Bankruptcy is a legal process that helps individuals or businesses eliminate or repay debts under the protection of the bankruptcy court. It provides a structured way to address financial difficulties, often resulting in debt discharge or reorganization of obligations. Explore the rest of the article to understand how bankruptcy might impact your financial future and the options available to you.
Table of Comparison
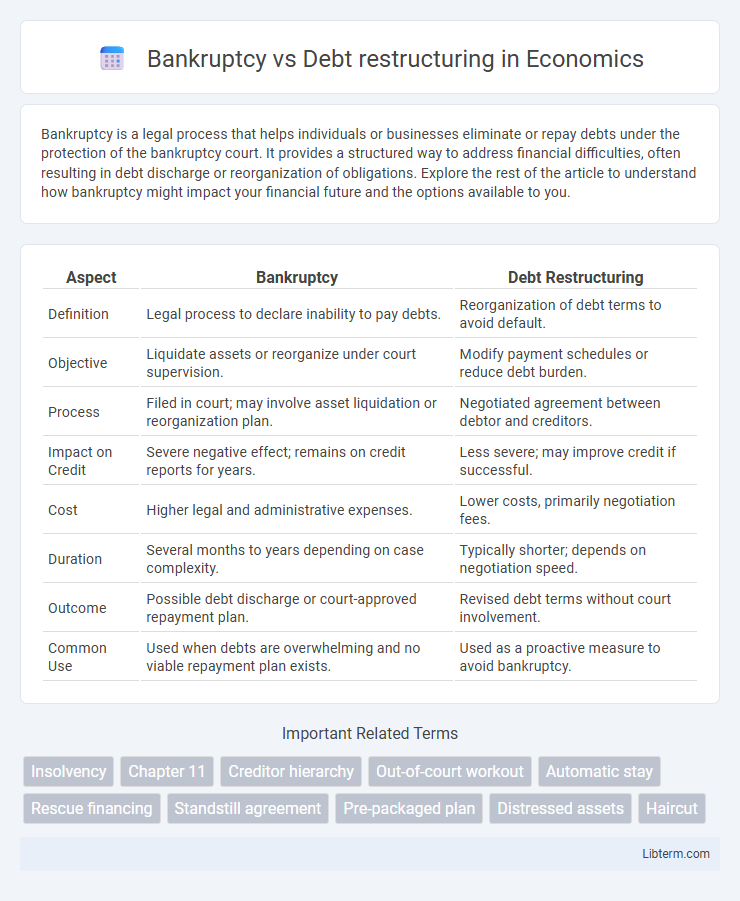
| Aspect | Bankruptcy | Debt Restructuring |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal process to declare inability to pay debts. | Reorganization of debt terms to avoid default. |
| Objective | Liquidate assets or reorganize under court supervision. | Modify payment schedules or reduce debt burden. |
| Process | Filed in court; may involve asset liquidation or reorganization plan. | Negotiated agreement between debtor and creditors. |
| Impact on Credit | Severe negative effect; remains on credit reports for years. | Less severe; may improve credit if successful. |
| Cost | Higher legal and administrative expenses. | Lower costs, primarily negotiation fees. |
| Duration | Several months to years depending on case complexity. | Typically shorter; depends on negotiation speed. |
| Outcome | Possible debt discharge or court-approved repayment plan. | Revised debt terms without court involvement. |
| Common Use | Used when debts are overwhelming and no viable repayment plan exists. | Used as a proactive measure to avoid bankruptcy. |
Understanding Bankruptcy: Definition and Types
Bankruptcy is a legal process that allows individuals or businesses unable to repay debts to seek relief or discharge of obligations under court supervision. Common types include Chapter 7, which involves liquidation of assets to pay creditors, Chapter 11, focusing on business reorganization to restructure debt, and Chapter 13, designed for individuals to create a repayment plan over time. Understanding these types helps determine the appropriate path between complete financial reset and managed debt restructuring.
What is Debt Restructuring? Key Concepts
Debt restructuring involves reorganizing existing debt obligations to improve a company's liquidity and avoid bankruptcy by negotiating new terms with creditors, such as extended payment periods, reduced interest rates, or partial debt forgiveness. Key concepts include consensus among creditors, debt maturity extension, and cash flow optimization to maintain solvency. This approach helps distressed businesses stabilize financial operations without liquidating assets or fully defaulting.
