Cryptocurrency is revolutionizing the financial landscape by enabling secure, decentralized transactions through blockchain technology. Understanding its impact on investments, security, and global markets is crucial for maximizing your digital asset portfolio. Explore the detailed insights in the rest of this article to navigate the evolving world of cryptocurrency.
Table of Comparison
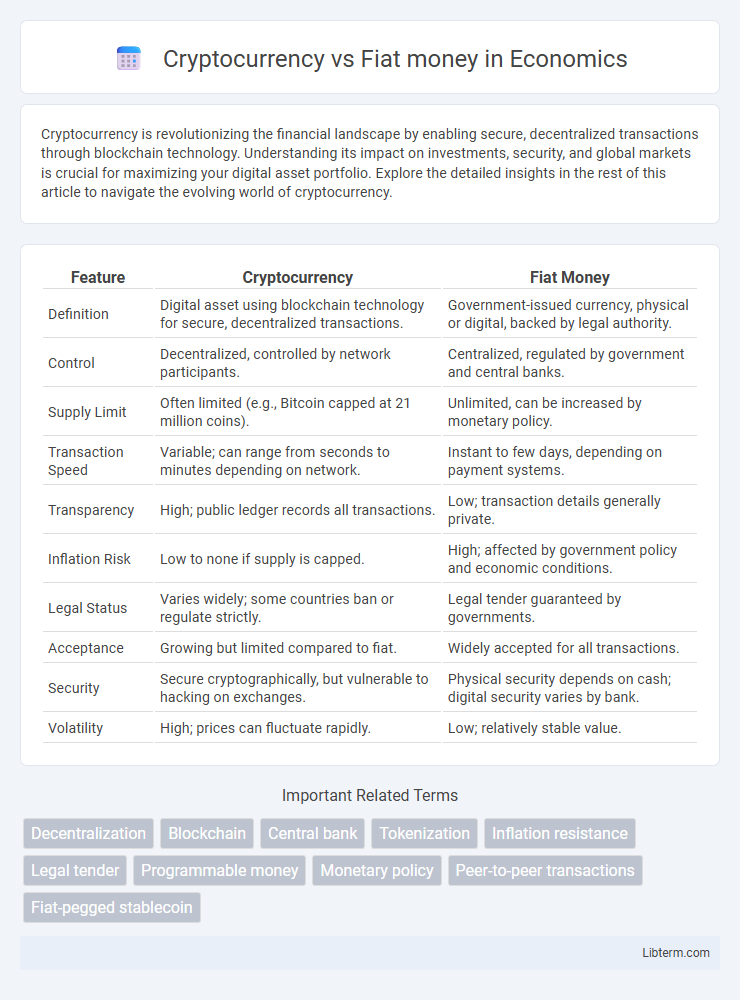
| Feature | Cryptocurrency | Fiat Money |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Digital asset using blockchain technology for secure, decentralized transactions. | Government-issued currency, physical or digital, backed by legal authority. |
| Control | Decentralized, controlled by network participants. | Centralized, regulated by government and central banks. |
| Supply Limit | Often limited (e.g., Bitcoin capped at 21 million coins). | Unlimited, can be increased by monetary policy. |
| Transaction Speed | Variable; can range from seconds to minutes depending on network. | Instant to few days, depending on payment systems. |
| Transparency | High; public ledger records all transactions. | Low; transaction details generally private. |
| Inflation Risk | Low to none if supply is capped. | High; affected by government policy and economic conditions. |
| Legal Status | Varies widely; some countries ban or regulate strictly. | Legal tender guaranteed by governments. |
| Acceptance | Growing but limited compared to fiat. | Widely accepted for all transactions. |
| Security | Secure cryptographically, but vulnerable to hacking on exchanges. | Physical security depends on cash; digital security varies by bank. |
| Volatility | High; prices can fluctuate rapidly. | Low; relatively stable value. |
Understanding Cryptocurrency and Fiat Money
Cryptocurrency operates as a decentralized digital asset secured by cryptography, enabling peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries, contrasting with fiat money issued and regulated by central governments as legal tender. While fiat money depends on trust in the issuing authority and is influenced by monetary policies, cryptocurrencies rely on blockchain technology to ensure transparency, immutability, and limited supply, exemplified by Bitcoin's capped issuance of 21 million coins. The fundamental distinctions between these two forms of currency involve their issuance mechanisms, regulatory oversight, and underlying technological frameworks, shaping their roles in modern economies.
