Supply-side policy focuses on boosting economic growth by improving the productive capacity of an economy through measures such as tax cuts, deregulation, and investment in human capital. These policies aim to enhance efficiency, increase labor market flexibility, and stimulate innovation to create long-term sustainable growth. Discover how supply-side policy can impact your economy and what strategies might work best by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
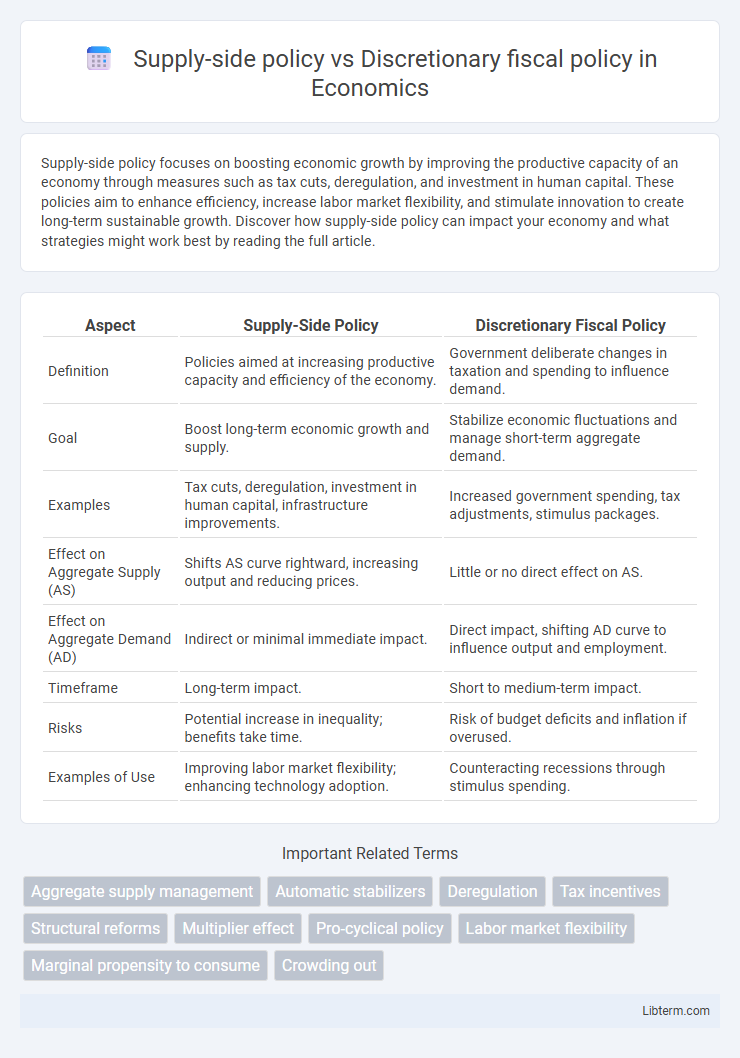
| Aspect | Supply-Side Policy | Discretionary Fiscal Policy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Policies aimed at increasing productive capacity and efficiency of the economy. | Government deliberate changes in taxation and spending to influence demand. |
| Goal | Boost long-term economic growth and supply. | Stabilize economic fluctuations and manage short-term aggregate demand. |
| Examples | Tax cuts, deregulation, investment in human capital, infrastructure improvements. | Increased government spending, tax adjustments, stimulus packages. |
| Effect on Aggregate Supply (AS) | Shifts AS curve rightward, increasing output and reducing prices. | Little or no direct effect on AS. |
| Effect on Aggregate Demand (AD) | Indirect or minimal immediate impact. | Direct impact, shifting AD curve to influence output and employment. |
| Timeframe | Long-term impact. | Short to medium-term impact. |
| Risks | Potential increase in inequality; benefits take time. | Risk of budget deficits and inflation if overused. |
| Examples of Use | Improving labor market flexibility; enhancing technology adoption. | Counteracting recessions through stimulus spending. |
Understanding Supply-Side Policy
Supply-side policy focuses on enhancing the productive capacity of an economy by improving factors such as labor market flexibility, innovation, and capital investment. It aims to increase aggregate supply through tax incentives, deregulation, and education reforms, encouraging businesses to expand and boost long-term economic growth. Unlike discretionary fiscal policy, which adjusts government spending and taxation to manage demand, supply-side policies target structural changes that create sustainable growth and improve overall economic efficiency.
