BRICS economies, consisting of Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa, represent rapidly growing markets with significant influence on global trade, natural resources, and emerging technologies. In contrast, G7 economies, including the United States, Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, and the United Kingdom, dominate global finance, innovation, and policy-making with advanced infrastructure and high GDP per capita. Explore the rest of this article to understand how the dynamics between BRICS and G7 shape the future of international economic relations.
Table of Comparison
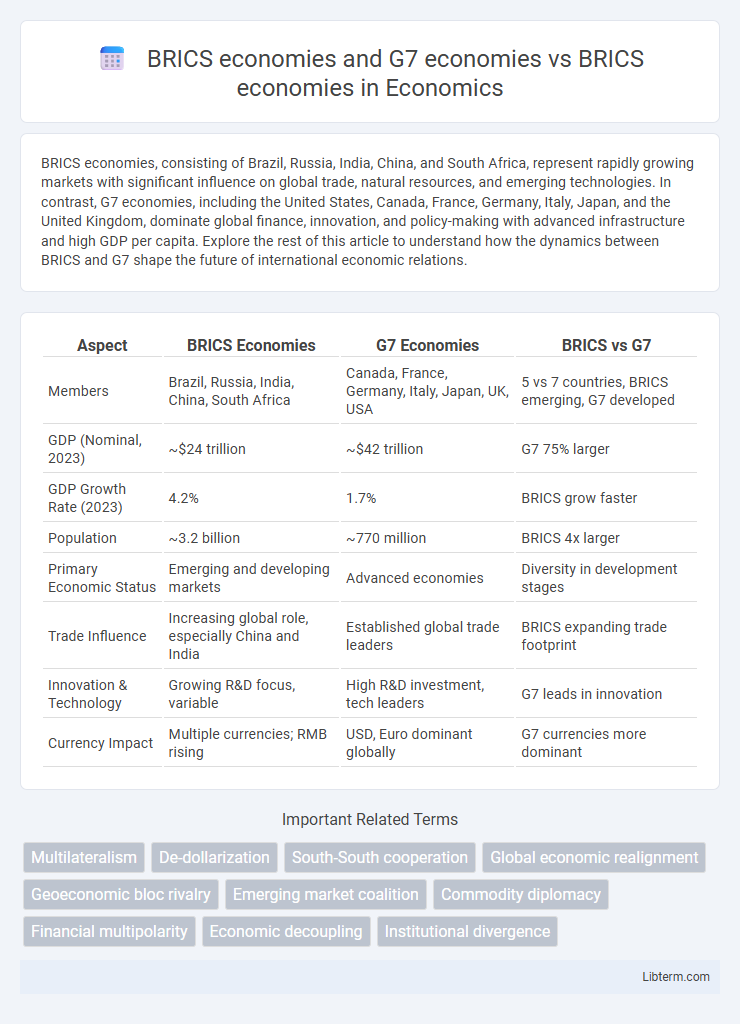
| Aspect | BRICS Economies | G7 Economies | BRICS vs G7 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Members | Brazil, Russia, India, China, South Africa | Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, UK, USA | 5 vs 7 countries, BRICS emerging, G7 developed |
| GDP (Nominal, 2023) | ~$24 trillion | ~$42 trillion | G7 75% larger |
| GDP Growth Rate (2023) | 4.2% | 1.7% | BRICS grow faster |
| Population | ~3.2 billion | ~770 million | BRICS 4x larger |
| Primary Economic Status | Emerging and developing markets | Advanced economies | Diversity in development stages |
| Trade Influence | Increasing global role, especially China and India | Established global trade leaders | BRICS expanding trade footprint |
| Innovation & Technology | Growing R&D focus, variable | High R&D investment, tech leaders | G7 leads in innovation |
| Currency Impact | Multiple currencies; RMB rising | USD, Euro dominant globally | G7 currencies more dominant |
Introduction: BRICS vs G7 Economies
BRICS economies--Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa--represent a significant portion of global GDP, driven by rapid industrialization, abundant natural resources, and a growing consumer market. In contrast, G7 economies--Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, the United Kingdom, and the United States--dominate in advanced technology, financial services, and high-value manufacturing. The dynamic between BRICS and G7 highlights the shift in global economic power, with BRICS countries increasing their influence through expanding trade and investment networks.
