Organizational resilience enables companies to adapt swiftly to disruptions and maintain continuous operations during crises. Strengthening your business through strategic planning, risk management, and agile leadership ensures long-term sustainability and competitive advantage. Explore the rest of the article to discover practical steps for building resilience in your organization.
Table of Comparison
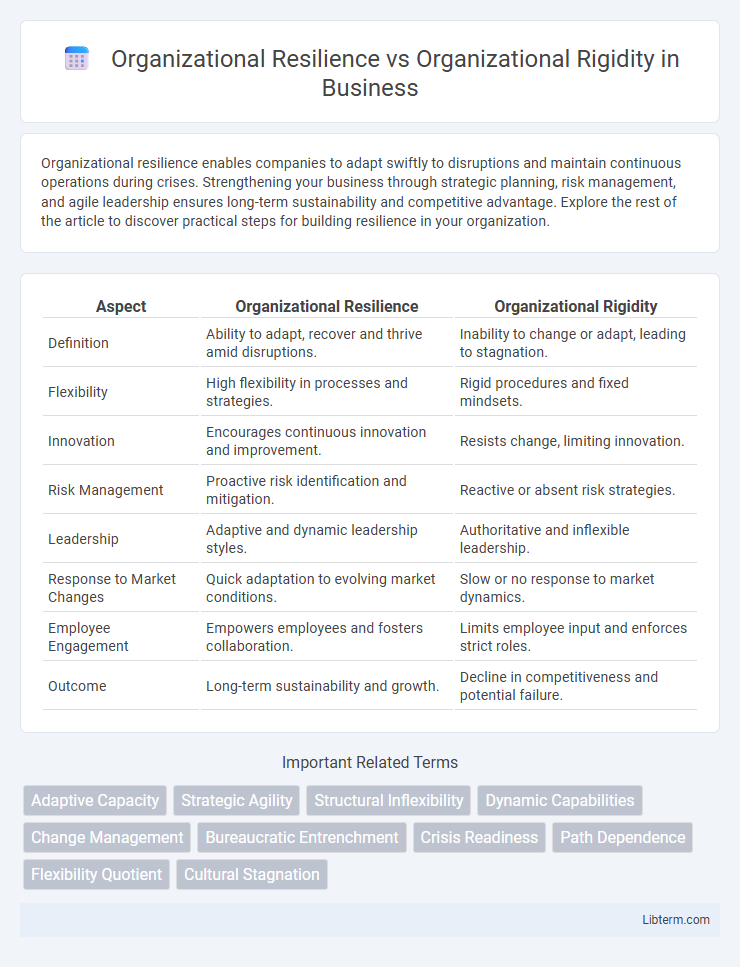
| Aspect | Organizational Resilience | Organizational Rigidity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ability to adapt, recover and thrive amid disruptions. | Inability to change or adapt, leading to stagnation. |
| Flexibility | High flexibility in processes and strategies. | Rigid procedures and fixed mindsets. |
| Innovation | Encourages continuous innovation and improvement. | Resists change, limiting innovation. |
| Risk Management | Proactive risk identification and mitigation. | Reactive or absent risk strategies. |
| Leadership | Adaptive and dynamic leadership styles. | Authoritative and inflexible leadership. |
| Response to Market Changes | Quick adaptation to evolving market conditions. | Slow or no response to market dynamics. |
| Employee Engagement | Empowers employees and fosters collaboration. | Limits employee input and enforces strict roles. |
| Outcome | Long-term sustainability and growth. | Decline in competitiveness and potential failure. |
Understanding Organizational Resilience
Organizational resilience refers to a company's ability to adapt, recover, and thrive amid disruptions, market changes, and uncertainties, emphasizing flexibility and proactive risk management. It involves strategic foresight, robust communication channels, and continuous learning cultures that enable rapid response to crises and sustain long-term performance. In contrast, organizational rigidity often results from bureaucratic structures and resistance to change, limiting innovation and increasing vulnerability during environmental shocks.
