A joint venture combines the strengths and resources of two or more businesses to achieve a common goal, often leading to increased market reach and shared risks. It allows companies to pool expertise, share costs, and drive innovation in competitive industries. Discover how forming a joint venture can benefit your business by exploring the detailed insights in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
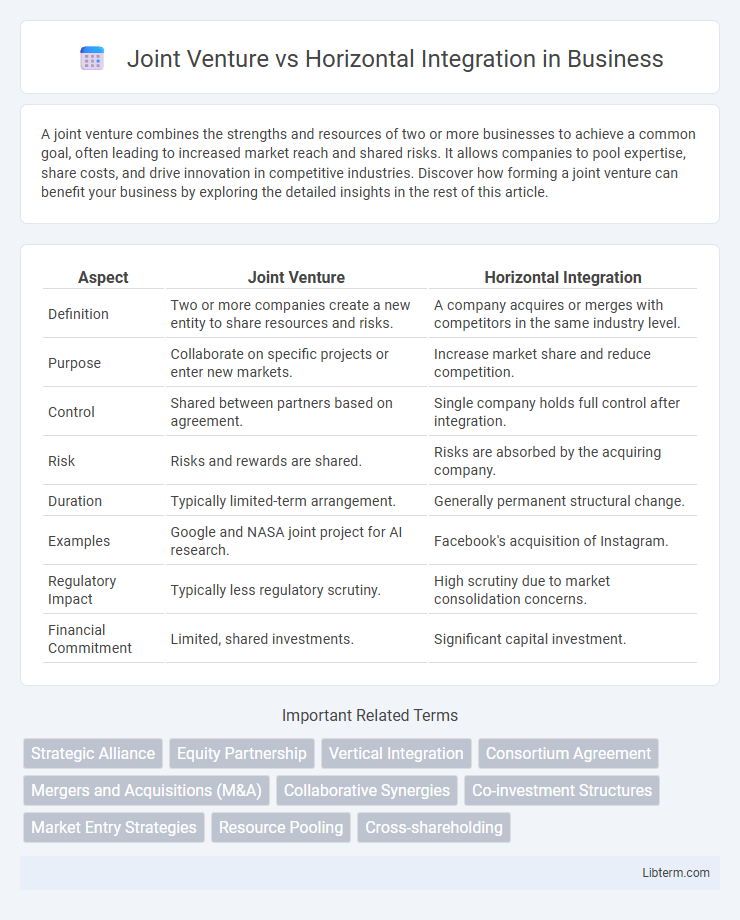
| Aspect | Joint Venture | Horizontal Integration |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Two or more companies create a new entity to share resources and risks. | A company acquires or merges with competitors in the same industry level. |
| Purpose | Collaborate on specific projects or enter new markets. | Increase market share and reduce competition. |
| Control | Shared between partners based on agreement. | Single company holds full control after integration. |
| Risk | Risks and rewards are shared. | Risks are absorbed by the acquiring company. |
| Duration | Typically limited-term arrangement. | Generally permanent structural change. |
| Examples | Google and NASA joint project for AI research. | Facebook's acquisition of Instagram. |
| Regulatory Impact | Typically less regulatory scrutiny. | High scrutiny due to market consolidation concerns. |
| Financial Commitment | Limited, shared investments. | Significant capital investment. |
Introduction to Joint Ventures and Horizontal Integration
Joint ventures involve two or more companies pooling resources to achieve a specific business objective while remaining separate entities, fostering collaboration and risk-sharing. Horizontal integration occurs when a company acquires or merges with a competitor at the same stage of the supply chain, enhancing market share and reducing competition. Both strategies influence organizational growth, with joint ventures emphasizing partnership and integration focusing on consolidation within the industry.
Key Definitions: Joint Venture vs. Horizontal Integration
A joint venture is a strategic partnership where two or more companies collaborate to achieve specific goals while remaining independent entities, sharing resources, risks, and profits. Horizontal integration involves the acquisition or merger of companies operating at the same level in an industry to increase market share, reduce competition, and achieve economies of scale. Understanding these key definitions highlights differences in ownership, control, and strategic objectives between joint ventures and horizontal integration.
Strategic Objectives Behind Each Approach
Joint ventures aim to combine complementary strengths and share resources between companies, targeting market expansion, innovation, and risk mitigation. Horizontal integration focuses on acquiring or merging with competitors within the same industry to increase market share, achieve economies of scale, and reduce competition. Strategic objectives of joint ventures emphasize collaboration and synergy creation, while horizontal integration prioritizes consolidation and dominance in the market.
Structural Differences and Legal Implications
A joint venture involves two or more independent companies creating a new, separate legal entity to pursue specific business objectives, maintaining their distinct identities and sharing profits, losses, and control based on agreed terms. Horizontal integration occurs when a company acquires or merges with competitors operating at the same industry level, resulting in a single, unified entity that consolidates market share and eliminates competition. Legal implications for joint ventures include contract law and regulatory approvals focused on collaboration terms, while horizontal integration often triggers antitrust scrutiny to prevent monopolistic practices and ensure competitive markets.
Financial Considerations and Investment Requirements
Joint ventures typically require shared financial investments, distributing the capital burden and risks between partners, which can lead to more flexible funding structures and reduced individual financial exposure. Horizontal integration demands substantial upfront capital to acquire or merge with competitors, often involving significant costs related to due diligence, regulatory approval, and potential restructuring. Financially, joint ventures offer more limited liquidity risk and can facilitate resource pooling, whereas horizontal integration may yield greater economies of scale but necessitates large, concentrated investments with longer payback periods.
Risks and Challenges: A Comparative Analysis
Joint ventures face risks such as cultural clashes, misaligned objectives, and complex coordination between partners, which can lead to conflicts and project delays. Horizontal integration presents challenges including regulatory scrutiny for monopolistic behavior, integration difficulties across merged entities, and potential layoffs causing employee unrest. Both strategies require careful management of operational, financial, and legal risks to ensure successful outcomes.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Joint Ventures
Joint ventures offer advantages such as shared risks, combined resources, and access to new markets, enhancing competitive strength and innovation. However, disadvantages include potential conflicts due to differing management styles, unequal control, and complexities arising from cultural or operational differences. Unlike horizontal integration, which consolidates companies within the same industry to increase market share, joint ventures focus on cooperative partnerships without full mergers or acquisitions.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Horizontal Integration
Horizontal integration allows companies to increase market share by acquiring or merging with competitors, resulting in economies of scale and reduced competition. However, it can lead to regulatory scrutiny, potential monopolistic behavior, and challenges in managing a larger, more complex organization. Risks include cultural clashes, decreased innovation due to reduced competition, and the possibility of antitrust lawsuits.
Real-World Examples in Various Industries
Joint ventures in the automotive industry, such as the partnership between Toyota and Panasonic, focus on combining expertise to develop advanced battery technologies, enhancing innovation without full mergers. Horizontal integration is exemplified by Facebook's acquisition of Instagram, where companies within the same sector merge to consolidate market share and reduce competition. Real-world examples demonstrate joint ventures prioritize collaboration and resource sharing, while horizontal integration emphasizes market expansion and control within the industry.
Choosing the Right Strategy for Business Growth
Selecting between joint venture and horizontal integration depends on a company's growth objectives and resource capabilities. Joint ventures enable shared risks and access to new markets or technologies through strategic partnerships, ideal for entering unfamiliar industries. Horizontal integration focuses on expanding market share and eliminating competitors within the same industry, driving economies of scale and operational efficiencies.
Joint Venture Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com