Standardization ensures consistency and quality across products and services, streamlining processes and enhancing interoperability. It reduces costs and complexity while fostering innovation by providing a clear framework for development. Explore the rest of the article to understand how standardization can benefit your business and industry.
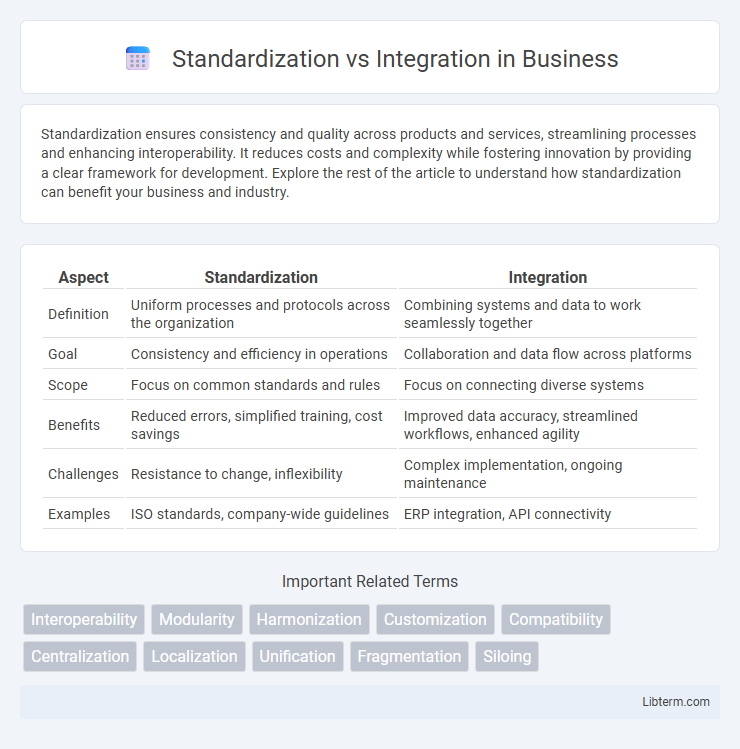
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Standardization | Integration |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Uniform processes and protocols across the organization | Combining systems and data to work seamlessly together |
| Goal | Consistency and efficiency in operations | Collaboration and data flow across platforms |
| Scope | Focus on common standards and rules | Focus on connecting diverse systems |
| Benefits | Reduced errors, simplified training, cost savings | Improved data accuracy, streamlined workflows, enhanced agility |
| Challenges | Resistance to change, inflexibility | Complex implementation, ongoing maintenance |
| Examples | ISO standards, company-wide guidelines | ERP integration, API connectivity |
Introduction: Defining Standardization and Integration
Standardization refers to the process of implementing and developing technical standards to ensure consistency, compatibility, and quality across products, services, or systems. Integration involves combining different systems, processes, or components to function together seamlessly, enhancing efficiency and interoperability. Both concepts are essential for optimizing operations in complex environments, with standardization providing uniform guidelines and integration enabling cohesive functionality.
Historical Context of Standardization and Integration
Standardization emerged during the Industrial Revolution to ensure uniformity in manufacturing processes and product quality, facilitating mass production and global trade. Integration gained prominence in the late 20th century with advances in information technology, enabling seamless connectivity between disparate systems and processes. Together, these concepts have shaped modern business operations by balancing consistent practices with interconnected workflows.
Core Principles of Standardization
Standardization revolves around establishing uniform guidelines, protocols, and specifications to ensure consistency and compatibility across systems or processes. Key principles include interoperability, repeatability, and quality assurance, enabling products and services to meet predefined benchmarks. This approach reduces variability, fosters efficiency, and facilitates seamless collaboration within and across industries.
Key Benefits of Standardization
Standardization enhances operational efficiency by creating uniform processes and reducing variability, leading to consistent quality and faster decision-making. It facilitates easier training and onboarding by providing clear guidelines and standardized tools across teams. Cost reduction is achieved through economies of scale and simplified supply chains, improving overall profitability.
Core Principles of Integration
Integration revolves around the core principles of interoperability, data consistency, and seamless communication between diverse systems, enabling efficient information flow and real-time updates. Unlike standardization, which enforces uniform protocols or formats, integration emphasizes the flexible connection of heterogeneous platforms through APIs, middleware, and data transformation tools. Key elements include maintaining system autonomy while ensuring unified processes, synchronization of data sources, and minimizing redundancy to enhance operational efficiency.
Key Benefits of Integration
Integration streamlines business processes by enabling seamless data flow across multiple systems, which enhances operational efficiency and reduces errors. It fosters real-time information sharing, improving decision-making and collaboration among departments and external partners. Integration supports scalability by accommodating new applications and technologies without disrupting existing workflows.
Standardization vs Integration: Major Differences
Standardization focuses on creating uniform processes, protocols, or products across an organization to ensure consistency, efficiency, and quality control. Integration involves combining different systems, applications, or data sources to work seamlessly together, enabling improved communication and data flow. The key difference lies in standardization enforcing uniformity, while integration emphasizes interoperability and connectivity between diverse components.
Challenges in Balancing Standardization and Integration
Balancing standardization and integration presents significant challenges, including managing conflicting organizational priorities and ensuring system compatibility across diverse platforms. Standardization can limit flexibility, while integration requires customized solutions to connect disparate systems smoothly. Organizations must navigate data consistency issues, varying technical standards, and the complexity of aligning processes without disrupting operational efficiency.
Real-World Examples and Case Studies
Standardization enables companies like McDonald's to maintain consistent quality and customer experience across global locations by using uniform processes and menus. Integration is exemplified by Tesla's supply chain, where vertical integration allows control over battery production and vehicle assembly, improving efficiency and innovation. Case studies of Amazon highlight successful integration of logistics and technology platforms, while global manufacturers like Toyota rely on standardization to streamline production across multiple countries.
Choosing the Right Approach: Factors to Consider
Choosing between standardization and integration depends on factors such as organizational goals, system compatibility, and scalability requirements. Assessing the impact on operational efficiency, maintenance costs, and user experience is crucial for making an informed decision. Evaluating industry regulations and technological infrastructure further guides the selection of the most suitable approach.
Standardization Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com