Cryptocurrency systems leverage blockchain technology to enable secure, decentralized digital transactions without intermediaries. These systems use cryptographic algorithms to ensure transparency, immutability, and user privacy across a distributed ledger. Discover how your participation in this transformative financial ecosystem can empower your transactions by exploring the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
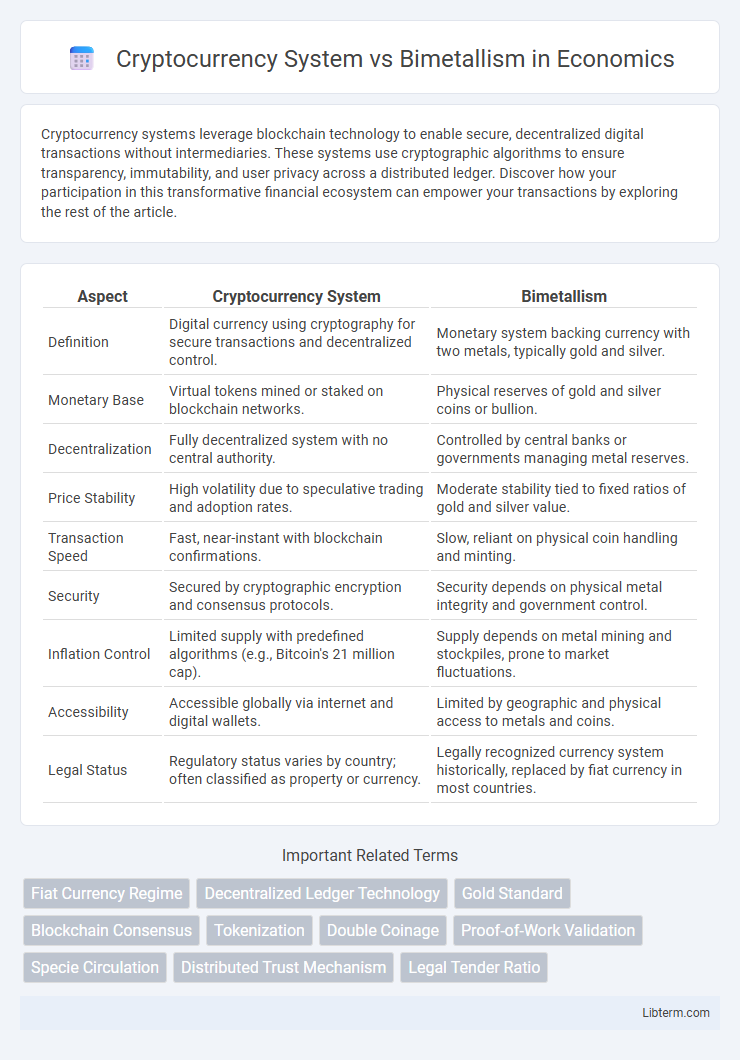
| Aspect | Cryptocurrency System | Bimetallism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Digital currency using cryptography for secure transactions and decentralized control. | Monetary system backing currency with two metals, typically gold and silver. |
| Monetary Base | Virtual tokens mined or staked on blockchain networks. | Physical reserves of gold and silver coins or bullion. |
| Decentralization | Fully decentralized system with no central authority. | Controlled by central banks or governments managing metal reserves. |
| Price Stability | High volatility due to speculative trading and adoption rates. | Moderate stability tied to fixed ratios of gold and silver value. |
| Transaction Speed | Fast, near-instant with blockchain confirmations. | Slow, reliant on physical coin handling and minting. |
| Security | Secured by cryptographic encryption and consensus protocols. | Security depends on physical metal integrity and government control. |
| Inflation Control | Limited supply with predefined algorithms (e.g., Bitcoin's 21 million cap). | Supply depends on metal mining and stockpiles, prone to market fluctuations. |
| Accessibility | Accessible globally via internet and digital wallets. | Limited by geographic and physical access to metals and coins. |
| Legal Status | Regulatory status varies by country; often classified as property or currency. | Legally recognized currency system historically, replaced by fiat currency in most countries. |
Introduction to Cryptocurrency Systems and Bimetallism
Cryptocurrency systems operate on decentralized blockchain technology, enabling secure, transparent digital transactions without central authority. Bimetallism, a historical monetary system, relied on fixed ratios between gold and silver to stabilize currency value and facilitate trade. Both systems address monetary trust and value storage, yet cryptocurrencies utilize cryptographic algorithms, whereas bimetallism depends on physical metal reserves.