Historical Evolution of BRICS and G7
BRICS economies, comprising Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa, emerged in the early 21st century as influential players in global economic dynamics, driven by rapid industrialization and significant demographic advantages. G7 economies, including the United States, Japan, Germany, the United Kingdom, France, Italy, and Canada, originated post-World War II, establishing dominance through advanced industrialization, technological innovation, and financial markets. The historical evolution of BRICS reflects a shift towards multipolar economic governance, challenging the longstanding dominance of G7 in international trade and economic policymaking.
Economic Size and Growth Trends
BRICS economies, including China, India, Brazil, Russia, and South Africa, collectively represent a significant portion of global GDP with rapid growth rates, particularly driven by China and India's expanding middle classes and industrial sectors. In contrast, G7 economies--comprising the United States, Canada, United Kingdom, Germany, France, Italy, and Japan--hold a larger share of global GDP but experience slower growth trends due to mature markets and demographic challenges. The economic size gap between the G7 and BRICS narrows as emerging market growth outpaces developed economies, highlighting shifts in global economic power.
Trade Relations and Global Influence
BRICS economies--Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa--have rapidly expanded their trade relations by focusing on intra-BRICS cooperation and emerging markets, challenging the established dominance of G7 economies in global trade. While G7 nations, including the US, UK, Germany, Japan, Canada, France, and Italy, maintain significant influence through advanced technological innovation and established financial institutions, BRICS countries are driving growth via resource exports, manufacturing, and expanding consumer bases. This shift in trade dynamics has resulted in BRICS gaining considerable global influence, reshaping international economic governance and fostering alternative financial mechanisms such as the New Development Bank.
Financial Systems: Strengths and Weaknesses
BRICS economies exhibit rapid growth and expanding financial markets, driven by large domestic populations and increasing industrialization, but face challenges such as regulatory inconsistencies, currency volatility, and less mature financial infrastructure compared to G7 countries. G7 economies benefit from stable financial systems with advanced regulatory frameworks, deep capital markets, and strong institutional governance, yet often experience slower economic growth and higher debt levels. The comparative strengths of BRICS lie in growth potential and market size, while G7 economies lead in financial stability, transparency, and access to global capital.
Technological Advancements and Innovation
BRICS economies, notably China and India, have rapidly accelerated technological advancements through substantial investments in AI, 5G, and renewable energy technologies, challenging the innovation dominance traditionally held by G7 economies. While G7 countries like the United States, Germany, and Japan maintain leadership in high-tech research and advanced manufacturing, BRICS nations leverage their large markets and growing tech sectors to drive disruptive innovations and scale digital infrastructure. The competitive dynamic between G7 and BRICS economies increasingly centers on developing cutting-edge technologies and fostering innovation ecosystems that influence global economic growth and geopolitical power balances.
Geopolitical Power and Diplomacy
BRICS economies, comprising Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa, wield growing geopolitical power through strategic alliances and influence in global institutions like the UN and IMF, challenging traditional Western dominance. G7 economies--Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, the UK, and the US--maintain substantial diplomatic clout rooted in advanced economies, military alliances such as NATO, and longstanding leadership in international governance structures. The evolving dynamics between BRICS and G7 highlight a multipolar world order where emerging economies assert greater influence in shaping global policies and economic governance.
Policy Approaches to Global Challenges
BRICS economies emphasize state-led development, infrastructure investment, and South-South cooperation to address global challenges such as climate change and economic inequality. G7 economies prioritize multilateralism, technological innovation, and regulatory frameworks to foster sustainable growth and coordinate responses to geopolitical risks. Divergent policy approaches reflect BRICS' focus on inclusive growth and resource mobilization, while G7 countries often lead on setting global standards and advancing environmental commitments.
Future Prospects: Cooperation or Competition?
BRICS economies, representing fast-growing markets like China, India, and Brazil, exhibit significant potential for economic expansion and innovation, challenging the traditional dominance of G7 nations such as the US, Germany, and Japan. Future prospects indicate a dual dynamic where BRICS and G7 countries may pursue cooperation in global issues like climate change and trade reforms while competing fiercely for technological leadership and geopolitical influence. Strategic partnerships and multilateral forums will play crucial roles in shaping whether their interactions evolve into collaborative growth or intensified rivalry.
Conclusion: Comparative Analysis of BRICS and G7
BRICS economies collectively exhibit rapid growth driven by large populations and abundant natural resources, whereas G7 economies lead in advanced technology, innovation, and high GDP per capita. Despite slower overall growth, G7 countries maintain stronger institutional frameworks and higher standards of living. The comparative analysis highlights BRICS as emerging market powerhouses with increasing global influence, while G7 remains dominant in economic stability and technological advancement.
BRICS economies and G7 economies Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com