Intrinsic value represents the true worth of an asset based on fundamental analysis, independent of its current market price or external factors. Understanding this concept helps you make informed investment decisions by evaluating the real potential of stocks, bonds, or other financial instruments. Discover how intrinsic value can guide your financial strategy by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
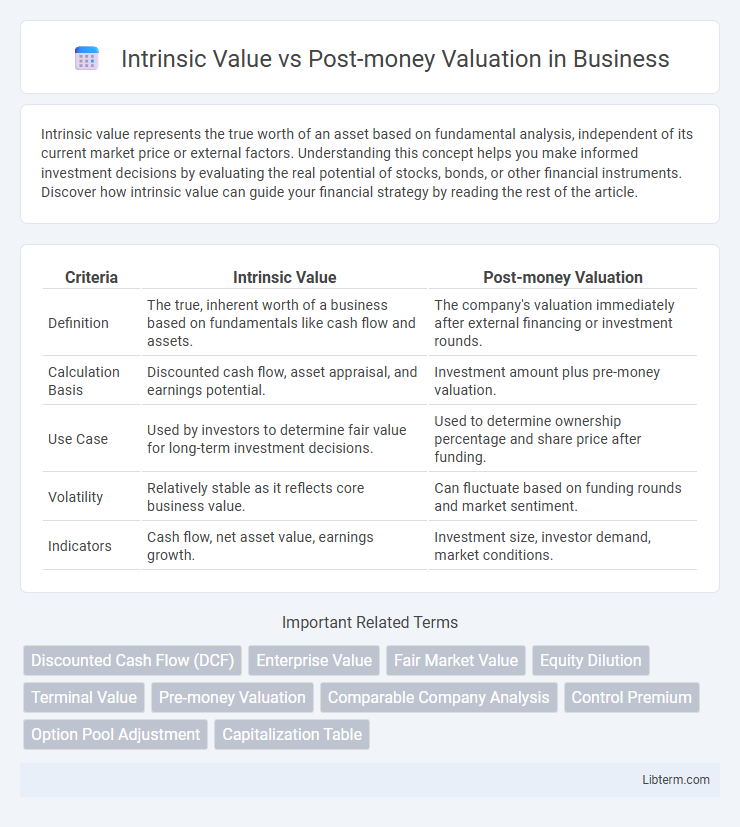
| Criteria | Intrinsic Value | Post-money Valuation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The true, inherent worth of a business based on fundamentals like cash flow and assets. | The company's valuation immediately after external financing or investment rounds. |
| Calculation Basis | Discounted cash flow, asset appraisal, and earnings potential. | Investment amount plus pre-money valuation. |
| Use Case | Used by investors to determine fair value for long-term investment decisions. | Used to determine ownership percentage and share price after funding. |
| Volatility | Relatively stable as it reflects core business value. | Can fluctuate based on funding rounds and market sentiment. |
| Indicators | Cash flow, net asset value, earnings growth. | Investment size, investor demand, market conditions. |
Introduction to Intrinsic Value and Post-money Valuation
Intrinsic value represents the true, inherent worth of an asset based on fundamental analysis, reflecting its actual financial health and future cash flow potential. Post-money valuation refers to the company's estimated value immediately after receiving external funding or investment, calculated by adding the investment amount to the pre-money valuation. Understanding the distinction between intrinsic value and post-money valuation is crucial for investors to assess real asset value compared to market-driven investor expectations.
Defining Intrinsic Value
Intrinsic value represents the true, inherent worth of an asset based on fundamental analysis, including cash flow, growth potential, and risk factors, rather than market perceptions. It is a critical measure used by investors to determine whether a stock or company is undervalued or overvalued relative to its post-money valuation. Understanding intrinsic value helps compare the company's actual financial health against post-money valuation, which is the startup's value immediately after receiving funding.
Understanding Post-money Valuation
Post-money valuation represents the total value of a company immediately after receiving investment, calculated by adding the new equity investment to the pre-money valuation. It is crucial for investors to understand this figure as it determines the ownership percentage they acquire in the company. Unlike intrinsic value, which reflects a company's fundamental worth based on assets and earnings, post-money valuation is primarily driven by market negotiations and investment rounds.
Key Differences Between Intrinsic Value and Post-money Valuation
Intrinsic value represents the true, fundamental worth of an asset based on underlying financial metrics, cash flow projections, and market conditions, reflecting a company's actual economic value. Post-money valuation is the company's estimated value immediately after receiving new capital from an investment round, calculated by adding the investment amount to the pre-money valuation. Key differences include intrinsic value's focus on long-term fundamentals versus post-money valuation's emphasis on current funding rounds and market sentiment, impacting investor decisions and startup equity assessments.
Methods for Calculating Intrinsic Value
Intrinsic value is calculated using discounted cash flow (DCF) analysis, which estimates the present value of expected future cash flows by applying a discount rate reflecting the asset's risk. Another method involves asset-based valuation, where intrinsic value is derived from the company's net asset value or book value adjusted for market conditions. These approaches contrast with post-money valuation, which reflects the company's value immediately after investment, based on the latest funding round and share price.
How Post-money Valuation is Determined
Post-money valuation is determined by adding the amount of new equity investment to the pre-money valuation, representing the company's total worth immediately after the funding round. This valuation reflects market perception, investor demand, and future growth potential but does not account for the company's intrinsic value based on fundamental assets or earnings. Understanding post-money valuation helps investors assess ownership percentages and dilution effects following capital infusion.
Advantages and Limitations of Intrinsic Value
Intrinsic value provides a fundamental assessment of an asset's worth based on its inherent financial metrics, offering a clear measure for long-term investment decisions and minimizing market noise. Its advantage lies in capturing true economic value independent of market fluctuations, but its limitation includes reliance on assumptions and projections that may introduce subjectivity and potential inaccuracies. Unlike post-money valuation, intrinsic value does not account for investor sentiment or market conditions immediately after fundraising events.
Pros and Cons of Post-money Valuation
Post-money valuation offers a clear snapshot of a company's worth immediately after investment, aiding investors and founders in understanding ownership percentages and dilution effects. However, it can overestimate value by including the new capital, potentially leading to inflated expectations and misaligned incentives in future funding rounds. Relying solely on post-money valuation may obscure intrinsic value factors like asset quality and long-term profitability, which are critical for accurate company assessment.
Impact on Investment Decisions and Startup Funding
Intrinsic value represents the true, fundamental worth of a startup based on its assets, earnings potential, and growth prospects, providing investors with a realistic assessment of risk and return. Post-money valuation reflects the company's estimated value immediately after receiving external funding, influencing the ownership percentage and control investors obtain. Understanding both metrics is crucial for making informed investment decisions and structuring startup funding deals that balance equity dilution with capital requirements.
Choosing the Right Valuation Approach
Choosing the right valuation approach depends on the purpose and context of the investment; intrinsic value focuses on the company's fundamental financial health, including cash flows, assets, and earnings projections, providing a deep, long-term perspective. Post-money valuation is crucial for startups and venture capital rounds, reflecting the company's worth immediately after external funding, incorporating the latest investment round data. Evaluating the balance between these methods ensures accurate assessment aligned with both strategic financial analysis and market-driven investment timing.
Intrinsic Value Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com