Defining Discretionary Fiscal Policy
Discretionary fiscal policy involves deliberate government actions through changes in taxation and public spending to influence economic activity and stabilize the economy during fluctuations. It contrasts with supply-side policies, which primarily focus on long-term economic growth by improving production efficiency, such as deregulation and tax incentives for investment. Effective discretionary fiscal measures require timely implementation and precise targeting to manage demand and mitigate recessions or overheating.
Core Objectives: Growth vs Stabilization
Supply-side policy aims to boost long-term economic growth by improving productivity, enhancing labor market flexibility, and encouraging investment through tax cuts and deregulation. Discretionary fiscal policy focuses on short-term economic stabilization by adjusting government spending and taxation to influence aggregate demand, thereby managing economic fluctuations such as recessions or inflation. While supply-side measures target structural improvements to increase potential output, discretionary fiscal policy seeks to smooth business cycles and maintain stable economic conditions.
Key Instruments of Supply-Side Policy
Supply-side policy primarily uses key instruments such as tax cuts, deregulation, and investment in human capital to enhance productive capacity and long-term economic growth. These policies aim to increase labor market flexibility, improve business efficiency, and incentivize innovation by reducing barriers and costs for producers. In contrast, discretionary fiscal policy relies on government spending and taxation adjustments to influence aggregate demand and manage economic fluctuations in the short term.
Tools Used in Discretionary Fiscal Policy
Discretionary fiscal policy employs tools such as government spending adjustments and changes in taxation to influence economic activity directly. These measures include increased public investment in infrastructure, alterations in income or corporate tax rates, and targeted subsidies or social welfare programs to stimulate demand. Unlike supply-side policies that focus on long-term productivity enhancements, discretionary fiscal policies aim for short-term economic stabilization by modulating aggregate demand.
Impact on Economic Output
Supply-side policies enhance economic output by improving productivity and incentivizing investment through tax cuts, deregulation, and labor market reforms, leading to long-term growth. Discretionary fiscal policy impacts output more directly and rapidly by adjusting government spending and taxation to influence aggregate demand, often aiming to stabilize business cycles. While supply-side policies drive sustainable expansion, discretionary fiscal measures provide short-term economic stimulus or contraction control.
Effects on Unemployment and Inflation
Supply-side policies enhance productivity and labor market flexibility, leading to long-term reductions in unemployment and containing inflation by increasing aggregate supply. Discretionary fiscal policy, involving government spending and taxation adjustments, targets short-term economic fluctuations to reduce unemployment but risks accelerating inflation if demand outpaces supply. The effectiveness of supply-side policies lies in structural improvements, whereas discretionary fiscal policy provides immediate stimulus with potential inflationary trade-offs.
Policy Implementation Challenges
Supply-side policies often face challenges such as long implementation lags, political resistance to deregulation, and uncertainty in achieving desired productivity gains. Discretionary fiscal policy encounters difficulties including timing issues, political constraints on budget adjustments, and risks of increasing public debt. Both approaches require careful coordination to balance economic growth objectives with fiscal sustainability and political feasibility.
Case Studies: Global Applications
Supply-side policies in countries like Germany have successfully boosted long-term economic growth by enhancing labor market flexibility and reducing corporate taxes, promoting investment and productivity. In contrast, discretionary fiscal policy in the United States, exemplified by stimulus packages during the 2008 financial crisis and COVID-19 pandemic, provided immediate demand boosts to counter recessions but often increased public debt. Comparative analysis reveals supply-side measures favor sustainable growth, while discretionary fiscal actions offer short-term economic stabilization, highlighting their complementary roles in global macroeconomic management.
Comparative Effectiveness and Long-Term Outcomes
Supply-side policy enhances economic growth by improving productive capacity through tax cuts, deregulation, and investment in human capital, leading to sustainable increases in output and employment. Discretionary fiscal policy offers short-term stabilization by adjusting government spending and taxes to manage aggregate demand, but risks inflation and debt accumulation if overused. Long-term outcomes favor supply-side measures due to their ability to foster innovation, efficiency, and permanent expansion of the economy's productive potential.
Supply-side policy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com