Sustained innovation drives long-term growth by continuously improving products, services, and processes to meet evolving market demands. Companies that prioritize consistent creativity maintain a competitive edge and adapt swiftly to technological advancements. Discover how you can foster sustained innovation in your organization by exploring the strategies outlined in this article.
Table of Comparison
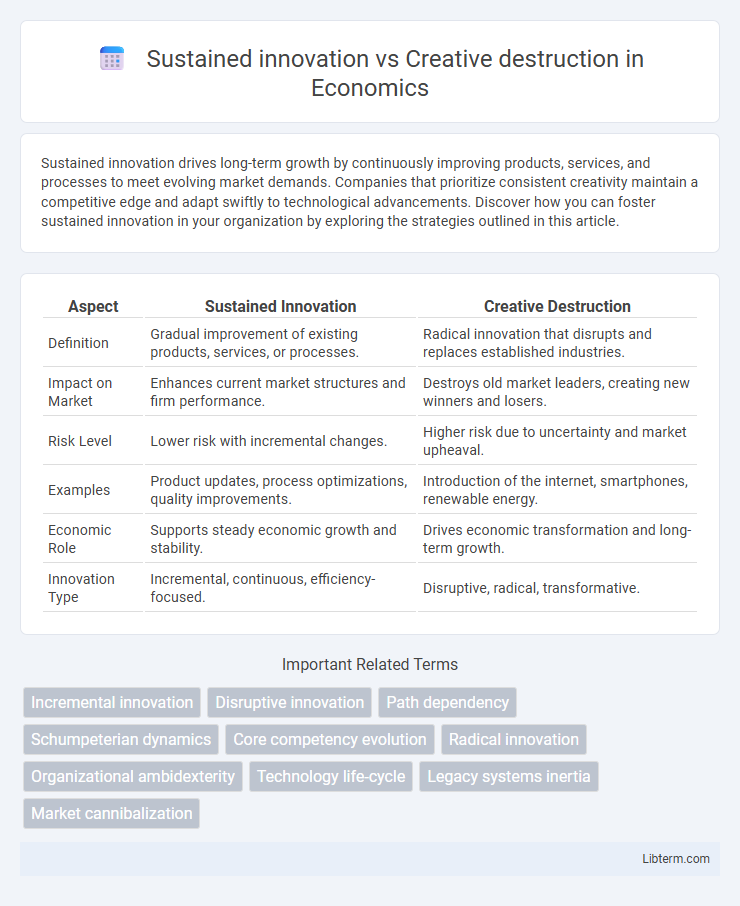
| Aspect | Sustained Innovation | Creative Destruction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Gradual improvement of existing products, services, or processes. | Radical innovation that disrupts and replaces established industries. |
| Impact on Market | Enhances current market structures and firm performance. | Destroys old market leaders, creating new winners and losers. |
| Risk Level | Lower risk with incremental changes. | Higher risk due to uncertainty and market upheaval. |
| Examples | Product updates, process optimizations, quality improvements. | Introduction of the internet, smartphones, renewable energy. |
| Economic Role | Supports steady economic growth and stability. | Drives economic transformation and long-term growth. |
| Innovation Type | Incremental, continuous, efficiency-focused. | Disruptive, radical, transformative. |
Defining Sustained Innovation
Sustained innovation refers to incremental improvements made to existing products, services, or processes that enhance performance, efficiency, or value without fundamentally disrupting the market. This type of innovation focuses on refining current technologies and meeting the evolving needs of customers within established frameworks. Companies leveraging sustained innovation often maintain competitive advantage by continuously optimizing offerings rather than radically transforming industries.
Understanding Creative Destruction
Creative destruction describes the relentless process by which new technologies and business models replace outdated ones, driving economic growth and market transformation. It emphasizes radical innovation that disrupts established industries, displacing existing firms and labor forces while creating opportunities for novel products and services. Understanding creative destruction is crucial for businesses to anticipate changes, adapt strategies, and sustain long-term competitiveness in dynamic markets.
Key Differences Between Sustained Innovation and Creative Destruction
Sustained innovation focuses on gradual improvements and enhancements within existing markets or products, emphasizing incremental progress that supports long-term stability and growth. Creative destruction involves disruptive innovations that radically transform or replace existing industries, often causing market upheaval and economic shifts. Key differences include the pace of change, with sustained innovation being evolutionary and creative destruction being revolutionary, and their impact on existing market structures, where sustained innovation strengthens them while creative destruction dismantles and reshapes them.
Historical Context and Theoretical Foundations
Sustained innovation refers to incremental improvements within existing frameworks, rooted in Joseph Schumpeter's early 20th-century theories emphasizing continuous development. Creative destruction, also coined by Schumpeter, describes the cyclical process where groundbreaking innovations dismantle established industries to foster economic evolution. Historically, this contrast shapes the understanding of technological progress and market dynamics, influencing both economic policy and business strategy.
Examples of Sustained Innovation in Business
Sustained innovation in business refers to continuous improvements or incremental updates to existing products, services, or processes, exemplified by Apple's yearly iPhone enhancements that boost performance and user experience without overhauling the core design. Toyota's implementation of the Toyota Production System exemplifies sustained innovation by consistently refining manufacturing efficiency and quality control, leading to long-term competitive advantage. Companies like Microsoft also practice sustained innovation through steady upgrades to software like Windows and Office, maintaining market dominance without disruptive upheavals.
Case Studies of Creative Destruction
Case studies of creative destruction highlight companies like Netflix, which disrupted traditional video rental markets by introducing streaming services, fundamentally altering consumer behavior and industry standards. Another example is Kodak's failure to adapt to digital photography, illustrating how creative destruction can eliminate established firms unable to innovate rapidly. These cases demonstrate how creative destruction fosters economic evolution by dismantling outdated technologies and business models to make way for innovative solutions.
Advantages and Drawbacks of Each Approach
Sustained innovation drives incremental improvements that enhance existing products and processes, fostering stability and long-term customer loyalty while minimizing market risks. Creative destruction generates breakthrough innovations that disrupt industries and create new markets but often lead to job displacement, high uncertainty, and short-term instability. Companies must balance the steady growth from sustained innovation with the transformative potential and volatility introduced by creative destruction to maintain competitive advantage.
Impact on Market Competitiveness
Sustained innovation enhances market competitiveness by incrementally improving products and services, fostering customer loyalty and stable growth. Creative destruction disrupts existing markets, enabling breakthrough innovations that can render incumbents obsolete and redefine industry standards. Both mechanisms drive competitive dynamics, with sustained innovation supporting gradual evolution and creative destruction catalyzing transformative change.
Choosing the Right Strategy for Organizational Growth
Sustained innovation focuses on incremental improvements to existing products or processes, enhancing organizational stability and long-term growth. Creative destruction involves radical innovation that disrupts markets and replaces outdated systems, driving transformative growth but with higher risk. Selecting the right strategy depends on the organization's risk tolerance, market dynamics, and long-term vision for competitive advantage.
Future Trends: Balancing Innovation and Disruption
Sustained innovation emphasizes incremental improvements in products or processes, fostering steady growth and stability in industries. Creative destruction drives radical change by replacing outdated technologies with groundbreaking advancements, often leading to temporary market disruption. Future trends indicate a strategic balance where businesses harness sustained innovation to enhance existing offerings while embracing creative destruction to pioneer disruptive breakthroughs, ensuring long-term competitiveness and adaptability.
Sustained innovation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com