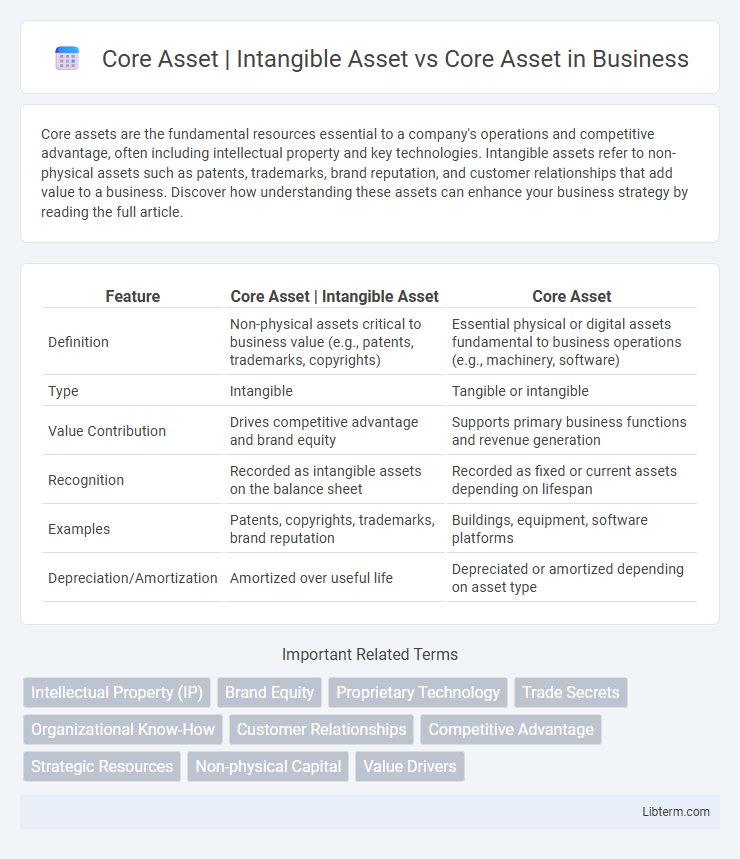
| Feature | Core Asset | Intangible Asset | Core Asset |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Non-physical assets critical to business value (e.g., patents, trademarks, copyrights) | Essential physical or digital assets fundamental to business operations (e.g., machinery, software) |
| Type | Intangible | Tangible or intangible |
| Value Contribution | Drives competitive advantage and brand equity | Supports primary business functions and revenue generation |
| Recognition | Recorded as intangible assets on the balance sheet | Recorded as fixed or current assets depending on lifespan |
| Examples | Patents, copyrights, trademarks, brand reputation | Buildings, equipment, software platforms |
| Depreciation/Amortization | Amortized over useful life | Depreciated or amortized depending on asset type |
Understanding Core Assets: Definition and Importance
Core assets represent essential resources or capabilities that provide a company with competitive advantage and long-term value, often including both tangible and intangible elements. Intangible assets, such as intellectual property, brand reputation, and proprietary technology, are critical components of core assets because they drive innovation and customer loyalty without physical substance. Understanding the distinction between core assets and intangible assets helps businesses strategically leverage their unique strengths for sustained growth and market differentiation.
What Are Intangible Assets? A Brief Overview
Intangible assets represent non-physical resources such as patents, trademarks, copyrights, and goodwill that provide long-term value to a company. Core assets, by contrast, include both tangible and intangible resources essential for a company's primary business operations and competitive advantage. Understanding intangible assets is crucial for assessing intellectual property value and innovation potential within a company's core assets portfolio.
Key Differences Between Core Assets and Intangible Assets
Core assets refer to essential physical or tangible assets such as machinery, buildings, and land that are critical to a company's operations and competitive advantage. Intangible assets include non-physical resources like intellectual property, brand reputation, patents, trademarks, and goodwill, which contribute to long-term value and market position. The key differences lie in tangibility and valuation methods: core assets are tangible and often depreciated over time, whereas intangible assets lack physical substance and are amortized or evaluated based on future economic benefits.
Types of Core Assets in Business
Core assets in business primarily include tangible resources such as machinery, real estate, and financial capital, which are essential for operational functions and revenue generation. Intangible assets, a subset of core assets, encompass intellectual property, brand reputation, patents, trademarks, and goodwill, all contributing to competitive advantage and market value. Effective management of both tangible and intangible core assets is critical for sustaining business growth and achieving strategic objectives.
Examples of Intangible Assets in Modern Enterprises
Core assets in modern enterprises often include intangible assets such as patents, trademarks, brand reputation, proprietary software, and customer relationships. These intangible assets drive competitive advantage by enabling innovation, market differentiation, and customer loyalty without physical form. Unlike tangible core assets like machinery or real estate, intangible core assets form the foundation for value creation and long-term growth in knowledge-driven industries.
The Role of Core Assets in Strategic Growth
Core assets serve as the foundational resources that drive a company's strategic growth by leveraging unique capabilities and competitive advantages. Unlike intangible assets, which include non-physical items such as patents, trademarks, and brand reputation, core assets encompass both tangible and intangible elements that are critical to delivering value to customers and sustaining long-term market leadership. Effective management of core assets enables organizations to innovate, expand market reach, and enhance profitability by aligning core competencies with evolving business opportunities.
Valuation: Measuring Core Assets vs Intangible Assets
Valuation of core assets involves quantifying tangible resources such as machinery, real estate, and technology that contribute directly to a company's operational capacity. Intangible asset valuation focuses on non-physical elements like patents, trademarks, and brand reputation, often using methods like discounted cash flow or relief-from-royalty to estimate future economic benefits. Measuring core assets typically relies on market value or replacement cost, while intangible asset valuation requires advanced financial modeling and market comparables to capture their potential impact on competitive advantage and revenue generation.
Protecting Core Assets and Intangible Assets
Protecting core assets involves safeguarding critical physical and intellectual property that drive a company's competitive advantage and operational efficiency. Intangible assets, such as patents, trademarks, and proprietary technology, require robust legal protection and strategic management to prevent unauthorized use and maintain market value. Implementing comprehensive security measures and continuous monitoring ensures both tangible and intangible core assets remain secure and contribute to sustained business growth.
Leveraging Both Asset Types for Competitive Advantage
Intangible assets such as brand reputation, intellectual property, and patents complement tangible core assets like factories, machinery, and technology infrastructure to drive sustained competitive advantage. Leveraging the synergy between intangible assets' innovation and core assets' operational efficiency enhances market differentiation and value creation. Effective integration of both asset types enables firms to optimize resource utilization, accelerate product development, and strengthen customer loyalty in dynamic markets.
Core Asset vs Intangible Asset: Which Drives Long-Term Value?
Core assets, which include both tangible and intangible components, serve as the fundamental resources that drive a company's strategic advantage and long-term value creation. Intangible assets, such as intellectual property, brand reputation, and proprietary technology, often provide higher scalability and competitive differentiation compared to traditional core assets like physical infrastructure or machinery. The interplay between core tangible assets and intangible assets determines sustainable growth, with intangible assets increasingly recognized as key drivers of market valuation in knowledge-driven industries.
Core Asset | Intangible Asset Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com