An invoice is a vital document that details the sale transaction between a buyer and seller, specifying the products or services provided, quantities, prices, and payment terms. It serves as both a legal record and a request for payment, ensuring clear communication and financial accountability. Explore the rest of the article to understand how invoicing can streamline Your business processes effectively.
Table of Comparison
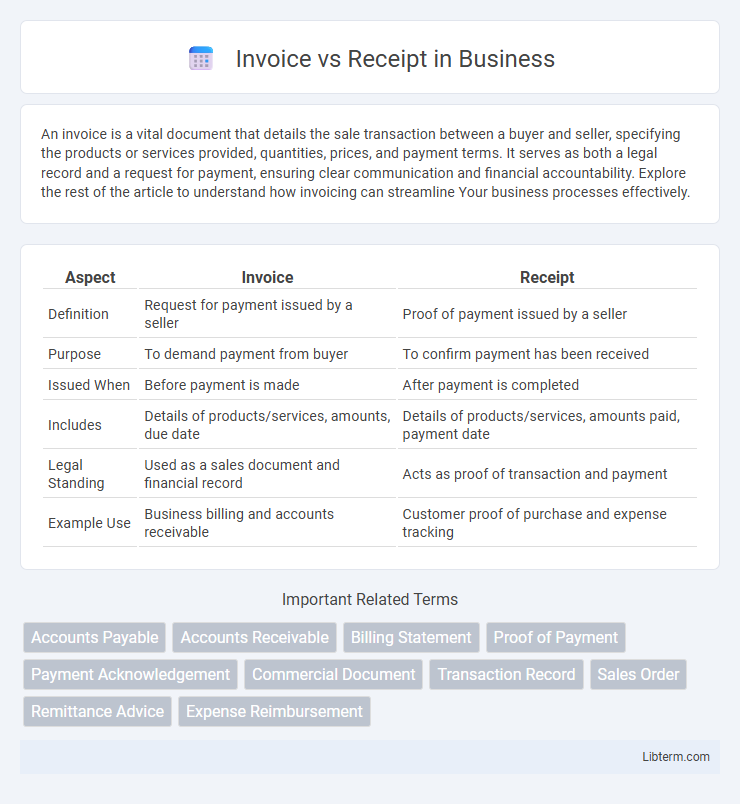
| Aspect | Invoice | Receipt |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Request for payment issued by a seller | Proof of payment issued by a seller |
| Purpose | To demand payment from buyer | To confirm payment has been received |
| Issued When | Before payment is made | After payment is completed |
| Includes | Details of products/services, amounts, due date | Details of products/services, amounts paid, payment date |
| Legal Standing | Used as a sales document and financial record | Acts as proof of transaction and payment |
| Example Use | Business billing and accounts receivable | Customer proof of purchase and expense tracking |
Introduction to Invoice vs Receipt
An invoice is a detailed document issued by a seller to a buyer, specifying products or services provided, their quantities, prices, payment terms, and due dates, serving as a formal request for payment. A receipt is proof of payment issued once the buyer has settled the invoice or made a purchase, confirming the transaction and the amount paid. Both documents play crucial roles in financial record-keeping, bookkeeping, and audit processes, ensuring transparency and accountability in business transactions.
Definition of Invoice
An invoice is a detailed document issued by a seller to a buyer, specifying the products or services provided, quantities, prices, and total amount owed. It serves as a formal request for payment and often includes payment terms, invoice number, and due date for financial record-keeping. Invoices are essential for businesses to track sales, manage accounts receivable, and comply with tax regulations.
Definition of Receipt
A receipt is a document that serves as proof of payment, issued by a seller to a buyer after a transaction is completed. It typically includes details such as the date of purchase, items or services purchased, total amount paid, and payment method. Unlike an invoice, a receipt confirms payment has been received rather than requesting payment.
Key Differences Between Invoice and Receipt
An invoice is a detailed commercial document issued by a seller to a buyer, specifying products or services provided, quantities, prices, payment terms, and due date, serving as a payment request. A receipt is a proof of payment issued after the buyer has settled the invoice or transaction, confirming the amount paid, date, and method of payment. Key differences include timing (invoice precedes payment, receipt follows payment), purpose (request vs confirmation), and content specificity (invoices include payment terms, receipts record completed transactions).
Purpose of an Invoice
An invoice serves as a formal request for payment issued by a seller to a buyer, detailing the products or services provided, quantities, prices, and total amount due. It functions as a legal document and accounting record to track sales transactions and payment obligations. Unlike receipts, invoices are issued before payment and help manage cash flow and financial reporting in businesses.
Purpose of a Receipt
A receipt serves as proof of payment confirming that a transaction has been completed successfully, providing the buyer with evidence of purchase for future reference or returns. It typically includes details such as the date, amount paid, payment method, and description of goods or services received. Receipts are essential for financial record-keeping, expense tracking, and warranty validation.
Essential Elements of an Invoice
An invoice includes essential elements such as the seller's and buyer's contact information, a unique invoice number for tracking, date of issue, and detailed description of goods or services provided. It specifies quantities, unit prices, total amounts, applicable taxes, payment terms, and due date to ensure clarity in financial transactions. These components establish a formal request for payment and serve as an important document for accounting and legal purposes.
Essential Elements of a Receipt
A receipt includes essential elements such as the seller's name and contact information, the date of the transaction, a unique receipt number, and a detailed description of the items or services purchased. It must show the total amount paid, including taxes, and the payment method used, providing proof of payment. Unlike invoices, receipts confirm completed transactions and serve as records for both buyers and sellers.
When to Use Invoices versus Receipts
Invoices are used when requesting payment for goods or services, typically issued before payment is made to detail amounts owed, due dates, and payment terms. Receipts are provided after payment confirmation as proof of transaction and serve as evidence that the buyer has settled the invoice or purchase. Businesses issue invoices to manage accounts receivable, while receipts help customers verify completed payments and facilitate record-keeping.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Document
Selecting the appropriate document depends on the transaction's purpose: an invoice requests payment by detailing goods or services provided, while a receipt confirms payment has been made. Businesses use invoices to manage accounts receivable and track sales, whereas receipts serve as proof of purchase for customers and support expense records. Understanding the distinct roles of invoices and receipts ensures accurate financial documentation and efficient cash flow management.
Invoice Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com