A callable bond grants the issuer the right to redeem the bond before its maturity date, typically at a premium price. This feature benefits the issuer by allowing refinancing when interest rates drop, but it introduces reinvestment risk for investors due to uncertain cash flows. Explore the rest of the article to understand how callable bonds could impact your investment strategy.
Table of Comparison
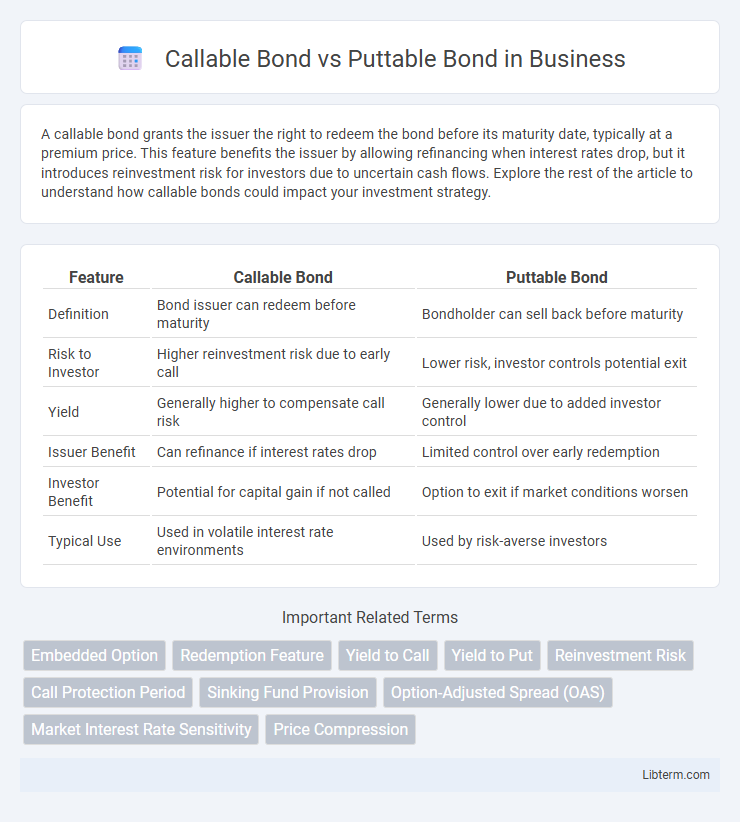
| Feature | Callable Bond | Puttable Bond |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Bond issuer can redeem before maturity | Bondholder can sell back before maturity |
| Risk to Investor | Higher reinvestment risk due to early call | Lower risk, investor controls potential exit |
| Yield | Generally higher to compensate call risk | Generally lower due to added investor control |
| Issuer Benefit | Can refinance if interest rates drop | Limited control over early redemption |
| Investor Benefit | Potential for capital gain if not called | Option to exit if market conditions worsen |
| Typical Use | Used in volatile interest rate environments | Used by risk-averse investors |
Introduction to Callable and Puttable Bonds
Callable bonds give issuers the right to redeem the bond before maturity at a predetermined call price, allowing them to refinance debt when interest rates decline. Puttable bonds provide bondholders the option to sell the bond back to the issuer at a specified price before maturity, offering protection against interest rate increases. These embedded options significantly influence bond pricing, yield, and risk profiles in fixed-income markets.
Key Features of Callable Bonds
Callable bonds give issuers the right to redeem the bonds before maturity at a predetermined call price, allowing them to refinance debt if interest rates decline. These bonds typically offer higher yields compared to non-callable bonds to compensate investors for the call risk. Investors face reinvestment risk, as the bond may be called away when interest rates fall, limiting potential price appreciation.
Key Features of Puttable Bonds
Puttable bonds grant the bondholder the right to sell the bond back to the issuer at predetermined dates before maturity, providing protection against rising interest rates and credit risk deterioration. These bonds often feature specified put dates and predetermined prices, enhancing investor flexibility and reducing downside risk. The key characteristics include lower yields compared to non-puttable bonds due to the embedded put option and increased appeal to risk-averse investors seeking capital preservation.
How Callable Bonds Work
Callable bonds allow issuers to redeem the bond before its maturity date at a predetermined call price, giving them flexibility to refinance debt when interest rates decline. The call feature benefits issuers by reducing interest expenses but poses reinvestment risk to investors who may receive principal back when yields are lower. Investors typically demand higher yields on callable bonds compared to non-callable bonds to compensate for this embedded option risk.
How Puttable Bonds Work
Puttable bonds grant the bondholder the right to sell the bond back to the issuer at a predetermined price before maturity, providing protection against interest rate increases and credit risk. This feature enhances bondholder flexibility by allowing exit from the investment if market conditions deteriorate, effectively reducing the bond's duration and interest rate sensitivity. Issuers generally offer lower yields on puttable bonds compared to non-puttable bonds due to this embedded option that benefits investors.
Advantages of Callable Bonds for Issuers
Callable bonds offer issuers the advantage of refinancing debt at lower interest rates when market conditions improve, reducing overall borrowing costs. Issuers gain flexibility to redeem bonds before maturity, managing capital structure strategically and responding to changing financial needs. This built-in call option protects issuers against rising interest expenses, enhancing financial control and risk management.
Advantages of Puttable Bonds for Investors
Puttable bonds offer investors the advantage of increased protection against interest rate fluctuations by allowing them to sell the bond back to the issuer before maturity, mitigating potential losses when rates rise. These bonds provide enhanced liquidity and flexibility, enabling investors to react promptly to changing market conditions. The embedded put option effectively reduces the bond's duration risk, making puttable bonds a safer investment choice in volatile interest environments.
Risks and Drawbacks of Callable Bonds
Callable bonds carry the risk of reinvestment at lower interest rates if the issuer calls the bond before maturity, reducing potential returns for investors. They often come with higher price volatility compared to puttable bonds due to fluctuating interest rate environments and call provisions. Investors face uncertainty in cash flow timing, which can negatively impact portfolio income stability and market value.
Risks and Drawbacks of Puttable Bonds
Puttable bonds carry the risk that issuers may exploit the put option during unfavorable market conditions, leading to reinvestment risk for bondholders who must find new investments at potentially lower interest rates. The drawback includes limited price appreciation since the bond's value is capped by the put price, reducing profit potential when interest rates decline. Furthermore, the issuer's credit risk remains, and the put option may not fully protect investors against default or insolvency events.
Callable vs Puttable Bonds: Which Should You Choose?
Callable bonds give issuers the right to redeem the bond before maturity, typically when interest rates decline, allowing them to refinance at lower costs but exposing investors to reinvestment risk. Puttable bonds grant investors the option to sell the bond back to the issuer at predetermined times, offering downside protection in rising interest rate environments or credit deterioration. Choosing between callable and puttable bonds depends on your risk tolerance: opt for callable bonds if you seek higher yields with some reinvestment risk or puttable bonds for greater flexibility and protection against interest rate hikes.
Callable Bond Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com