Exchange rate policy shapes how a country manages its currency's value relative to others, impacting trade balances, inflation, and foreign investment flows. Governments may choose fixed, floating, or hybrid exchange rate systems to stabilize their economies and promote growth. Explore the rest of this article to understand how your country's exchange rate policy influences the global market and your financial decisions.
Table of Comparison
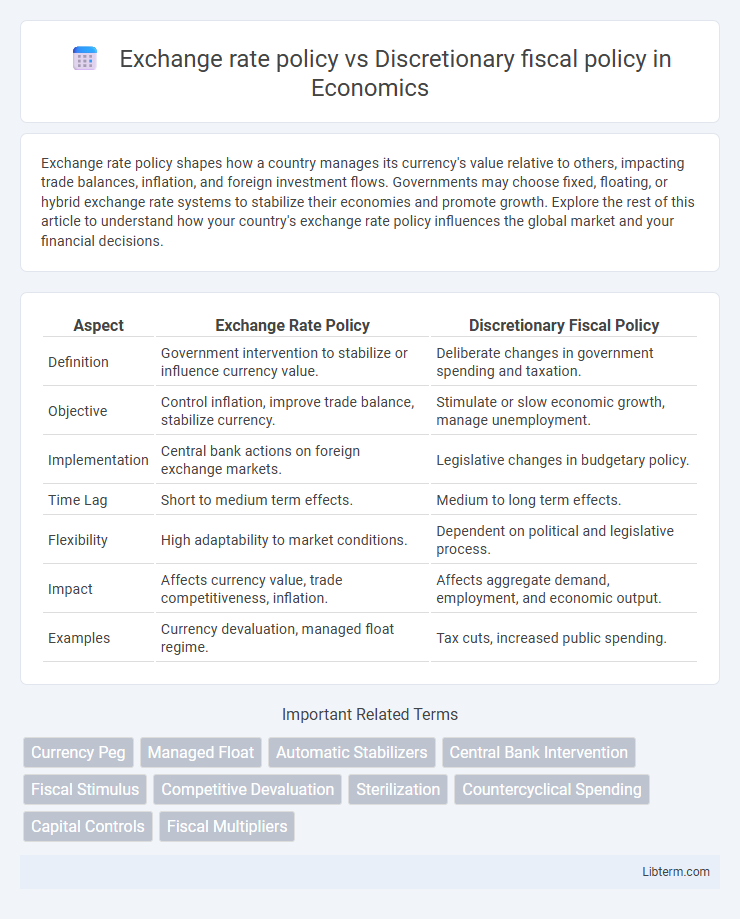
| Aspect | Exchange Rate Policy | Discretionary Fiscal Policy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Government intervention to stabilize or influence currency value. | Deliberate changes in government spending and taxation. |
| Objective | Control inflation, improve trade balance, stabilize currency. | Stimulate or slow economic growth, manage unemployment. |
| Implementation | Central bank actions on foreign exchange markets. | Legislative changes in budgetary policy. |
| Time Lag | Short to medium term effects. | Medium to long term effects. |
| Flexibility | High adaptability to market conditions. | Dependent on political and legislative process. |
| Impact | Affects currency value, trade competitiveness, inflation. | Affects aggregate demand, employment, and economic output. |
| Examples | Currency devaluation, managed float regime. | Tax cuts, increased public spending. |
Overview of Exchange Rate Policy
Exchange rate policy involves managing a country's currency value relative to others through fixed, floating, or pegged exchange rate systems, directly influencing import-export competitiveness and inflation rates. Central banks and governments intervene in foreign exchange markets to stabilize their currency, control inflation, and promote economic growth. This contrasts with discretionary fiscal policy, which uses government spending and taxation adjustments to influence economic activity without directly targeting currency valuation.
Understanding Discretionary Fiscal Policy
Discretionary fiscal policy involves active government intervention through changes in taxation and public spending to influence economic activity and stabilize the economy. Unlike exchange rate policy, which manages currency values to affect trade balances, discretionary fiscal policy targets aggregate demand directly to control inflation, unemployment, and growth. Effective use of discretionary fiscal policy requires timely decisions and precise adjustments to avoid crowding out private investment or exacerbating deficits.
