Outsourcing allows businesses to delegate non-core tasks to specialized third-party providers, reducing operational costs and increasing efficiency. By leveraging external expertise, companies can focus on their core competencies while accessing advanced technologies and global talent pools. Discover how outsourcing can transform your business strategy and boost productivity in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
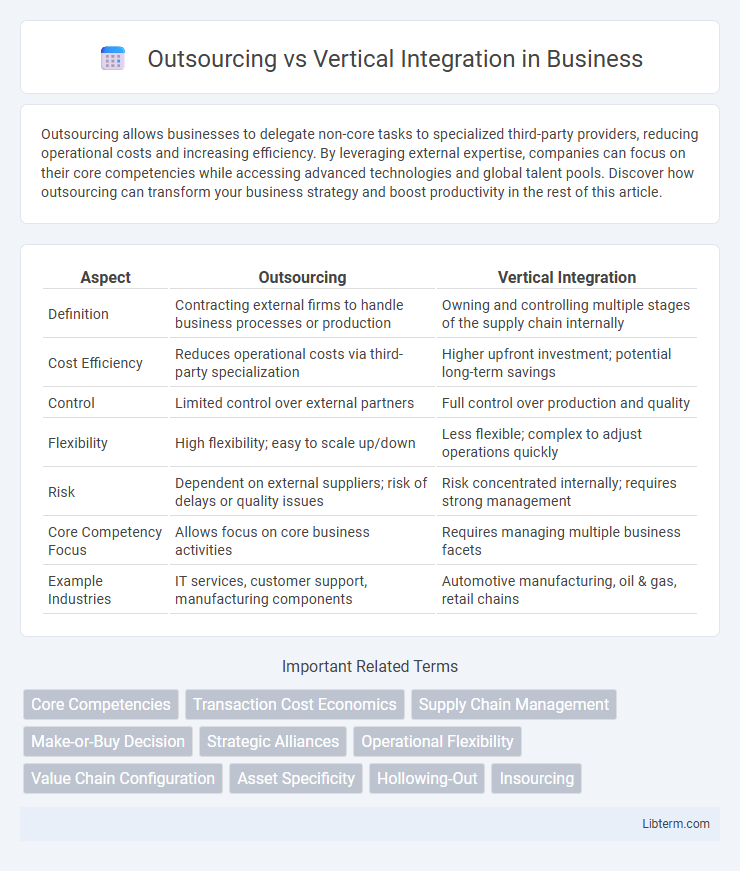
| Aspect | Outsourcing | Vertical Integration |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Contracting external firms to handle business processes or production | Owning and controlling multiple stages of the supply chain internally |
| Cost Efficiency | Reduces operational costs via third-party specialization | Higher upfront investment; potential long-term savings |
| Control | Limited control over external partners | Full control over production and quality |
| Flexibility | High flexibility; easy to scale up/down | Less flexible; complex to adjust operations quickly |
| Risk | Dependent on external suppliers; risk of delays or quality issues | Risk concentrated internally; requires strong management |
| Core Competency Focus | Allows focus on core business activities | Requires managing multiple business facets |
| Example Industries | IT services, customer support, manufacturing components | Automotive manufacturing, oil & gas, retail chains |
Introduction to Outsourcing vs Vertical Integration
Outsourcing involves delegating specific business processes or functions to external third-party providers to leverage cost efficiency and specialized expertise. Vertical integration refers to a company's expansion into different stages of its supply chain, enhancing control over production, distribution, and costs. Both strategies impact operational agility, with outsourcing emphasizing flexibility and vertical integration focusing on comprehensive oversight and resource consolidation.
Defining Outsourcing: Pros and Cons
Outsourcing involves delegating specific business processes or services to third-party providers, enabling companies to reduce operational costs and access specialized expertise. Key advantages include increased flexibility, scalability, and the ability to focus on core competencies, while drawbacks encompass potential quality control issues, dependency on external vendors, and risks to data security. Evaluating outsourcing requires balancing cost savings against challenges like communication barriers and loss of managerial oversight.
Understanding Vertical Integration: Benefits and Challenges
Vertical integration enhances control over the supply chain by owning multiple production stages, resulting in improved efficiency and reduced costs. It enables better coordination, quality control, and faster response to market changes but requires significant capital investment and increased operational complexity. Challenges include reduced flexibility, potential for higher overhead, and risks associated with managing diverse business activities internally.
Key Differences Between Outsourcing and Vertical Integration
Outsourcing involves contracting third-party firms to handle specific business functions, whereas vertical integration entails a company owning and managing its supply chain internally. Key differences include control levels, with vertical integration offering greater oversight and consistency, while outsourcing provides cost efficiency and flexibility. Risk factors also vary, as vertical integration reduces dependency on external suppliers, but outsourcing allows companies to leverage specialized expertise and scale operations quickly.
Strategic Factors Influencing the Choice
Strategic factors influencing the choice between outsourcing and vertical integration include cost efficiency, control over the supply chain, and core competency focus. Firms prioritize outsourcing when aiming to reduce operational costs and leverage specialized expertise, while vertical integration is favored to enhance supply chain reliability and protect proprietary technologies. Market dynamics, risk management, and long-term strategic goals also play crucial roles in determining the optimal approach for achieving competitive advantage.
Cost Implications: Outsourcing vs Vertical Integration
Outsourcing typically reduces fixed costs by leveraging external suppliers and converting expenses into variable costs, leading to lower capital investment and operational flexibility. Vertical integration often involves higher initial capital expenditures and fixed costs due to owning multiple stages of production but can result in long-term cost savings through improved coordination and control. Analyzing cost implications requires evaluating transaction costs, economies of scale, and potential risks associated with both outsourcing and vertical integration strategies.
Impact on Quality and Control
Outsourcing often results in reduced direct control over production processes, potentially affecting product quality due to reliance on third-party standards and practices. Vertical integration enhances quality control by allowing companies to oversee every stage of production, ensuring consistent standards and quicker response to defects. Companies seeking stringent quality management and process oversight typically benefit more from vertical integration than from outsourcing.
Risk Management and Flexibility
Outsourcing offers enhanced flexibility by allowing companies to quickly scale operations and adapt to market changes without significant capital investment. Vertical integration reduces risk by providing greater control over the supply chain, minimizing dependency on external suppliers and ensuring quality consistency. Balancing outsourcing and vertical integration strategies enables businesses to optimize risk management while maintaining operational agility.
Case Studies: Successes and Failures
Case studies reveal diverse outcomes in outsourcing vs vertical integration strategies, highlighting how companies like Apple benefited from outsourcing manufacturing to focus on design and innovation, while Tesla's vertical integration enabled tighter control over production and supply chains. Failures include Boeing's outsourcing challenges leading to delays and quality issues in the 787 Dreamliner program, contrasting with Zara's vertically integrated model that ensures rapid fashion retail responsiveness. These examples emphasize the critical role of strategic alignment between business goals and operational execution in determining success or failure.
Choosing the Right Strategy for Your Business
Choosing the right strategy between outsourcing and vertical integration depends on factors like cost efficiency, control over production, and scalability. Outsourcing allows businesses to reduce operational expenses and focus on core competencies, leveraging specialized external providers for tasks like manufacturing or IT services. Vertical integration enhances control over the supply chain, ensuring quality consistency and reducing dependency, but requires significant investment and resource commitment.
Outsourcing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com