Compliance risk refers to the potential for legal or regulatory sanctions, financial loss, or reputational damage resulting from a failure to adhere to laws, regulations, or internal policies. Managing this risk effectively involves implementing robust policies, continuous monitoring, and employee training to ensure adherence and mitigate potential violations. Explore the rest of this article to understand how you can safeguard your organization from compliance pitfalls.
Table of Comparison
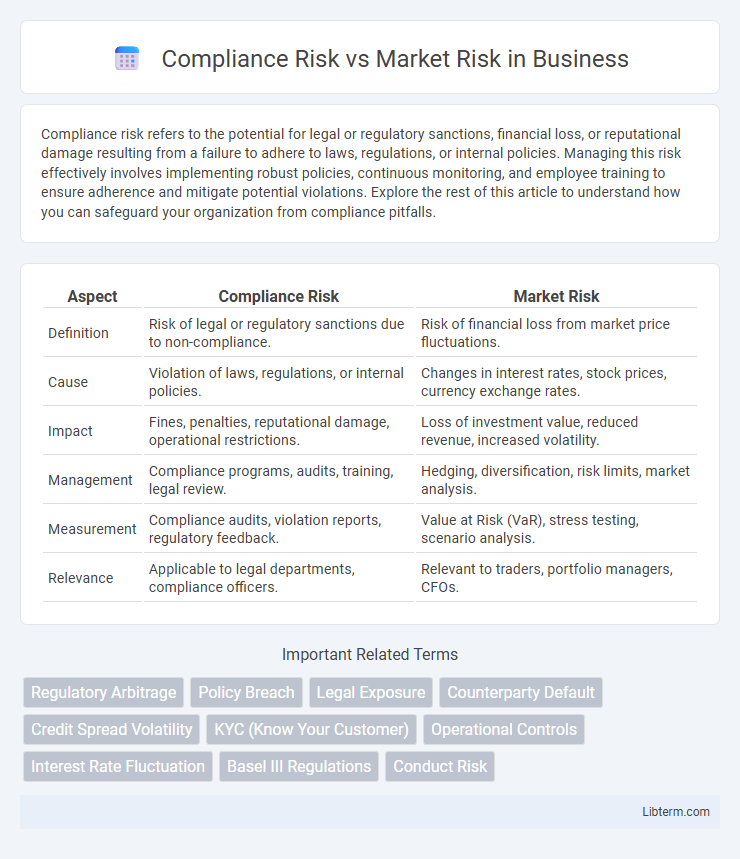
| Aspect | Compliance Risk | Market Risk |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Risk of legal or regulatory sanctions due to non-compliance. | Risk of financial loss from market price fluctuations. |
| Cause | Violation of laws, regulations, or internal policies. | Changes in interest rates, stock prices, currency exchange rates. |
| Impact | Fines, penalties, reputational damage, operational restrictions. | Loss of investment value, reduced revenue, increased volatility. |
| Management | Compliance programs, audits, training, legal review. | Hedging, diversification, risk limits, market analysis. |
| Measurement | Compliance audits, violation reports, regulatory feedback. | Value at Risk (VaR), stress testing, scenario analysis. |
| Relevance | Applicable to legal departments, compliance officers. | Relevant to traders, portfolio managers, CFOs. |
Understanding Compliance Risk
Compliance risk involves the possibility of legal or regulatory sanctions, financial loss, or reputational damage due to failure to comply with laws, regulations, or internal policies. It requires monitoring changes in regulatory environments and implementing effective controls to prevent violations that could lead to penalties or operational restrictions. Understanding compliance risk is crucial for organizations to safeguard their operations and maintain stakeholder trust in a dynamic legal landscape.
Defining Market Risk
Market risk refers to the potential financial loss due to fluctuations in market prices such as equities, interest rates, foreign exchange, and commodities. It is driven by factors including economic conditions, geopolitical events, and investor sentiment that affect asset valuations. Unlike compliance risk, which arises from regulatory breaches, market risk quantifies exposure to unpredictable changes in market variables impacting portfolio performance.
Key Differences Between Compliance and Market Risk
Compliance risk involves the potential for legal penalties or financial forfeiture due to failure to adhere to laws, regulations, or internal policies, whereas market risk relates to losses caused by fluctuations in market prices such as interest rates, currency exchange rates, and stock prices. Compliance risk is primarily managed through regulatory frameworks and internal controls, while market risk requires quantitative analysis, risk modeling, and hedging strategies. Understanding these key differences helps organizations allocate resources effectively between regulatory adherence and financial risk management.
Common Sources of Compliance Risk
Common sources of compliance risk include regulatory changes, inadequate internal controls, and failures in employee training or ethical standards. These risks arise from the organization's inability to comply with laws, regulations, and internal policies, potentially leading to fines, legal penalties, and reputational damage. Market risk, by contrast, stems from factors impacting asset prices and market volatility, while compliance risk is centered on adherence to legal and regulatory requirements.
Major Drivers of Market Risk
Market risk is primarily driven by factors such as interest rate fluctuations, currency exchange rate volatility, and equity price changes that impact portfolio valuations and trading positions. Compliance risk arises from failures to adhere to laws, regulations, and internal policies, leading to legal penalties and reputational damage. Understanding the major drivers of market risk enables firms to develop risk mitigation strategies like hedging and diversification to protect assets against adverse market movements.
Impact of Compliance Risk on Organizations
Compliance risk can lead to significant financial penalties, legal sanctions, and reputational damage for organizations, directly affecting their operational stability and market position. Failure to adhere to regulatory requirements increases the likelihood of costly audits, litigation, and loss of stakeholder trust. Unlike market risk, which is driven by external economic factors, compliance risk stems from internal governance and regulatory adherence gaps, making proactive risk management essential for long-term business sustainability.
Consequences of Market Risk in Financial Markets
Market risk in financial markets results in significant financial losses due to fluctuations in asset prices, interest rates, and currency exchange rates. These adverse movements can lead to decreased portfolio values, liquidity shortages, and reduced investor confidence, triggering market volatility and systemic risk. Institutions exposed to market risk often face regulatory scrutiny, credit rating downgrades, and heightened operational challenges that exacerbate financial instability.
Risk Mitigation Strategies: Compliance vs Market Risk
Compliance risk mitigation strategies emphasize robust internal controls, regular audits, and comprehensive employee training to ensure adherence to legal and regulatory requirements. Market risk mitigation relies heavily on diversification, hedging techniques using derivatives, and real-time market monitoring to manage exposure to price fluctuations. Both approaches require tailored risk assessment frameworks to effectively identify, measure, and address the specific nature of compliance and market risks.
Regulatory Requirements and Market Fluctuations
Compliance Risk involves potential losses due to violations of regulatory requirements, including fines, sanctions, and legal penalties imposed by financial authorities such as the SEC or FCA. Market Risk arises from market fluctuations affecting asset values, interest rates, currency exchange rates, and equity prices, directly impacting portfolio performance and financial stability. Effective risk management requires adherence to regulatory frameworks to mitigate Compliance Risk while employing hedging strategies and diversification to address Market Risk.
Integrating Risk Management Frameworks
Integrating risk management frameworks enhances organizational resilience by aligning compliance risk controls with market risk strategies, ensuring comprehensive risk identification and mitigation. A unified framework leverages regulatory requirements and financial market dynamics to optimize risk assessment accuracy and response efficiency. This approach reduces silos, improves data sharing, and supports proactive decision-making across compliance and market risk domains.
Compliance Risk Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com