Key Differences Between Cryptocurrency and Fiat Money
Cryptocurrency operates on decentralized blockchain technology, providing transparency and security without the need for central authority, unlike fiat money which is government-issued and regulated. Cryptocurrency transactions are pseudonymous and recorded on a distributed ledger, whereas fiat currency relies on physical notes or electronic banking systems controlled by central banks. Volatility in cryptocurrency prices contrasts with the relative stability of fiat money, which benefits from monetary policy and legal tender status.
The Technology Behind Cryptocurrencies
Cryptocurrencies operate on blockchain technology, a decentralized ledger system that ensures transparent, immutable, and secure transactions without relying on central authorities. This technology uses cryptographic algorithms to validate transactions and maintain user anonymity, contrasting sharply with fiat money, which is managed by centralized banks and governments. The decentralized consensus mechanisms, such as Proof of Work or Proof of Stake, provide enhanced security and reduce the risk of fraud inherent in traditional fiat currency systems.
The Role of Governments in Fiat Money
Governments play a central role in the issuance and regulation of fiat money, controlling its supply through monetary policies implemented by central banks to maintain economic stability and control inflation. Fiat currency derives its value from government decree and legal tender laws, ensuring widespread acceptance for transactions and tax payments within a nation. This government-backed trust contrasts with decentralized cryptocurrencies, which operate independently of state control, relying on cryptographic protocols and blockchain technology.
Security and Transparency: Crypto vs Fiat
Cryptocurrency utilizes blockchain technology, providing enhanced security through decentralized ledger systems that minimize fraud and unauthorized access. Fiat money relies on centralized institutions, which can be vulnerable to counterfeiting, inflation, and manipulation by governments or banks. Transparency in cryptocurrencies is inherent, with all transactions publicly recorded on the blockchain, while fiat transactions often lack such openness, leading to less accountability.
Transaction Speed and Costs Comparison
Cryptocurrency transactions typically offer faster confirmation times compared to traditional fiat money transfers, which can take several days depending on the banking system and geographic locations. Transaction fees for cryptocurrencies vary widely, often being lower for smaller transactions but can spike during network congestion, whereas fiat money transfers usually incur consistent fees set by banks or intermediaries. The decentralized nature of cryptocurrencies eliminates the need for intermediaries, reducing both the time and cost associated with cross-border payments compared to fiat currencies.
Inflation and Supply Control: Crypto vs Fiat
Cryptocurrency offers a fixed or algorithmically controlled supply, effectively limiting inflation risk compared to fiat money, which central banks can increase at will, often leading to currency devaluation. Bitcoin, for example, has a capped supply of 21 million coins, ensuring scarcity and potential value preservation, whereas fiat currencies rely on monetary policy tools that can result in inflationary pressures. This fundamental difference in supply control creates contrasting economic dynamics between decentralized cryptocurrencies and centralized fiat systems.
Global Acceptance and Usability
Cryptocurrency adoption varies widely with significant acceptance in tech-savvy and financially underserved regions, while fiat money remains universally accepted due to government backing and regulatory frameworks. Digital currencies offer borderless transactions and lower fees, enhancing usability for international trade and remittances but face challenges like volatility and limited merchant acceptance. Central banks and global institutions continue to influence the integration of cryptocurrencies within existing financial systems, impacting their broader usability and regulatory acceptance.
Risks and Volatility: Cryptocurrency vs Fiat
Cryptocurrency exhibits significantly higher volatility compared to fiat money, with price swings often exceeding 10% within a single day, driven by market speculation, regulatory changes, and technological risks. Fiat money, backed by government authorities and central banks, generally maintains more stable value, supported by monetary policies and economic fundamentals, yet remains susceptible to inflation and currency devaluation risks. Investors in cryptocurrency must navigate threats such as hacking, fraud, and lack of regulatory protection, while fiat currency risks primarily involve inflation, geopolitical instability, and monetary policy shifts.
Future Outlook: Will Crypto Replace Fiat Money?
Cryptocurrency's future outlook suggests a potential coexistence rather than complete replacement of fiat money, driven by factors like decentralization, security, and borderless transactions. Central banks worldwide are exploring digital currencies (CBDCs) to integrate blockchain benefits while retaining regulatory control, signaling hybrid financial ecosystems. Adoption challenges such as volatility, legal frameworks, and technological infrastructure remain critical hurdles for crypto's mass acceptance as mainstream currency.
Cryptocurrency Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com