Value-based pricing focuses on setting product or service prices based on the perceived value to the customer rather than solely on cost or market competition. This strategy emphasizes understanding customer needs and willingness to pay, enabling businesses to maximize profit while delivering meaningful benefits. Explore the rest of the article to discover how value-based pricing can transform Your pricing strategy and boost sales.
Table of Comparison
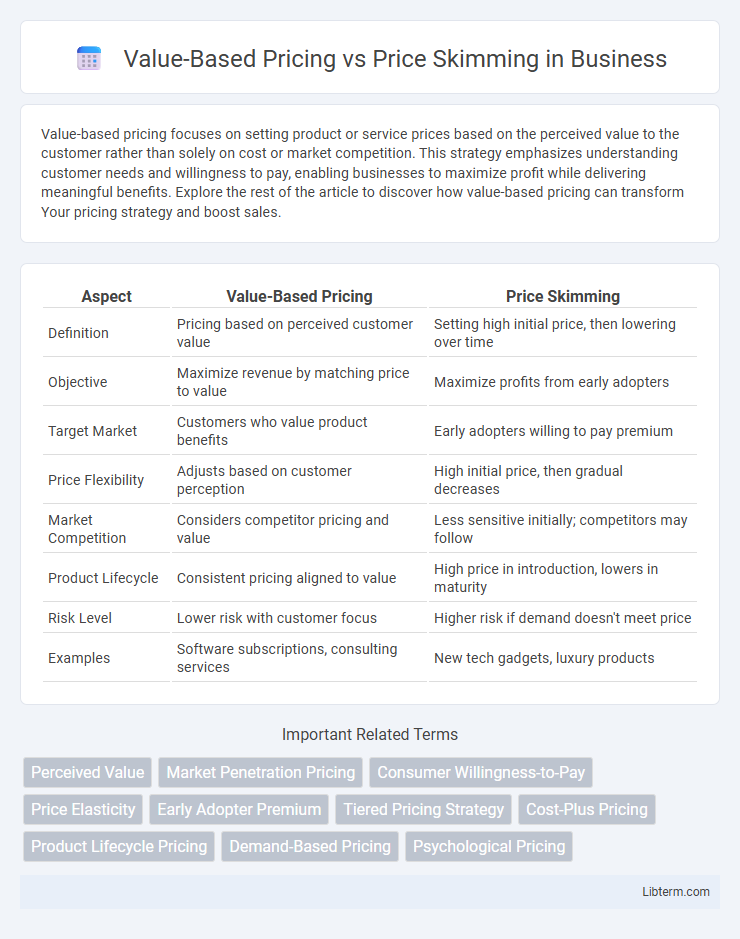
| Aspect | Value-Based Pricing | Price Skimming |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pricing based on perceived customer value | Setting high initial price, then lowering over time |
| Objective | Maximize revenue by matching price to value | Maximize profits from early adopters |
| Target Market | Customers who value product benefits | Early adopters willing to pay premium |
| Price Flexibility | Adjusts based on customer perception | High initial price, then gradual decreases |
| Market Competition | Considers competitor pricing and value | Less sensitive initially; competitors may follow |
| Product Lifecycle | Consistent pricing aligned to value | High price in introduction, lowers in maturity |
| Risk Level | Lower risk with customer focus | Higher risk if demand doesn't meet price |
| Examples | Software subscriptions, consulting services | New tech gadgets, luxury products |
Understanding Value-Based Pricing
Value-based pricing sets product prices based on the perceived value to customers rather than production costs, aligning pricing strategies with consumer willingness to pay. This approach requires in-depth market research and customer insights to accurately assess value propositions and competitive positioning. By emphasizing customer-centric metrics, value-based pricing maximizes profitability and fosters stronger brand loyalty compared to price skimming, which sets high initial prices to capitalize on early adopters before gradually lowering prices.
Exploring Price Skimming Strategies
Price skimming strategies involve setting a high initial price for a new or innovative product to maximize early profit margins from customers willing to pay a premium. This approach capitalizes on consumer segments with a high willingness to pay before gradually lowering prices to attract more price-sensitive buyers. Effective price skimming requires careful market segmentation, competitive analysis, and timing to balance profitability with market penetration.
Key Differences Between Value-Based Pricing and Price Skimming
Value-based pricing sets prices based on the perceived value to the customer, maximizing willingness to pay, while price skimming involves setting high initial prices to target early adopters before gradually lowering them. Value-based pricing requires deep market and customer insights to tailor prices to specific segments, whereas price skimming leverages product novelty and limited competition to capture maximum revenue early. The main difference lies in pricing strategy focus: customer value perception versus market penetration and product lifecycle stage.
Benefits of Value-Based Pricing
Value-Based Pricing maximizes revenue by aligning product prices with customer perceived value, fostering stronger customer loyalty and higher profit margins. Unlike Price Skimming, which captures short-term gains from early adopters, Value-Based Pricing sustains long-term market competitiveness by adapting to customer demand and willingness to pay. This pricing strategy enhances brand positioning and drives innovation by focusing on delivering superior value rather than just initial high prices.
Advantages of Price Skimming
Price skimming allows companies to maximize revenue quickly by targeting early adopters willing to pay a premium for new or innovative products. This strategy helps recover research and development costs more efficiently while creating a perception of high value and exclusivity. By gradually lowering prices, businesses can then attract more price-sensitive customers without diluting the brand's initial prestige.
Challenges with Value-Based Pricing
Value-based pricing faces significant challenges including accurately assessing customer perceived value and continuously adapting to market changes, which requires extensive customer insights and data analytics. Companies often struggle with quantifying intangible benefits, making it difficult to set a precise price that maximizes profitability while remaining attractive to consumers. Unlike price skimming, value-based pricing demands ongoing communication and education efforts to justify prices that may not align with competitors' pricing strategies.
Limitations of Price Skimming
Price skimming faces limitations such as attracting competitors quickly due to high initial prices, which can erode market share. It is less effective in markets with price-sensitive customers who may delay purchases until prices drop. Furthermore, maintaining premium pricing requires continuous innovation and strong brand loyalty to justify higher costs.
Choosing the Right Pricing Strategy for Your Business
Value-based pricing maximizes revenue by setting prices based on customer perceived value, ideal for products with strong differentiation and unique benefits. Price skimming targets early adopters with high initial prices, gradually lowering them to capture broader market segments, effective for innovation-driven markets or new technology launches. Choosing the right pricing strategy depends on factors like product lifecycle, market demand elasticity, competitive landscape, and customer willingness to pay.
Industry Examples: Value-Based Pricing vs Price Skimming
Value-Based Pricing is effectively used by luxury brands like Apple, which set prices based on perceived customer value and product differentiation, maximizing profit while maintaining brand prestige. Price Skimming is evident in technology industries, such as with Samsung's Galaxy smartphones, where high initial prices capture early adopters before gradually lowering prices to attract broader markets. Both strategies leverage market segments but differ in timing and customer perception to optimize revenue.
Future Trends in Pricing Strategies
Value-based pricing increasingly leverages advanced data analytics and AI to personalize prices based on customer perceived value, driving higher profitability in dynamic markets. Price skimming remains viable for innovative tech products but faces pressure from fast market saturation and increased transparency fueled by digital platforms. Future pricing strategies integrate real-time market feedback and customer behavioral insights, blending value-based models with adaptive skimming to optimize revenue across product life cycles.
Value-Based Pricing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com