Defining Organizational Rigidity
Organizational rigidity refers to a company's inability to adapt to market changes due to entrenched processes, hierarchical structures, and resistance to innovation. This inflexibility hampers responsiveness to emerging trends, which undermines long-term competitiveness and growth. High organizational rigidity is often characterized by rigid policies, slow decision-making, and reduced employee empowerment.
Core Differences Between Resilience and Rigidity
Organizational resilience centers on adaptability, enabling businesses to absorb shocks and swiftly recover from disruptions, while organizational rigidity is marked by inflexibility and resistance to change, often leading to stagnation. Resilience fosters continuous learning and innovation through dynamic processes, contrasting with rigidity's reliance on established routines and hierarchical decision-making. Core differences lie in resilience's emphasis on agility and proactive risk management, whereas rigidity emphasizes control and stability at the expense of responsiveness.
Impact of Resilience on Business Performance
Organizational resilience significantly enhances business performance by enabling companies to adapt swiftly to market disruptions and maintain operational continuity, leading to sustained profitability and competitive advantage. Unlike organizational rigidity, which limits flexibility and responsiveness, resilience promotes innovation, employee engagement, and customer satisfaction, directly impacting revenue growth and risk mitigation. Studies show that resilient organizations experience faster recovery times and improved stakeholder trust, solidifying their long-term success in volatile environments.
Risks and Consequences of Organizational Rigidity
Organizational rigidity leads to increased risks such as inability to adapt to market changes, stagnation in innovation, and diminished competitive advantage. This inflexibility often results in operational inefficiencies, employee dissatisfaction, and vulnerability to external disruptions like economic downturns or technological advancements. Consequently, organizations that fail to evolve may face declining performance, loss of market share, and potential business failure.
Drivers of Organizational Adaptability
Organizational adaptability is driven by dynamic leadership, a culture of continuous learning, and agile decision-making processes that enable quick responses to market changes. In contrast, organizational rigidity stems from hierarchical structures, resistance to change, and entrenched routines that inhibit flexibility. Emphasizing innovation, cross-functional collaboration, and real-time feedback systems enhances resilience by fostering an environment that supports rapid adaptation to external disruptions.
Warning Signs of Emerging Rigidity
Emerging organizational rigidity often manifests through decreased adaptability, resistance to change, and entrenched hierarchical structures that limit innovation and responsiveness. Warning signs include prolonged decision-making processes, reliance on outdated procedures, and a decline in employee engagement or creative problem-solving. Monitoring these indicators is crucial for fostering organizational resilience, enabling timely interventions that promote flexibility and sustained competitive advantage.
Strategies for Building Resilient Organizations
Building resilient organizations involves adopting adaptive strategies such as continuous learning, flexible decision-making, and proactive risk management to respond effectively to uncertainties. Emphasizing decentralized leadership and fostering a culture of innovation enable organizations to pivot during disruptions without succumbing to rigidity. Embedding robust communication channels and cross-functional collaboration ensures agility and sustains long-term organizational resilience amidst dynamic market conditions.
Case Studies: Resilient vs Rigid Organizations
Case studies reveal that resilient organizations, such as Toyota and Amazon, adapt quickly to market changes by fostering innovation and flexible decision-making processes. In contrast, rigid organizations like Kodak suffered significant losses due to slow adaptation and resistance to technological disruption. These examples highlight the critical impact of organizational culture and leadership on maintaining competitive advantage through resilience versus rigidity.
Future Trends in Organizational Agility
Organizational resilience emphasizes adaptability and the capacity to recover quickly from disruptions, while organizational rigidity often leads to resistance against change and stagnation. Future trends in organizational agility highlight the integration of AI-driven decision-making, real-time data analytics, and flexible workforce models to anticipate market shifts and innovate continuously. Embracing these advancements fosters a dynamic culture that balances stability with the ability to pivot rapidly in response to evolving business environments.
Organizational Resilience Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com