Effective risk management identifies, assesses, and prioritizes potential threats to minimize their impact on your organization's objectives. Implementing structured strategies helps in mitigating risks before they escalate into significant issues. Explore the rest of the article to learn practical steps for strengthening your risk management approach.
Table of Comparison
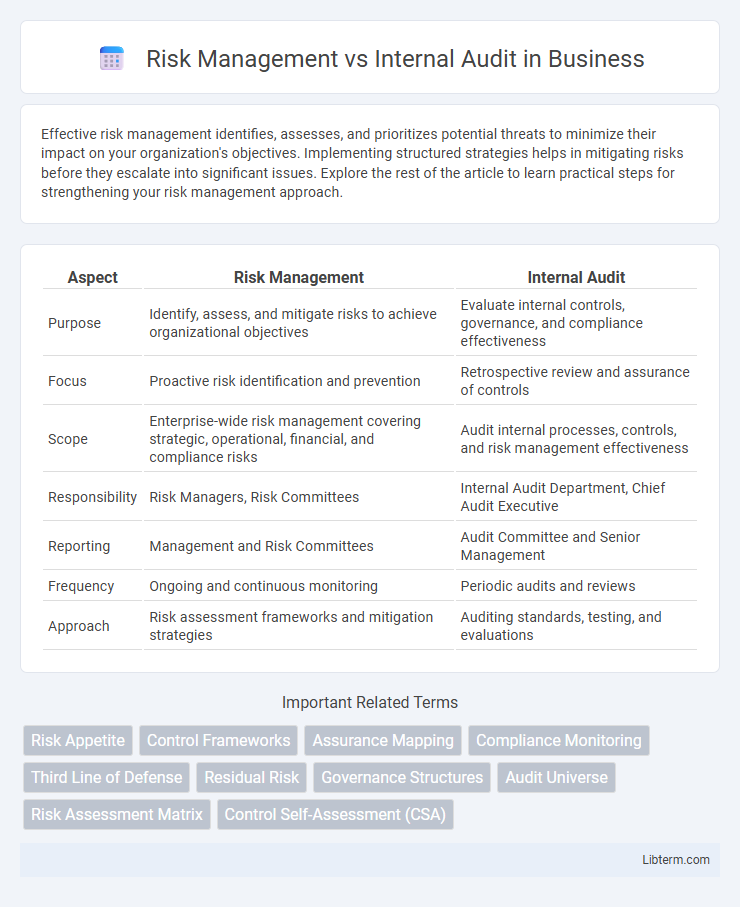
| Aspect | Risk Management | Internal Audit |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Identify, assess, and mitigate risks to achieve organizational objectives | Evaluate internal controls, governance, and compliance effectiveness |
| Focus | Proactive risk identification and prevention | Retrospective review and assurance of controls |
| Scope | Enterprise-wide risk management covering strategic, operational, financial, and compliance risks | Audit internal processes, controls, and risk management effectiveness |
| Responsibility | Risk Managers, Risk Committees | Internal Audit Department, Chief Audit Executive |
| Reporting | Management and Risk Committees | Audit Committee and Senior Management |
| Frequency | Ongoing and continuous monitoring | Periodic audits and reviews |
| Approach | Risk assessment frameworks and mitigation strategies | Auditing standards, testing, and evaluations |
Introduction to Risk Management and Internal Audit
Risk management involves identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential threats to an organization's assets and objectives, ensuring business continuity and minimizing financial losses. Internal audit provides an independent evaluation of risk management processes, controls, and compliance, verifying the effectiveness of risk mitigation strategies. Together, risk management and internal audit create a framework for proactive risk identification and assurance, enhancing overall governance and operational resilience.
Defining Risk Management: Scope and Objectives
Risk management encompasses the identification, assessment, and prioritization of risks to minimize, monitor, and control the probability or impact of adverse events across an organization. Its scope includes strategic, operational, financial, and compliance risks, aiming to protect assets, optimize performance, and ensure regulatory adherence. The primary objective is to establish a proactive framework that supports informed decision-making and promotes organizational resilience.
Understanding Internal Audit: Purpose and Functions
Internal audit serves as an independent, objective assurance and consulting activity designed to add value and improve an organization's operations by evaluating risk management, control, and governance processes. Its primary functions include assessing the effectiveness of internal controls, ensuring compliance with laws and policies, and identifying opportunities for operational improvements. By providing management and the board with insights and recommendations, internal audit supports informed decision-making and enhances organizational accountability.
Key Differences Between Risk Management and Internal Audit
Risk Management primarily focuses on identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential risks that could impact an organization's objectives, while Internal Audit evaluates the effectiveness of governance, risk management, and internal controls. Risk Management is proactive, aiming to prevent risks, whereas Internal Audit is more reactive, providing independent assurance through systematic reviews. The key difference lies in Risk Management being an operational function embedded within management, whereas Internal Audit operates independently, reporting directly to the audit committee or board.
Roles and Responsibilities: A Comparative Overview
Risk management focuses on identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks that could impact organizational objectives, while internal audit independently evaluates the effectiveness of risk management processes and internal controls. Risk managers are responsible for developing risk mitigation strategies and facilitating risk awareness, whereas internal auditors provide assurance through objective assessments and compliance audits. Both functions collaborate to enhance enterprise risk governance but maintain distinct roles involving proactive risk handling versus retrospective evaluation.
Interrelationship Between Risk Management and Internal Audit
Risk management and internal audit share a critical interrelationship in organizational governance, with risk management identifying and assessing potential threats while internal audit independently evaluates the effectiveness of risk controls. Internal audit provides assurance on the adequacy of risk management processes through continuous monitoring and testing, supporting proactive risk mitigation. Effective collaboration between these functions enhances risk transparency and ensures compliance with regulatory requirements, fostering stronger corporate resilience.
Impact on Organizational Governance
Risk management strengthens organizational governance by proactively identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential threats to achieve strategic objectives, thereby safeguarding assets and ensuring regulatory compliance. Internal audit provides an independent evaluation of governance processes, controls, and risk management effectiveness, offering insights and recommendations to enhance accountability and transparency. Together, they create a robust governance framework that supports informed decision-making and continuous improvement across the organization.
Strategic Importance in Enterprise Management
Risk management identifies, assesses, and mitigates potential threats that could impact an organization's strategic objectives, ensuring proactive decision-making and resource allocation. Internal audit provides an independent evaluation of risk management effectiveness, internal controls, and governance processes, reinforcing accountability and compliance across enterprise operations. Both functions are strategically crucial, with risk management driving risk-aware culture and internal audit validating risk frameworks to safeguard organizational value.
Best Practices for Collaboration and Independence
Effective risk management relies on collaboration with internal audit to identify, assess, and mitigate organizational risks while maintaining clear boundaries to preserve audit independence. Best practices include establishing defined roles and responsibilities, implementing regular communication protocols, and ensuring internal audit remains objective by avoiding involvement in risk management decision-making. This balance enhances overall governance, strengthens control environments, and supports informed strategic decision-making.
Future Trends in Risk Management and Internal Audit
Future trends in risk management and internal audit emphasize the integration of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and data analytics to enhance predictive capabilities and real-time monitoring. Embracing automation and continuous auditing allows organizations to identify emerging risks and improve compliance efficiency. The evolving regulatory landscape drives a shift towards a more proactive, risk-aware culture supported by strategic collaboration between risk management and internal audit functions.
Risk Management Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com