Exchange rate risk arises from fluctuations in currency values that can impact the profitability of cross-border transactions and investments. Companies and investors must carefully assess these risks to protect their financial positions and optimize international trade strategies. Explore the rest of the article to understand how you can effectively manage exchange rate risk in your business or portfolio.
Table of Comparison
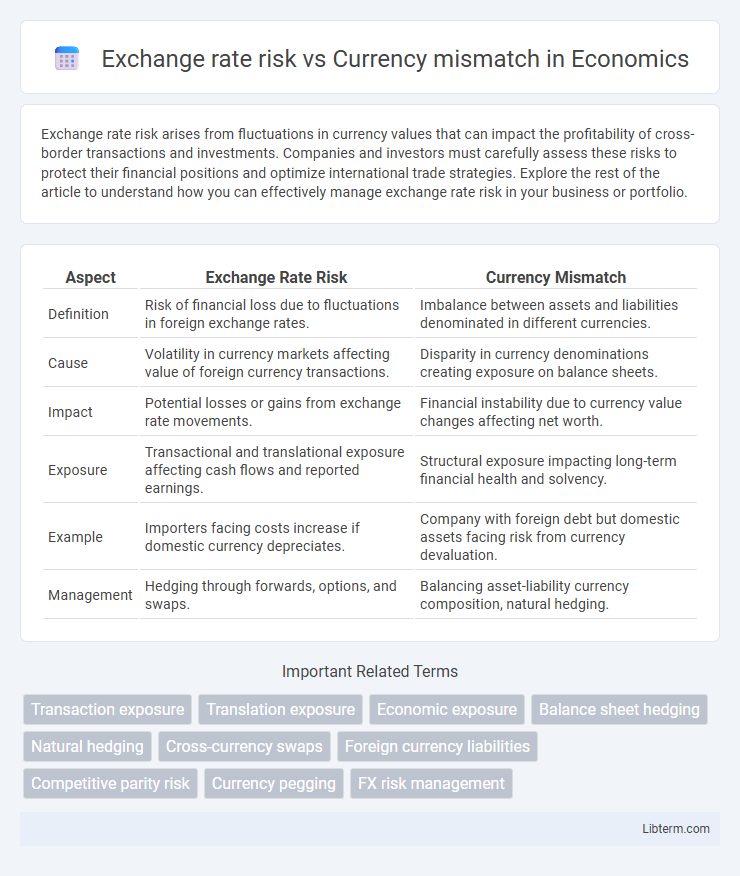
| Aspect | Exchange Rate Risk | Currency Mismatch |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Risk of financial loss due to fluctuations in foreign exchange rates. | Imbalance between assets and liabilities denominated in different currencies. |
| Cause | Volatility in currency markets affecting value of foreign currency transactions. | Disparity in currency denominations creating exposure on balance sheets. |
| Impact | Potential losses or gains from exchange rate movements. | Financial instability due to currency value changes affecting net worth. |
| Exposure | Transactional and translational exposure affecting cash flows and reported earnings. | Structural exposure impacting long-term financial health and solvency. |
| Example | Importers facing costs increase if domestic currency depreciates. | Company with foreign debt but domestic assets facing risk from currency devaluation. |
| Management | Hedging through forwards, options, and swaps. | Balancing asset-liability currency composition, natural hedging. |
Understanding Exchange Rate Risk
Exchange rate risk arises from fluctuations in currency values that can impact the cost of international transactions and the value of foreign assets or liabilities. Currency mismatch occurs when a company's assets and liabilities are denominated in different currencies, amplifying exposure to exchange rate risk. Understanding exchange rate risk is crucial for effective financial management, as it enables businesses to implement hedging strategies and mitigate potential losses from adverse currency movements.
Defining Currency Mismatch
Currency mismatch occurs when a company's assets and liabilities are denominated in different currencies, exposing it to fluctuations in exchange rates. This risk arises because changes in currency values can affect the real value of cash flows, leading to potential losses or gains in financial statements. Exchange rate risk specifically refers to the broader vulnerability of any entity to losses caused by unpredictable changes in foreign exchange rates.