Major Differences: Bankruptcy vs Debt Restructuring
Bankruptcy involves a legal declaration of insolvency where assets are liquidated or reorganized under court supervision, often leading to debt discharge or business closure. Debt restructuring, by contrast, is a negotiated process between debtor and creditors aimed at modifying payment terms to avoid bankruptcy, preserving business operations and credit standing. The major differences lie in legal involvement, impact on credit, and the potential for business continuity, with bankruptcy typically resulting in more severe financial consequences and loss of control.
Pros and Cons of Filing for Bankruptcy
Filing for bankruptcy offers the significant advantage of providing legal protection from creditors and the possibility of discharging unsecured debts, which can offer a fresh financial start. However, bankruptcy has long-lasting negative impacts on credit scores and may lead to the loss of assets, depending on the bankruptcy type filed, such as Chapter 7 or Chapter 13. It also involves strict court oversight and can remain on credit reports for up to ten years, affecting future lending and financing opportunities.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Debt Restructuring
Debt restructuring offers the advantage of improving cash flow by extending payment terms, reducing interest rates, or partially forgiving debt, which helps businesses avoid bankruptcy and maintain operations. Disadvantages include potential damage to credit ratings, strained creditor relationships, and the risk that restructuring may only provide a temporary solution if underlying financial issues persist. Compared to bankruptcy, debt restructuring tends to preserve more of the company's value and allows for greater flexibility in negotiation with creditors.
Eligibility Criteria: Who Qualifies for Each Option?
Eligibility for bankruptcy typically requires proving insolvency, where debts exceed assets and income is insufficient to cover obligations, often favoring individuals or businesses with overwhelming financial distress. Debt restructuring applies to those with viable income streams and assets who can negotiate modified terms to avoid liquidation or loss of control, suitable for businesses aiming to preserve operations or individuals seeking more manageable repayment plans. Lenders and courts assess criteria such as debt-to-income ratios, asset valuations, and repayment capacity to determine qualification for bankruptcy or restructuring options.
The Legal Process: Bankruptcy vs Debt Restructuring
Bankruptcy involves a formal legal proceeding where a debtor's assets are liquidated or reorganized under court supervision to repay creditors, often leading to discharge of remaining debts. Debt restructuring is a negotiated process between the debtor and creditors to modify debt terms without court intervention, aiming to improve liquidity and avoid insolvency. Bankruptcy filings are public records subject to strict legal standards, whereas debt restructuring agreements are typically private and flexible, allowing tailored repayment plans.
Impact on Credit Score and Financial Future
Bankruptcy significantly damages credit scores, often causing a drop of 200 to 300 points, and remains on credit reports for up to 10 years, severely limiting access to loans and financial opportunities. Debt restructuring, by contrast, usually results in a more moderate credit score impact and can improve financial stability by making debts more manageable without the long-term stigma of bankruptcy. Choosing debt restructuring over bankruptcy can preserve creditworthiness and provide a pathway to recovery, enhancing prospects for future borrowing and financial health.
Choosing the Best Option: Factors to Consider
Choosing between bankruptcy and debt restructuring depends on factors such as the extent of financial distress, the ability to repay creditors, and the desire to preserve credit rating. Bankruptcy often offers a fresh start by legally discharging debts but can severely impact credit and business operations, whereas debt restructuring negotiates modified payment terms to avoid liquidation and maintain business continuity. Evaluating cash flow stability, creditor cooperation, and long-term financial goals is critical to selecting the optimal debt relief strategy.
Expert Tips for Navigating Financial Distress
Navigating financial distress requires understanding the distinction between bankruptcy and debt restructuring to choose the best path for recovery. Expert tips emphasize assessing the company's cash flow, liabilities, and long-term viability before opting for bankruptcy, which involves legal liquidation or reorganization under court supervision. Debt restructuring can preserve business operations by negotiating new terms with creditors, often improving cash flow without the reputational damage linked to bankruptcy filings.
Bankruptcy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com