A trade deficit occurs when a country imports more goods and services than it exports, leading to an outflow of domestic currency to foreign markets. This imbalance can impact your nation's economic health by influencing currency value, foreign debt, and job markets in specific industries. Explore the rest of our article to understand how trade deficits shape global economies and your everyday financial environment.
Table of Comparison
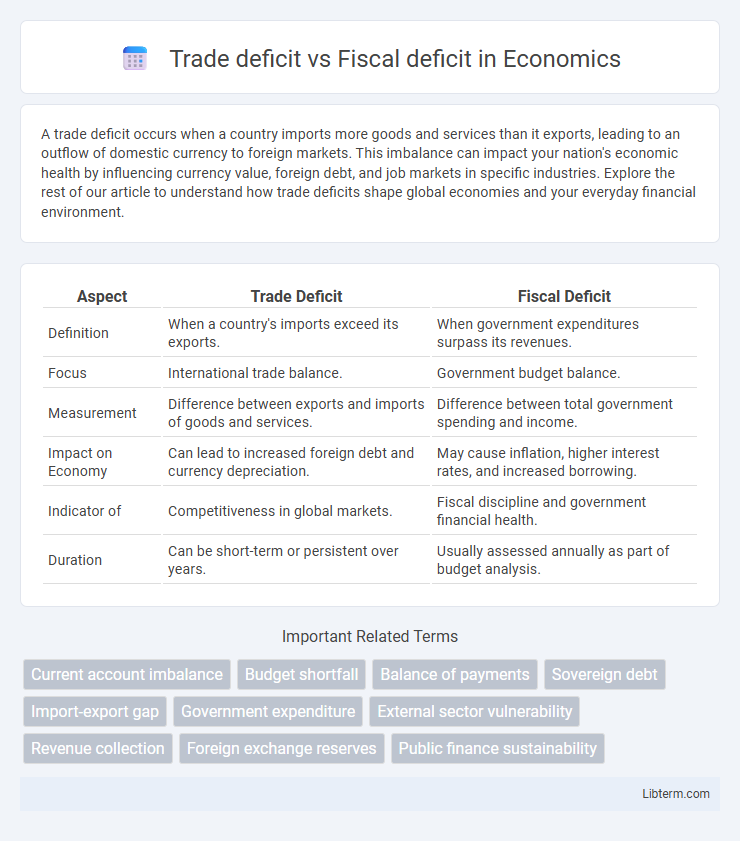
| Aspect | Trade Deficit | Fiscal Deficit |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | When a country's imports exceed its exports. | When government expenditures surpass its revenues. |
| Focus | International trade balance. | Government budget balance. |
| Measurement | Difference between exports and imports of goods and services. | Difference between total government spending and income. |
| Impact on Economy | Can lead to increased foreign debt and currency depreciation. | May cause inflation, higher interest rates, and increased borrowing. |
| Indicator of | Competitiveness in global markets. | Fiscal discipline and government financial health. |
| Duration | Can be short-term or persistent over years. | Usually assessed annually as part of budget analysis. |
Overview of Trade Deficit vs Fiscal Deficit
Trade deficit occurs when a country's imports exceed its exports, resulting in a negative balance of trade that affects the current account of the balance of payments. Fiscal deficit reflects the shortfall in a government's budget where expenditures surpass revenues, leading to increased borrowing and impacting the national debt. Both deficits indicate economic imbalances but operate in different sectors: trade deficit in external economic transactions and fiscal deficit in domestic government finances.
Defining Trade Deficit
A trade deficit occurs when a country's imports of goods and services exceed its exports, indicating that more capital is leaving the country than entering through foreign trade. This imbalance impacts the balance of payments and can influence exchange rates, foreign debt, and economic growth. Trade deficits must be distinguished from fiscal deficits, which relate to government spending exceeding revenue within a national budget.
Understanding Fiscal Deficit
Fiscal deficit represents the gap between a government's total expenditure and its total revenue, excluding borrowings, indicating the need for borrowing to finance the shortfall. It reflects the financial health of a country's public sector and impacts economic policies such as taxation and public spending. Managing fiscal deficit is crucial for maintaining macroeconomic stability and avoiding excessive debt accumulation that can hinder long-term growth.
Key Differences Between Trade Deficit and Fiscal Deficit
Trade deficit occurs when a country's imports exceed its exports, reflecting an imbalance in international trade, while fiscal deficit happens when government expenditures surpass tax revenues, indicating a budget shortfall. Trade deficits focus on external economic relations and the flow of goods and services across borders, whereas fiscal deficits relate to domestic government financial management and public sector borrowing. The trade deficit impacts exchange rates and foreign reserves, whereas the fiscal deficit influences national debt levels and interest rates.
Causes of Trade Deficit
A trade deficit occurs when a country's imports exceed its exports, often caused by factors such as a strong domestic currency, high consumer demand for foreign goods, and competitive disadvantages in global markets. Structural issues like lack of industrial diversification and reliance on imported raw materials can also contribute significantly to persistent trade deficits. Governments may address these causes by promoting export-oriented industries, adjusting monetary policies, or implementing trade agreements to enhance international competitiveness.
Causes of Fiscal Deficit
Fiscal deficit primarily arises from the government's expenditure exceeding its revenue, often due to excessive public spending on subsidies, infrastructure, and welfare programs without corresponding tax income. Structural factors such as inefficient tax systems, revenue shortfalls, and increased borrowing to finance budgetary gaps also contribute significantly. Economic downturns and unforeseen expenses like natural disasters or defense spending can exacerbate the fiscal imbalance, deepening the deficit further.
Economic Impacts of Trade Deficit
A trade deficit occurs when a country's imports exceed its exports, leading to a net outflow of domestic currency to foreign markets. This imbalance can weaken the domestic currency, increase foreign debt, and reduce domestic employment in import-competing industries. Persistent trade deficits often signal structural economic issues, such as declining competitiveness or overreliance on foreign goods, which can hamper long-term economic growth.
Economic Impacts of Fiscal Deficit
Fiscal deficit, representing government overspending beyond its revenue, often leads to higher public debt and increased borrowing costs. Persistent fiscal deficits can crowd out private investment and trigger inflationary pressures, undermining long-term economic growth. Unlike trade deficit effects that influence external balances, fiscal deficits primarily impact domestic financial stability and monetary policy effectiveness.
Policy Measures to Address Trade and Fiscal Deficits
Policy measures to address trade deficits include promoting export diversification, implementing currency stabilization, and enhancing competitiveness through innovation and infrastructure investment. Fiscal deficits can be managed by increasing tax revenues, cutting non-essential public expenditure, and improving fiscal transparency and accountability. Coordinated fiscal and trade policies, such as targeted subsidies and trade agreements, help balance external accounts and ensure sustainable economic growth.
Trade Deficit vs Fiscal Deficit: Which Is More Concerning?
Trade deficit reflects the gap between a country's imports and exports, potentially signaling weaker domestic production or competitiveness, whereas fiscal deficit indicates government overspending beyond its revenue, which may lead to higher public debt and inflation. Persistent trade deficits can undermine currency stability and increase reliance on foreign capital, but chronic fiscal deficits often pose more significant risks to economic sovereignty and long-term growth. Evaluating which is more concerning depends on the country's economic context, debt levels, and policy response, with fiscal deficits generally warranting greater attention due to their direct impact on fiscal sustainability.
Trade deficit Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com