Key Objectives: Exchange Rate vs Fiscal Policy
Exchange rate policy primarily aims to stabilize currency values, control inflation, and maintain international trade competitiveness by adjusting exchange rates through market interventions or fixed pegs. Discretionary fiscal policy focuses on influencing aggregate demand, reducing unemployment, and stimulating economic growth via government spending and taxation decisions. Both policies target economic stability but operate through distinct mechanisms: exchange rate policy on external balance and price stability, while fiscal policy impacts domestic economic activity and distribution.
Mechanisms of Exchange Rate Management
Exchange rate policy involves central bank interventions in foreign exchange markets to stabilize or guide currency values through tools such as fixed, floating, or managed exchange rate regimes. Mechanisms include direct market operations, foreign currency reserves management, and setting interest rates to influence currency demand and supply. In contrast, discretionary fiscal policy uses government spending and taxation adjustments to influence economic activity without directly targeting exchange rate levels.
Fiscal Tools and Government Intervention
Discretionary fiscal policy involves direct government intervention in the economy through changes in taxation and public spending to influence aggregate demand and stabilize economic fluctuations. Exchange rate policy manages currency value via interventions in foreign exchange markets or monetary tools to affect trade balances and inflation. Fiscal tools specifically adjust budgetary measures, while exchange rate policies utilize currency valuation adjustments, both serving as strategic government actions to achieve macroeconomic objectives.
Impact on Economic Growth
Exchange rate policy influences economic growth by stabilizing trade balances and controlling inflation through currency value adjustments, thereby enhancing export competitiveness and attracting foreign investment. Discretionary fiscal policy impacts growth by altering government spending and taxation, directly stimulating demand and investment during economic downturns or cooling expansion to prevent overheating. Coordinated implementation of both policies can optimize economic stability and sustainable growth by balancing external competitiveness with internal demand management.
Influence on Inflation and Employment
Exchange rate policy stabilizes inflation by controlling currency value fluctuations, impacting import prices and export competitiveness to influence domestic price levels. Discretionary fiscal policy directly affects employment by adjusting government spending and taxation, stimulating demand and job creation during economic downturns. While exchange rate policy indirectly moderates inflation and employment through external trade effects, discretionary fiscal policy offers more immediate control over domestic economic conditions.
Policy Effectiveness in Economic Crises
Exchange rate policy can stabilize economies during crises by adjusting currency values to enhance export competitiveness and control inflation, providing a buffer against external shocks. Discretionary fiscal policy, involving targeted government spending and taxation changes, directly influences aggregate demand to stimulate growth or contain inflation, but often faces implementation lags and political constraints. Policy effectiveness depends on the flexibility of exchange rate regimes and the fiscal space available, with coordinated use enhancing crisis resilience and economic recovery speed.
Case Studies: Global Policy Comparisons
Exchange rate policy and discretionary fiscal policy have shown varied effectiveness across global case studies, with countries like China leveraging managed exchange rates to stabilize exports while the U.S. employs discretionary fiscal measures to stimulate economic growth during recessions. Emerging economies, such as Brazil, demonstrate how exchange rate interventions can counteract inflationary pressures, whereas discretionary fiscal policies in European nations like Germany focus on balancing stimulus with long-term debt sustainability. Comparative analyses reveal that exchange rate policy often provides quicker external adjustment mechanisms, while discretionary fiscal policy offers targeted internal economic support, highlighting the importance of context-specific strategy selection.
Choosing the Right Policy Mix
Choosing the right policy mix involves balancing exchange rate policy, which stabilizes currency values and controls inflation, with discretionary fiscal policy aimed at influencing economic growth through government spending and taxation. Exchange rate interventions provide immediate effects on trade balances, while discretionary fiscal measures require longer implementation periods but can target specific sectors or social objectives. Combining these tools effectively enhances macroeconomic stability, optimizes resource allocation, and supports sustainable economic development.
Exchange rate policy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com