Representative money is a type of currency backed by a physical commodity, such as gold or silver, which guarantees its value. Unlike fiat money, its worth is directly linked to the reserve it represents, providing a tangible assurance of stability. Discover how representative money has shaped financial systems and why understanding its role can benefit your financial knowledge.
Table of Comparison
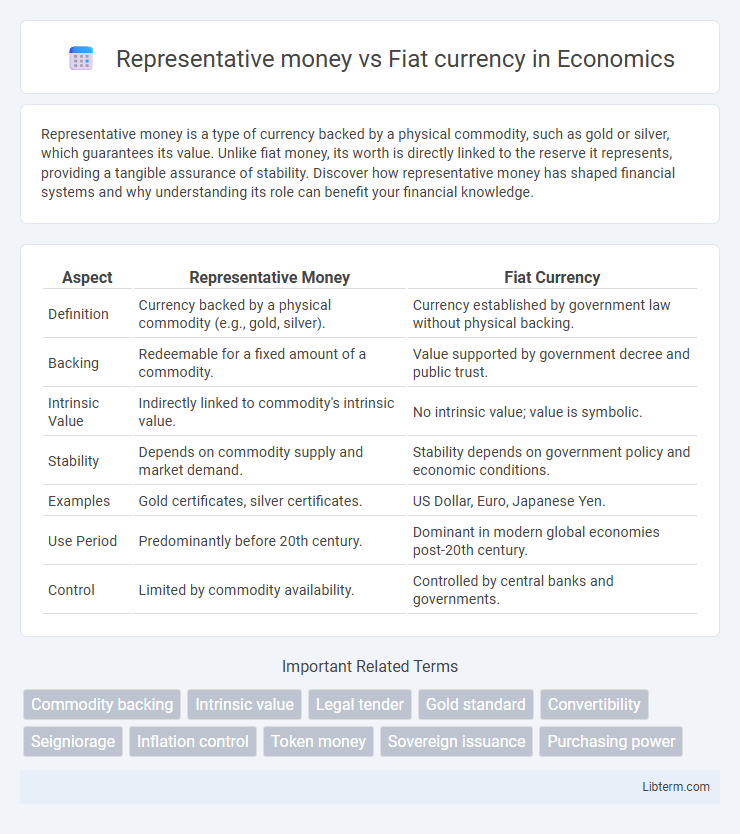
| Aspect | Representative Money | Fiat Currency |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Currency backed by a physical commodity (e.g., gold, silver). | Currency established by government law without physical backing. |
| Backing | Redeemable for a fixed amount of a commodity. | Value supported by government decree and public trust. |
| Intrinsic Value | Indirectly linked to commodity's intrinsic value. | No intrinsic value; value is symbolic. |
| Stability | Depends on commodity supply and market demand. | Stability depends on government policy and economic conditions. |
| Examples | Gold certificates, silver certificates. | US Dollar, Euro, Japanese Yen. |
| Use Period | Predominantly before 20th century. | Dominant in modern global economies post-20th century. |
| Control | Limited by commodity availability. | Controlled by central banks and governments. |
Definition of Representative Money
Representative money is a type of currency that represents a claim on a commodity, such as gold or silver, held in reserve and can be exchanged for that commodity upon demand. Unlike fiat currency, which has value solely based on government decree and trust, representative money's value is directly linked to the physical commodity it symbolizes. This form of money was widely used before the abandonment of the gold standard and provides a tangible backing that fiat currencies lack.
Definition of Fiat Currency
Fiat currency is government-issued money that is not backed by a physical commodity but derives its value solely from government decree and public trust. Unlike representative money, which represents a claim on a commodity like gold or silver, fiat currency operates as legal tender for all debts and transactions within the issuing country. Central banks control fiat currency supply through monetary policies, influencing inflation and economic stability.
Historical Evolution of Money Types
Representative money emerged as early societies transitioned from barter systems by using certificates or tokens backed by a physical commodity like gold or silver, facilitating easier trade while maintaining intrinsic value. Over time, the limitations of storing and transporting precious metals led to the advent of fiat currency, which governments began issuing as legal tender without backing by physical reserves, relying instead on public trust and government authority. This historical shift from asset-backed representative money to fiat currency enabled the expansion of monetary supply and modern economic systems, reflecting evolving financial needs and regulatory frameworks.
Key Differences Between Representative and Fiat Money
Representative money is backed by a physical commodity like gold or silver, giving it intrinsic value, while fiat currency has no intrinsic value and is established as legal tender by government decree. Representative money can be exchanged for a fixed amount of the backing commodity, whereas fiat currency relies on public trust and government regulation for its value. Fiat currency's supply is controlled by central banks, allowing for greater flexibility in monetary policy compared to the limited supply of representative money.
Advantages of Representative Money
Representative money provides a tangible backing, usually in the form of precious metals like gold or silver, which enhances public trust and reduces inflation risk. Unlike fiat currency, its value is directly linked to a physical commodity, offering stability and limiting arbitrary government control over money supply. This tangible backing allows for easier international trade and more confidence in monetary transactions.
Advantages of Fiat Currency
Fiat currency offers greater flexibility in monetary policy, enabling central banks to regulate the economy by controlling money supply and interest rates. Unlike representative money, which is limited by physical assets like gold or silver, fiat currency is not constrained by reserves, allowing for easier adjustment to economic demands. This adaptability supports economic growth, price stability, and the ability to respond effectively to financial crises.
Disadvantages of Representative Money
Representative money depends entirely on the value of the physical commodity it represents, making it vulnerable to fluctuations in the availability and market price of that commodity. Limited convertibility can lead to liquidity issues, as holders must exchange the money for the underlying asset to realize its value, restricting its practical use in everyday transactions. This system also faces risks of loss or damage to the backing commodity, which can undermine public confidence and destabilize the currency's value.
Disadvantages of Fiat Currency
Fiat currency often faces challenges such as susceptibility to inflation due to government overissuance, which can erode purchasing power and destabilize economies. Unlike representative money backed by physical commodities like gold or silver, fiat lacks intrinsic value, relying solely on government trust and regulatory enforcement. This dependence can lead to loss of confidence, currency devaluation, and increased risk of hyperinflation during economic crises.
Impact on Monetary Policy
Representative money, backed by physical commodities like gold, limits central banks' ability to expand the money supply, constraining monetary policy flexibility and often resulting in deflationary pressures. Fiat currency, lacking intrinsic value and not backed by tangible assets, enables central banks to implement expansive or contractionary monetary policies more effectively, facilitating economic stabilization and growth management. The shift from representative money to fiat currency has expanded the toolbox for controlling inflation, interest rates, and overall economic activity through targeted policy interventions.
Future Trends in Currency Systems
Future trends in currency systems indicate a gradual shift from traditional representative money, which is backed by physical commodities, to purely fiat currency governed by trust in central authorities. Technological advancements such as blockchain and digital currencies are enhancing the efficiency and security of fiat money, making it more adaptable to global economic demands. Central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) represent the next evolution, potentially reducing reliance on cash while increasing transparency and control over monetary policy.
Representative money Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com