Historical Overview of Bimetallism
Bimetallism emerged in the 19th century as a monetary system where both gold and silver were used as legal tender at a fixed ratio, aiming to stabilize economies through dual backing. This system faced challenges due to fluctuating metal values, which often led to market imbalances and the eventual dominance of the gold standard by the early 20th century. In contrast, cryptocurrency systems rely on decentralized digital ledgers and cryptographic proof, offering a modern alternative free from the limitations of physical metal reserves and government control.
Emergence and Evolution of Cryptocurrency Systems
Cryptocurrency systems emerged in the early 21st century as decentralized digital currencies leveraging blockchain technology to enable secure, transparent transactions without central authorities, contrasting the historical bimetallism system based on fixed ratios of gold and silver as monetary standards. The evolution of cryptocurrency has been marked by rapid technological advancements, increased adoption, and regulatory challenges, evolving from Bitcoin's inception in 2009 to diverse altcoins with varied consensus mechanisms and uses. Bimetallism's decline in the late 19th century due to market fluctuations and political debates underscores the shift toward purely digital monetary systems that prioritize scalability and cryptographic security over metal-backed value.
Underlying Principles: Decentralization vs Metal Standards
Cryptocurrency systems operate on the principle of decentralization, utilizing blockchain technology to enable secure, peer-to-peer transactions without central authority, contrasting sharply with bimetallism's reliance on fixed ratios between gold and silver as metal standards to maintain currency value. Decentralization allows cryptocurrencies to achieve transparency and resilience through distributed ledger protocols, while bimetallism depends on governmental control and market consensus to balance the value of two precious metals. The underlying innovation in cryptocurrencies challenges traditional metal-based monetary systems by emphasizing algorithmic trust and cryptographic security over physical commodity backing.
Security and Trust: Blockchain vs Physical Assets
Cryptocurrency systems leverage blockchain technology to ensure security through decentralized, immutable ledgers that prevent fraud and unauthorized alterations, fostering trust via transparent consensus mechanisms. In contrast, bimetallism relies on physical assets--gold and silver--which derive trust from their tangible value and government backing but face risks like theft, counterfeiting, and storage vulnerabilities. Blockchain's cryptographic security offers enhanced protection against manipulation, while physical assets depend heavily on historical acceptance and institutional assurance to maintain trust.
Monetary Supply Control: Algorithms vs Government Policy
Cryptocurrency systems rely on decentralized algorithms, such as blockchain consensus mechanisms and predefined issuance schedules, to control monetary supply, ensuring transparency and resistance to inflationary manipulation. In contrast, bimetallism depends on government policies to regulate the quantity and exchange rates of two metals, typically gold and silver, which can be influenced by political decisions and economic pressures. Algorithmic control in cryptocurrencies offers predictable supply parameters, whereas bimetallism's monetary supply fluctuates with legislative actions and market valuations of the metals.
Economic Stability: Volatility in Crypto vs Metal-Based Standards
Cryptocurrency systems exhibit high volatility due to decentralized market dynamics, speculative trading, and lack of intrinsic asset backing, which challenges economic stability. Bimetallism, anchored by fixed ratios between gold and silver, historically provided more predictable value but faced issues from fluctuating metal supplies affecting price stability. While metal-based standards offer tangible reserves supporting confidence, cryptocurrencies rely on network consensus and offer potential for rapid adaptation despite price unpredictability.
Transaction Mechanisms and Accessibility
Cryptocurrency systems utilize decentralized blockchain technology, enabling peer-to-peer transactions with cryptographic security and minimal intermediaries, offering near-instant settlement worldwide. In contrast, bimetallism relies on fixed exchange rates between gold and silver coins, limiting transaction speed and accessibility due to physical currency handling and regional monetary policies. Cryptocurrencies provide greater financial inclusion through digital wallets accessible via smartphones, whereas bimetallism requires access to physical mints and banks, often excluding unbanked populations.
Global Acceptance and Regulatory Challenges
Cryptocurrency systems face significant regulatory challenges due to their decentralized nature and lack of centralized control, leading to varied acceptance across global markets. Bimetallism, historically based on gold and silver standards, had more uniform acceptance but limited adaptability in modern financial systems. The evolving regulatory frameworks for cryptocurrencies aim to balance innovation with security, contrasting with the predictable but rigid regulatory environment of bimetallism.
Future Outlook: Digital Age Currencies vs Traditional Standards
Cryptocurrency systems offer enhanced transparency, decentralization, and faster transaction speeds compared to bimetallism, which relies on fixed ratios of gold and silver, limiting flexibility in monetary policy. The future outlook shows digital currencies integrating blockchain technology to enable secure, borderless transactions and programmable money, surpassing the constraints of traditional metal-backed standards. Increasing global adoption and regulatory frameworks suggest cryptocurrencies will play a central role in the evolving digital economy, while bimetallism remains a historical monetary framework with limited relevance.
Cryptocurrency System Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com