Key Differences Between Exchange Rate Risk and Currency Mismatch
Exchange rate risk refers to the potential financial loss due to fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates affecting cross-border transactions or investments. Currency mismatch occurs when a company's assets and liabilities are denominated in different currencies, leading to balance sheet exposure and potential financial distress. Unlike exchange rate risk, which impacts transaction values, currency mismatch primarily affects the structural financial position and solvency of an entity.
Common Causes of Exchange Rate Risk
Exchange rate risk commonly arises from fluctuations in foreign currency values affecting multinational corporations' revenues and expenses, particularly when transactions are denominated in multiple currencies. Currency mismatch typically occurs due to differences between the currency denomination of a company's assets and liabilities, often caused by borrowing in one currency while generating income in another. Key causes include volatile exchange rates, unpredictable market demand, and mismatched timings of foreign currency cash flows.
How Currency Mismatch Occurs in International Finance
Currency mismatch occurs in international finance when a company's assets and liabilities are denominated in different currencies, exposing it to exchange rate risk due to fluctuations in currency values. This mismatch often arises when firms raise capital or incur debt in a foreign currency while generating revenue primarily in their domestic currency, increasing vulnerability to adverse currency movements. Such divergence in currency denominations complicates financial management and can lead to significant economic losses if exchange rates shift unfavorably.
Impact of Exchange Rate Risk on Businesses
Exchange rate risk directly affects businesses engaged in international trade by causing uncertainty in cash flows and profit margins when currency values fluctuate. Currency mismatch arises when a company's assets and liabilities are denominated in different currencies, increasing vulnerability to exchange rate movements, which can lead to significant financial losses. Managing exchange rate risk is crucial for maintaining stable earnings and protecting the firm's competitive position in global markets.
Financial Consequences of Currency Mismatch
Currency mismatch occurs when a firm's assets and liabilities are denominated in different currencies, exposing the company to exchange rate risk that can significantly impact its financial statements and cash flows. This mismatch can lead to increased volatility in earnings, potential balance sheet devaluation, and higher refinancing costs when foreign currency liabilities appreciate relative to the domestic currency. Managing currency mismatch is crucial for maintaining financial stability and reducing the risk of insolvency due to adverse currency movements.
Risk Management Strategies for Exchange Rate Exposure
Managing exchange rate risk involves hedging techniques such as forward contracts, options, and swaps to lock in currency values and reduce volatility impacts on cash flows. Currency mismatch risk occurs when assets and liabilities are denominated in different currencies, increasing vulnerability to exchange rate fluctuations, and can be mitigated through balance sheet hedging and natural hedging by matching currency exposures. Effective risk management strategies combine financial instruments and operational approaches to align currency inflows and outflows, minimizing potential losses from exchange rate movements.
Solutions to Address Currency Mismatch
Currency mismatch occurs when a company's liabilities and assets are denominated in different currencies, exposing it to exchange rate risk that can impact cash flows and financial stability. Solutions to address currency mismatch include natural hedging by matching the currency of revenues with expenses, using financial instruments such as forward contracts, options, and swaps to lock in exchange rates, and diversifying currency exposure across multiple markets. Implementing robust risk management frameworks and regularly monitoring foreign exchange exposures also helps mitigate the adverse effects of currency fluctuations.
Real-world Examples: Exchange Rate Risk vs Currency Mismatch
Companies like Toyota face exchange rate risk when fluctuations in the yen-dollar rate affect their profit margins on exports, while currency mismatch occurs when sub-Saharan African banks borrow in U.S. dollars but earn revenue in local currencies, exposing them to repayment difficulties if local currencies depreciate. Real estate investors in Eastern Europe experience currency mismatch when loans are denominated in Swiss francs, yet rental income is collected in weaker local currencies, increasing debt burden during currency depreciations. Multinational corporations navigating diverse markets must manage exchange rate risk through hedging strategies while addressing currency mismatches by aligning asset and liability currencies to maintain financial stability.
Exchange rate risk Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com